![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define mathematical models? |
Mathematical models are analytical descriptions of physical phenomena and processes. They are a set of equations that expresses the essential features of a physical system in terms of variables that describe the system. |
|
|
Define numerical simulation? |
The use of a numerical method and a computer to evaluate the mathematical model of a process and estimate its characteristics |
|
|
What are mathematical models of physical phenomena based on? Give some examples. |
They are based on fundamental scientific laws of physics such as the principle of conservation of mass, conservation of linear momentum, and conservation of energy. |
|
|
What do numerical methods allow since exact methods of analysis are usually difficult due to geometric and material complexities? |
Numerical methods transform differential equations governing a continuum to a set of algebraic equations of a discrete model of the continuum that are to be solved using computers. |
|
|
What is calculus of variations? |
A field of mathematical analysis that deals with maximizing or minimizing functionals, which are mappings from a set of functions to the real numbers. Functionals are often expressed as definite integrals involving functions and their derivatives. |
|
|
What is a functional? |
It is a function from a vector space into its underlying scalar field, or a set of functions of the real numbers. |
|
|
What are the 3 distinct features of the finite element methods superiority? |
1) A geometrically complex domain is represented as a collection of geometrically simple subdomains. 2) Over each finite element, algebraic equations among the quantities of interest are developed using the governing equations 3) Interelement relationships are used to assemble the elements |
|
|
What are some of the sources of error in the finite element method? |
- Division of the whole domain might not be exact - Representation of the dependent unknowns - Evaluation of the integrals - Solving the assembled system of equations |
|
|
What ar ethe three fundamental steps of the finite element method? |
1. Divide the whole domain into parts 2. Seek an approximation to the solution as a linear combination of nodal values and approximation functions, and derive the algebraic relations among the nodal values of the solution over each part 3. Assemble the parts and obtain the solution to the whole. |
|
|
What is the form of the equation typically used to determine the solution of differential and/or integral equations? |
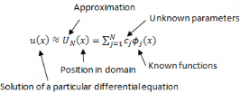
|
|
|
How is a vector A expressed in three-dimensional space? |
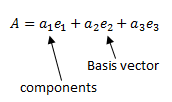
|
|
|
What is the name of the coordinate system which basis vectors that are constants (with fixed lengths and directions)? |
Cartesian coordinate system |
|
|
True or false? The laws of nature are independent of the choice of coordinate system? |
TRUE |
|
|
What is the definition of the cross product of two vectors? |
sdf |

