![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The individual disks inside a traditional HDD are called what? |

Platters
|
|
|
|
The distance between the read/write heads and the HDD disk is called what?
|
Flying Height
|
|
|
|
Hard drives store data in tiny magnetic fields called what
|
Flux
|
|
|
|
the tiny magnetic fields in an HDD can switch north/south polarity back and forth through a process called what
|
Flux Reversal
|
|
|
|
what are groups of flux reversals called?
|
Runs
|
|
|
|
What data endoding system allows any combination of ones and zeroes to be stored in a preset combination of about 15 different runs?
|
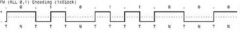
RLL (Run Length limited)
|
|
|
|
What range is the maximum run length for PRML drives?
|
16 to 20 fluxes
|
|
|
|
What are the only two technologies HDD manufacturers used to move the actuator arms?
|
Stepper motor
Voice Coil |
|
|
|
Which HDD technology moved the actuator arm in fixed increments?
|

stepper motor
|
|
|
|
Which HDD technology uses a permanent magnet surrounding a coil on the actuator arm?
|

Voice coil
|
|
|
|
what are the 3 critical values that define a hard drive’s geometry?
|
(CHS)
1. Cylinders 2. Heads 3. Sectors per track |
|
|
|
Older HDD's would spread data a little farther apart
once it got to a particular cylinder. What was this cylinder called? |
Write Precompensation Cylinder
|
Older hard drives had a real problem with the fact that sectors toward the inside of the drives were much smaller than sectors toward the outside.
|
|
|
What was the unused cylinder used as a “parking place” for the read/write heads of older HDD's called?
|
Landing zone
|
used only on stepper motor HDD's
|
|
|
What type of Hard Drives use memory chips to store data instead of platters, arms etc.
|

SSD (Solid State Drive)
|
|
|
|
What are the 2 type of ATA drives?
|

1. SATA
2. PATA (Older technology) |
|
|
|
How many wires do a PATA ribbon cable have. (2 Sizes)
|

|
|
|

What does the colored stripe down one side of an IDE ribbon represent?
|
Pin 1
|
|
|
|
The real layout of the CHS inside an HDD is called what?
|
Physical geometry
|
|
|
|
The "fake" CHS described to the CMOS by the onboard circuitry of an HDD was called what?
|
Logical geometry
|
|
|
|
What the name of the ATA2 extension that enabled non–hard drive devices such as CD-ROM drives and tape backups to connect to the PC via the ATA controllers?
|
Advanced Technology Attachment Packet Interface (ATAPI)
|
|
|
|
How many pins do ATAPI drives have?
|

40-pins
|
|
|
|
What new feature did ATA3 techonology introduce?
|
(S.M.A.R.T.) Self-Monitoring,
Analysis, and Reporting Technology |
|
|
|
what is S.M.A.R.T Techonology?
|
It helps predict when a hard drive is going to fail by monitoring the hard drive’s mechanical components
|
|
|
|
What new feature did ATA4 techonology introduce?
|
Ultra DMA
|
|
|
|
Which Ultra DMA mode transfered at 16.7 MBps?
|
Mode 0
|
|
|
|
Which Ultra DMA mode transfered at 25.0 MBps
|
Mode 1
|
|
|
|
Which Ultra DMA mode transfered at 33.3 MBps
|
Mode 2
|
|
|
|
Which Ultra DMA mode transfered at 44.4 MBps
|
Mode 3
|
|
|
|
Which Ultra DMA mode transfered at 66.6 MBps
|
Mode 4 aka ATA/33
|
|
|
|
A system with INT13 extensions can handle up to what size drives?
|
137 GB
|
|
|
|
what is the maximum length of SATA cables?
|

