![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Point
|
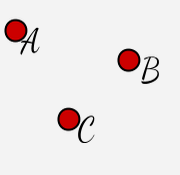
An undefined term thought of as a location with no size or dimension. It is the most basic building block of geometry. In a two dimensional coordinate system, a point´s location is represented by an ordered pair of numbers (x,y). |
|
|
Line |
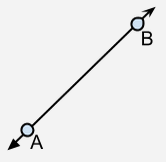
An undefined term thought of as a straight and continuous arrangement of infinitely many points. It has infinite length but no thickness (one dimensional), and extends forever into two directions. |
|
|
Plane |
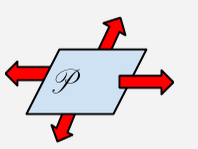
An undefined term thought of as a flat surface that extends infinitely along it's edges. A plane has length and width but no thickness, so it is two dimensional. |
|
|
Definition |
A statement that clarifies or explains the meaning of a word or phrase. |
|
|
|
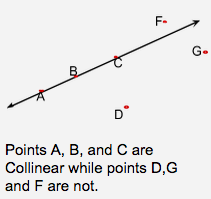
On the same line. |
|
|
Coplanar |
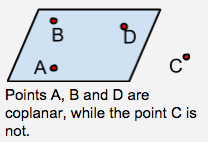
On the same plane. |
|
|
Line Segment |
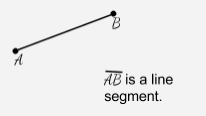
Two points and all the points between them that are collinear with the two points. It is measured in length and also called a segment. |
|
|
Endpoints |
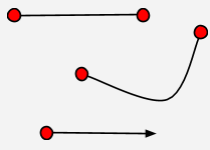
The points at either end of a segment or an arc or the first point of a ray. |
|
|
Congruent |
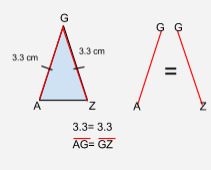
(Angles, lines, segments, or polygons) Identical in shape and size. |
|
|
Midpoint |

