![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the 4 forces of nature? |
1) gravitational 2) electromagnetic 3) strong nuclear force 4) weak nuclear force |
|
|
|
Example of gravitational? |
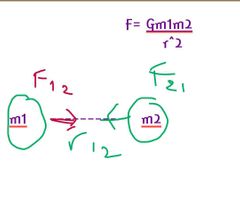
Universal law of gravitation
*Forces are always attractive FAB A=on, B=due |
|
|
|
electromagnetic? |
Electric and magnetic- interactions between atoms and molecules |
|
|
|
Strong nuclear force? |
Interaction that keeps neutrons and protons together in the atom nucleus |
|
|
|
Weak nuclear force |
Interaction b/w subatomic particles |
|
|
|
All matter is Made of _______ |
Atoms |
|
|
|
What is structure of the atom? |
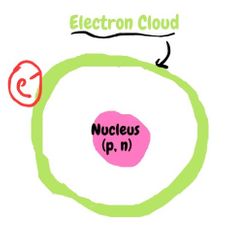
|
|
|
|
neutrons are electrically ________ |
neutral |
|
|
|
protons and electrons are both: |
charged particles |
|
|
|
what is charge? measured by? |
a physical quantity that in intrinsic to nature by the fact that its first electrons & electrons
measured by Coulombs' [c] |
|
|
|
2 types of charges? |
-positive (lacking in e-) -negative (rich in e-) |
|
|
|
Region within a magnetic field (like deflection; not super important) |
|
|
|
|
what are 7 fundamental principles applied to charge? |
1. charge is conserved 2. charge is quantisized 3. electromagnetic forces causes like charges to repel and unlike charges to attract |
|
|
|
explain how charge is conserved. |
there's no creation of charge in the process; only charge is transferred |
|
|
|
what is the law of conservation of charge? |
the net charge ( + & - charge combined) of a closed system never changes |
|
|
|
a system electrically neutral means that... |
it has the same amount of + charge as - charge |
|
|
|
explain, charge is quantisized |
charge of e-= most fundamental charge in the universe (also same for p+) this is 1.602 x10^-19 C this means; charge on charged system must be integer. |
|
|
|
ex: How many e- are in a system charged to -1uC? Note: milli (m)~ 10^-3 micro (u) ~ 10^-6 nano (n) ~ 10^-9 pico (p) ~ 10^-12 |
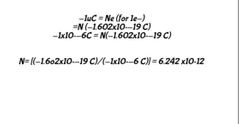
|
|
|
|
What is Coulomb's law? |

|
|
|
|
k (coulomb's constant) is? Eo (permittivity of free space in vaccumm) is? |
K= 9 x 10^9 Nm^2/C^2 Eo= 8.85x10^-12 C^2/Nm^2 |
|
|
|
does electrically neutral mean chargeless? |
no, = equal charge; but still charged |
|
|
|
how can you charge objects? (4) |
1. contact/friction 2. charging by induction 3. grounding 4. polarization |
|
|
|
charging by induction? |
without actually transferring charge by contact, the system acquires an induction. NOTE that this charge is temporary, once the object that is charged is removed of the vicinity of the system in question, this comes back to equilibrium |
|
|
|
what happens when you bring a (-) rod to a neutral electroscope (leaves were closed)? |
leaves open up, because all the (-) repel |
|
|
|
what is grounding |
charge removal-- you can put your finger onto the electroscope and have e- either return to Earth or enter electroscope |
|
|
|
is grounding charging by induction |
yes |
|
|
|
polarization visualizatuon (it's related with induction) |
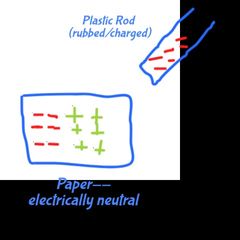
|
|
|
|
Topic: Types of materials according to their electrical properties |
😝 |
|
|
|
Conductors are... |
characterized by the fact that can be charged, or charge moves freely on them (ex: metals) |
|
|
|
Insulators: |
are materials that aren't entirely charged, & the charge resides only at an particlar location where material was charged (ex: plastic. polymers) |
|
|
|
superconductors |
conductors with no energy loss |
|
|
|
semiconductors are... |
materials that can behave as insulators/conductors, depending on voltage applied to them (Si, Ge, Ga, As) Application: LEDs, Microchips |
|
|
|
approach to Coloumb's law questions? |
1. analyze region 2. FBD 3. Fnet = 0 |
|
|
|
Electric Fields |
🛄 |
|
|
|
Electric Field is... |
A disturbance in space and time caused by the presence of charge |
|
|
|
Always use a ___ small test charge (or a visiting charge) to check field |
+ |
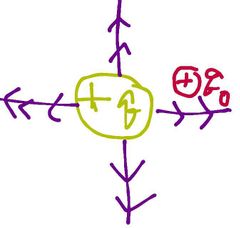
|
|
|
The formula for electric field produced by a point charge? |
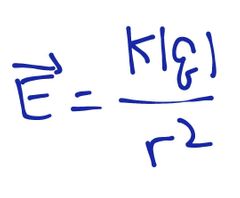
|
|
|
|
As the charge is further away, the field... |
Weakens, E inversely proportional to distance |
|
|
|
If a + test charge q° experiences a force F at a given location due to presence of electric field created by charge q, then the magnitude of electric field is given by: |
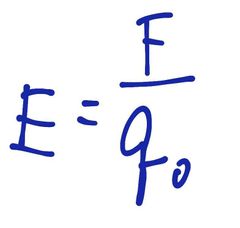
Hence, E= force per unit charge |
|
|
|
Electric field lines: + (Moves ______) - (moves ______) |
Away, towards |
|
|
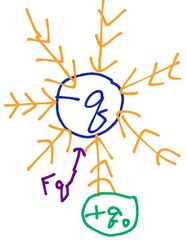
What is the orange things called? |
Electric field lines |
|

