![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a flower producing vascular plant in which the seed is enclosed ina fruit, such as an apple
|
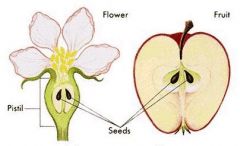
Angiosperm
|
|
|
Angiosperm
|
a flower producing vascular plant in which the seed is enclosed in a fruit, such as an apple (p. 288)
|
|
|
cambium
|
vascular plant tissue that produces new xylem and phloem cells (p. 294)
|
|
|
dicot
|
an angiosperm having two seed leaves inside its seed; for example a maple tree
(p. 288) |
|
|
guard cell
|
in a plant leaf, cells that surround the stomata to open and close them (p. 294)
|
|
|
gymnosperm
|
a vascular plant that produces seeds on the scales of female cones, such as pinecones. (p. 286)
|
|
|
monocot
|
an angiosperm having a single seed leaf inside its seed; for example, an orchid
(p. 288) |
|
|
ovary
|
in angiosperms, the swolen base of the pistil, where ovules form; in female animals, the organ that produces ova, or egg cells (p. 298)
|
|
|
ovule
|
the female reproductive part of a plant that produces eggs
(p. 296) |
|
|
phloem
|
vascular plant tissue made up of tubular cells that move food from leaves and stems to other parts of the plant for use or storage (p. 294)
|
|
|
pistil
|
the female reproductive organ of a flower
(p. 298) |
|
|
pollen grain
|
the male reproductive part of a plant that contains the sperm (p. 296)
|
|
|
pollination
|
the process that transfers pollen grains from the stamen to the stigmas (p. 299)
|
|
|
stamen
|
the male reproductive organ of a flower (p. 298)
|
|
|
stomata
|
small pores in the surface of a plant leaf that allow carbon dioxide, water, owygen to enter and leave
(p. 294) |
|
|
xylem
|
vascular plant tissue made up of tubular vessels that transport water and minerals from the roots up through the plant (p. 294)
|

