![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Strategy |
The actions that managers take to attain the goals of a firm
|
|
|
General purpose of a strategy? |
Maximize/make profit. •Differentiationstrategy: Differentiate products, increase price: add value, features, quality,service •Low-coststrategy: Achieve low cost |
|
|
Key means of strategy? |
Allocation of scarce resources to attain goals |
|
|
Value Creation |
A group of activities that increase the value of goods or services to consumers |
|
|
Firm as a chain of discrete value creating activities: Primary activities |
Upstream activities: manufacturing, research and development Downstream activities: marketing, sales, after sales service |
|
|
Firm as a chain of discrete value creating activities: Support activities |
Infrastructure (General and administrative), HR |
|
|
For firms to operate internationally, they are able to (4) |
1. Realize location economies 2. Realize greater cost economies 3. Earn a greater return from the firm's distinctive skills or core competencies 4. Earn a greater return by leveraging any valuable skills developed in foreign operations |
|
|
Location Economies |
Realized by performing a valuecreation activity in an optimal location anywhere around the globe, often arise due to differences in factor costs
|
|
|
Location economies: global web |
Different stages of value chain are dispersed to those locations where percieved value is maximized or costs of value creation are minimized |
|
|
The Experience Effect: Experience Curve |
Systematic reductions in production costs that have been observed to occur over the life of a product |
|
|
The Experience Effect: Learning Effects |
Cost savings that come from learning by doing |
|
|
The Experience Effect: Economies of Scale |
Refer to the reductions in unit cost achieved by producing a large volume of a product |
|
|
Core competence |
skills within the firm that competitors cannot easily match or imitate (aka things that your company does really really well) - earn greater returns by transferring these skills and/or unique product offerings to foreign markets who lack them (McDonalds) |
|
|
Challenges with leveraging subsidy skills |
- Managers must create anenvironment where incentives are given to take necessary risks and reward them - Needa process to identify new skilldevelopment - Needto facilitate transfer of new skills within the firm |
|
|
Firms that compete in the global marketplace typically face 2 types of competitive pressure |
1. Cost pressures 2. Pressures for local responsiveness These pressures place conflicting demands on a firm |
|
|
Pressures for cost reductions (4) |
- Intense in industries of standardized, commodity type product that serve universal needs - Major competitors are based in low-cost locations - Consumers are powerful and face low switching costs - Liberalization of world trade and investment environment |
|
|
Pressures for local responsiveness (4) |
1. Differencesin consumer tastes & preferences (families like pickup trucks in North America, while in Europe it is viewed as a utility vehicle for firms) - Differencesin infrastructure & traditional practices (different electrical sockets globally) - Differences in distribution channels (Germany has few retailers dominating food market while it is fragmented in Italy) - Host government demands (Health care system differencesbetween countries require pharmaceutical firms to change operating procedures) |
|
|
Four basic strategic choices |

|
|
|
Global Strategy |
- Focus is on achieving a low cost strategy by reaping cost reductions that come from experience curve effects and location economies - Production, marketing, and R&D concentrated in few favourable functions - Market standardized to keep costs low - Effective where strong pressures for cost reductions and low demand for local responsiveness |
|
|
International Strategy |
- Createvalue by transferring valuable core competencies to foreign markets thatindigenous competitors lack - Centralizeproduct development functions at home - Establishmanufacturing and marketing functions in local country but head officeexercises tight control over it - Limitcustomization of product offering and market strategy |
|
|
Multidomestic strategy |
- Mainaim is maximum local responsiveness - Customizeproduct offering, market strategy including production, and R&D accordingto national conditions - Generallyunable to realize value from experience curve effects and location economies - Possesshigh cost structure |
|
|
Transnational strategy |
- Tomeet competition, firms aim to reduce costs, transfer core competencies whilepaying attention to pressures for local responsiveness - Globallearning: Valuable skills can develop in any of the firm’s world wideoperations; Transfer of knowledge from foreign subsidiary to home country, to other foreign subsidiaries - Transnationalstrategy difficult task due to contradictory demands placed on the organization |
|
|
Advantages and disadvantages of each strategy |
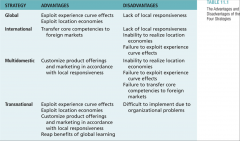
|