40 Inches
|
|
|
|
What device allows you to use a PATA drive with a SATA ribbon cable?
|
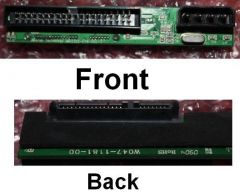
SATA Bridge
|
|
|
|
what disk-optimization feature for SATA drives enables faster read and write speeds?
|
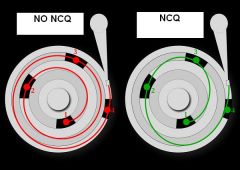
Native command queuing (NCQ)
|
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Native_Command_Queuing
|
|
|
What is the process of connecting a device directly to another device then to another device then on and on called?
|
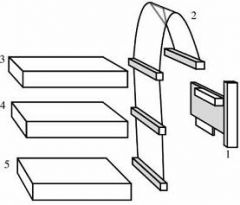
Daisy Chaining
|
|
|
|
The device at the end of a SCSI daisy chain must be have what setting enabled?
|
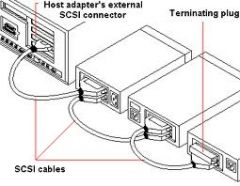
Termination
|
Some devices have this feature automatically enabled
|
|
|
What is Raid 0
|
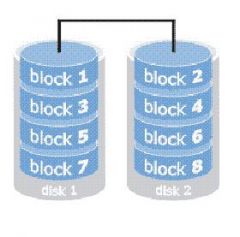
Disk Striping
|
http://www.prepressure.com/library/technology/raid
|
|
|
Which level of RAID requires at least two drives, does not provide redundancy to data and if any one drive fails, all data is lost?
|
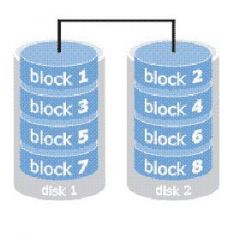
RAID 0—Disk Striping
|
http://www.prepressure.com/library/technology/raid
|
|
|
What is RAID 1
|
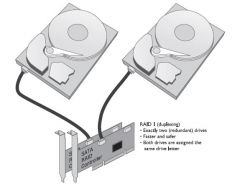
Disk Mirroring/Duplexing
|
http://www.prepressure.com/library/technology/raid
|
|
|
Which level of RAID stores data twice by writing them to both the data disk and mirror disk?
|
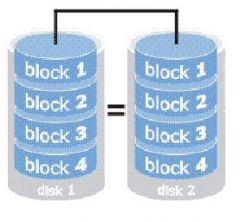
RAID 1
|
http://www.prepressure.com/library/technology/raid
|
|
|
Which level of RAID data had blocks subdivided (striped) and written in parallel on two or more drives had an additional drive to store parity information?
|

RAID 3
|
http://www.prepressure.com/library/technology/raid
|
|
|
On an ATA66 IDE cable what color is the connector that goes to the controller on the motherboard?
|

Blue
|
ATA 5 Cable
|
|
|
On an ATA 66 IDE ribbon cable what color is the connector that goes to a Slave drive?
|

Grey
|
ATA 5 IDE; has 40 pins
|
|
|
On an ATA66 IDE ribbon cable what color is the connector that connects to a Master drive?
|

Black
|
just think of 40 acres and a mule (Master / Black)
|
|
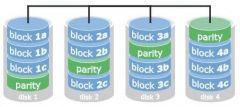
Data is transferred to disks by independent read and write operations (not in parallel). Which level of RAID is this?
|
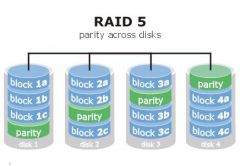
|
instead of a dedicated parity disk, parity information is spread across all the drives.
|
|
|
What is the maximum amount of SCSI devices can you put in a daisy chain?
|
15 Devices
|
|
|
|
Extra information that can be used to rebuild data if one of the drives in a RAID array fails are called what?
|
Parity Data
|
|
|
|
The hard drive lies to the computer about its geometry through an advanced
type of sector translation called what? |
(LBA) Logical Block Addressing
|
|
|
|
What NTFS feature enables administrators to set limits on drive space usage for users?
|
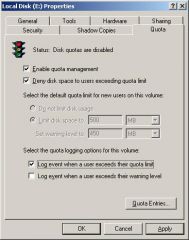
Disk Quotas
|
|