The point on the line segment that is the same distance from both endpoints. The midpoint bisects the segment. |
|
|
Bisect |
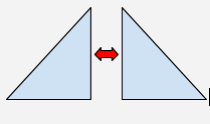
To divide into two congruent parts. |
|
|
Ray |
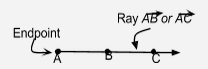
A point on a line, and all the points of the line that lie on one side of this point. |
|
|
Angle |
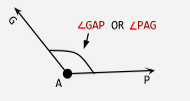
Two non-collinear rays having a common endpoint. |
|
|
Vertex |
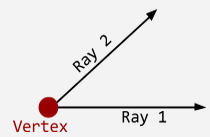
A point of intersection of two or more rays or line segments in a geometric figure (vertices). |
|
|
Side (of an angle) |
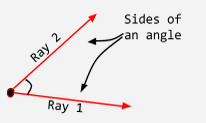
One of the two rays that form an angle. |
|
|
Measure of an angle |
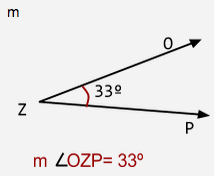
The smallest amount of rotation about the vertex from one ray to the other, measured in degrees |
|
|
Degrees |
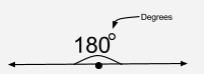
A unit of measure for angles and arcs equivalent to 1/360 of the rotation around a circle. |
|
|
Reflex measure of an angle |
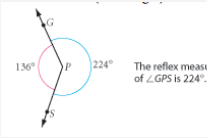
The largest amount of rotation less than 360 degrees about the vertex from one ray to another. |
|
|
Protractor |
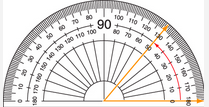
A tool used to measure the size of an angle in degrees. |
|
|
Angle Bisector |
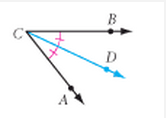
A ray that has its endpoint at the vertex of the angle and that divides the angle into two congruent angles. |
|
|
Incoming angle |
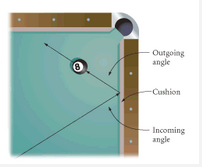
The angle formed between the path of an approaching object and the surface from which it rebounds. (Equal to Outgoing Angle) |
|
|
Outgoing Angle |
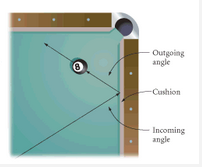
The angle formed between the path of a rebounding object and the surface it collided with. (Equal to Incoming Angle) |
|
|
Right Angles |
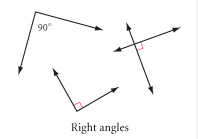
Angles that measure exactly 90º. |
|
|
Acute Angles |
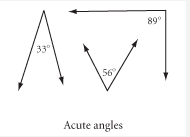
Angles that measure less than 90º. |
|
|
Obtuse Angles |
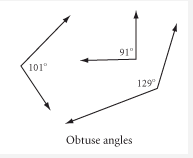
Angles that measure more than 90º. |
|
|
Complementary Angles |
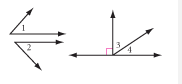
Angles that have measurements that together add up to 90º. |
|
|
Supplementary Angles |
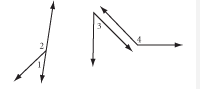
Angles that have measurements that together add up to 180º. |
|
|
Vertical Angles |
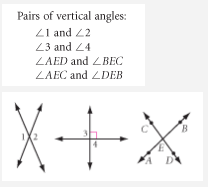
Angles opposite to each other when two lines cross, that have congruent angle measurements. |
|
|
Linear Pair of Angles |
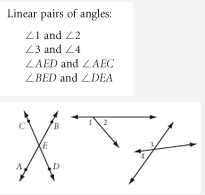
A couple of adjacent angles formed by intersecting lines that are also supplementary (add up to 180º). |
|
|
Polygon |
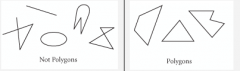
A closed figure in a plane, formed by connecting line segments endpoint to endpoint with each segment intersecting exactly with each other. |
|
|
Side (of the polygon) |
One of the line segments that form the polygon. |
|
|
Vertex (Of the polygon) |
A point of intersection of two or more rays or line segments in a geometric figure. |
|
|
Diagonal (of a polygon) |
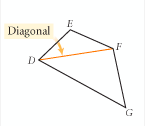
A line segment that connects two nonconsecutive vertices. |
|
|
Convex (Convex Polygon) |
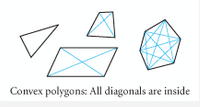
A polygon is Convex if no diagonal is outside the polygon. |
|
|
Concave (Concave Polygon) |
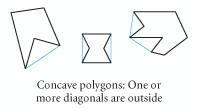
A polygon is concave if at least one diagonal is outside the polygon. |
|
|
Triangle |
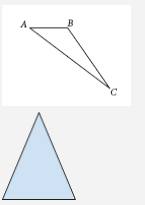
A polygon with 3 sides. |
|
|
Quadrilateral |
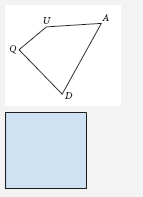
A polygon with 4 sides. |
|
|
Pentagon |
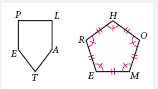
A polygon with 5 sides. |
|
|
Hexagon |
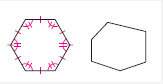
A polygon with 6 sides. |
|
|
Heptagon |
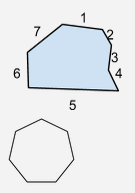
A polygon with 7 sides. |
|
|
Octagon |
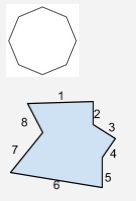
A polygon with 8 sides. |
|
|
Nonagon |
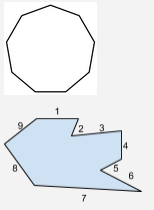
A polygon with 9 sides. |
|
|
Decagon |
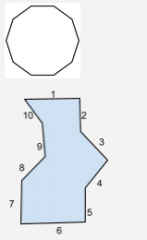
A polygon with 10 sides. |
|
|
Undecagon |
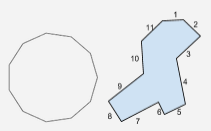
A polygon with 11 sides. |
|
|
Dodecagon |
A polygon with 12 sides. |
|
|
Perimeter |

The length of the boundary of a two dimensional figure. |
|
|
Equilateral Polygon |
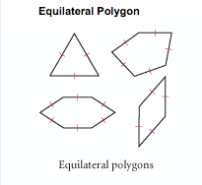
Polygon that has all congruent sides. |
|
|
Equiangular Polygon |
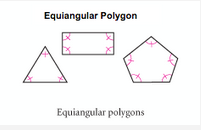
Polygon that has all congruent angles. |
|
|
Regular Polygon |
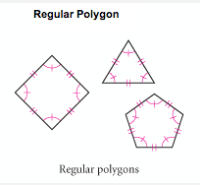
Polygon that has all congruent sides and angles. |
|
|
Assume |
To accept as true without facts or proof. |
|
|
Right Triangle |
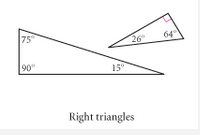
A three sided polygon that has at least one right angle. |
|
|
Acute Triangle |
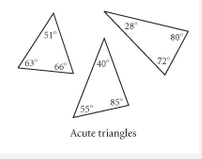
A three sided polygon that has all angle measures below 90º. |
|
|
Obtuse Triangle |
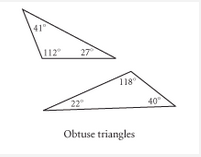
A three sided polygon that has at least one angle measures above 90º. |
|
|
Scalene Triangle |
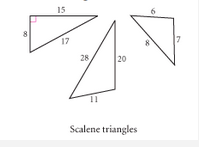
A three sided polygon that has three different measures for each side. |
|
|
Equilateral Triangle |
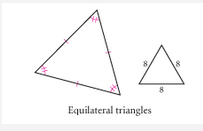
A three sided polygon that has all congruent sides and angles. |
|
|
Isosceles Triangle |
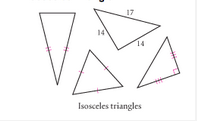
A three sided polygon with two equal sides or two equal measures. |
|
|
Vertex Angle of an isosceles triangle |
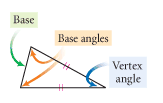
The angles between two congruent sides. |
|
|
Base Angles |
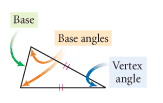
The two angles opposite the two sides of equal length are called the base angles of the isosceles triangle. |
|
|
Trapezoids |
A quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides.
|
|
|
Kite |
A quadrilateral with two pairs of congruent sides that are not parallel. |
|
|
Parallelogram |

A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. |
|
|
Rectangle |

A plane figure with four straight sides and four right angles, especially one with unequal adjacent sides, in contrast to a square.
|
|
|
Square |
A plane figure with four straight sides and four right angles. |
|
|
Space |
An undefined term thought of as the set of all points. Space extends infinitely in all directions, so it is three-dimensional. |
|
|
Isometric Drawing |
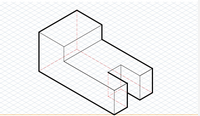
A drawing of a three-dimensional object that shows three faces in one view. Also called an edge view. |
|
|
Cylinder |
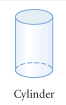
A solid consisting of two congruent, parallel circles and their interiors , and the segments having an endpoint on each circle that are parallel to the segment between the centers of the circles. |
|
|
Cone |
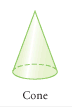
A solid consisting of a circle and its interior, a point not in the plane of the circle , and all points on line segments connecting that point to points on that circle. |
|
|
Prism |
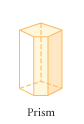
A polyhedron with two congruent , parallel bases connected by lateral faces that are parallelograms. |
|
|
Pyramid |
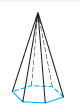
A polyhedron consisting of a polygon base and triangular lateral faces that share a common vertex. |
|
|
Sphere |
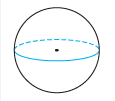
The set of all points in space given at a given distance from a given point. |
|
|
Hemisphere |
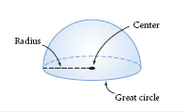
Half of a sphere and its great circle base. |
|
|
Net |
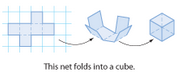
A two dimensional pattern that can be folded to form a three dimensional figure. |
|
|
Circle |
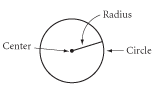
A circle is the set of all points in a plane at a given distance from a given point. |
|
|
Radius |
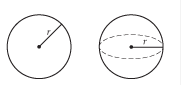
A line segment from the center of a circle or sphere to a point on the circle or sphere. Also, the length of that line segment. |
|
|
Chord |
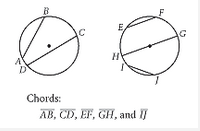
A line segment whose endpoints both lie on the circle, on the circle’s curve. |
|
|
Diameter |
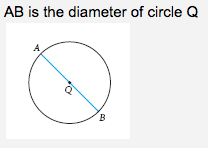
A chord of a circle that contains the center, or the length of that chord. |
|
|
Tangent of a circle |
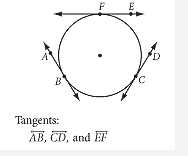
A line segment that just touches a curve of the circle at one point, without cutting across it. |
|
|
Point of Tangency |

The point of intersection of a tangent line and a circle. |
|
|
Concentric Circles |
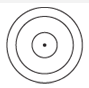
Two or more coplanar circles sharing the same center. |
|
|
Arc |

Two points of a circle and the continuous part of the circle between them. |
|
|
Arc A Semicircle |
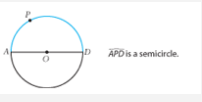
An arc of a circle whose endpoints are the endpoints of a diameter. |
|
|
Arc B Minor Arc
|
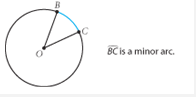
An arc of a circle that is smaller than a semicircle. |
|
|
Arc C Major Arc |
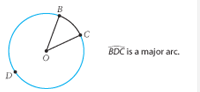
An arc of a circle that is larger than a semicircle. |
|
|
Central Angle |
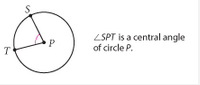
An angle with its vertex at the center of the circle, and sides passing through the endpoints of the arc. |
|
|
Arc Measure |
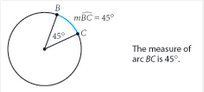
The measure of the central angle that intercepts an arc, measured in degrees. |

