![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Biochemistry
|
Study of properties of individual molecules within a living system & how they interact with one another
|
|
|
What is the purpose of biochemistry?
|
It seeks to describe the organization & function of living matters in molecular terms
|
|
|
What are the 3 disciplines of Biochemistry?
|
1. Structural
2. Metabolism 3. Genetic / Molecular Genetic |
|
|
Explain the Structural discipline.
|
Focus on components & relationship of biological function to chemical structures
|
|
|
Explain the Metabolism discipline.
|
Totality of chemical reaction in living matter.
|
|
|
Explain the Genetic / Molecular Genetic discipline.
|
Chemistry of storage and transmission of biological information.
|
|
|
What are the 3 properties that makes a collection of molecules a living system?
|
1. highly organized set of complex molecules that result in complicated structures with intricate internal structure
2. each component of a living organism has a specific purpose 3. ability to extract, transform, & utilize energy from the environment to build & maintain structures, work, move, reproduce, ect |
|
|
Of the 3 properties of a living system which is the most important?
|
3. ability to EXTRACT, TRANSFORM, UTILIZE ENERGY from environment to BUILD, MAINTAIN STRUCTURES, WORK, MOVE, REPRODUCE, ect
|
|
|
What are viruses considered as?
|
biological entities = parasite
|
|
|
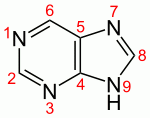
what are the 4 basic groups of biomolecules?
|
nucleic acid / proteins/ lipids / carbohydrates
|
|
|
Of the 4 basic groups of biomolecules which actually carry information?
|
protein, nucleic acid, and some times carbohydrates
|
|
|
What are the 4 basic structures of a cell?
|
plasma membrane / cytoplasm / genetic material / ribosomes
|
|
|
Adenine; purine
|
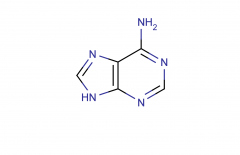
|
|
|
Guanine; purine
|
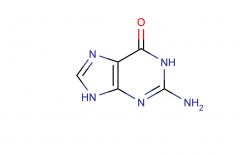
|
|
|
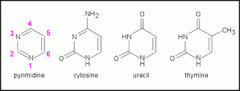
Uracil; pyrimidine
|
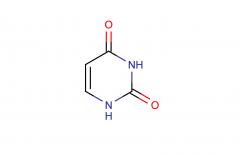
|
|
|
Thymine; pyrimidine
|
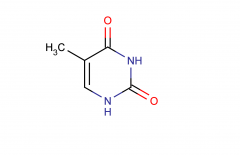
|
|
|
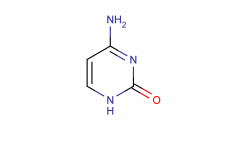
Cytosine; pyrimidine
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
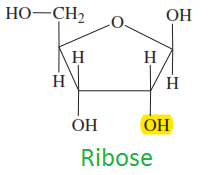
Ribose
|
|
|
|
Deoxyribose
|
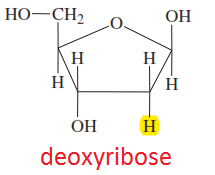
|
|
|
what are the 3 types of systems in thermodynamics?
|
open / closed / isolated
|
|
|
What are the difference between the 3 different types of thermodynamic systems?
|
Open allows for both matter & energy to be exchanged; Closed allows only energy; Isolated does not allow matter nor energy to be exchanged
|
|
|
State function
|
thermodynamic variable use to describe the thermal dynamics state of the system
|
|
|
How is a state function determined?
|
by initial & final state of the system and independent of the pathway in between the 2 states
|
|
|
What are some examples of state function? What is not a state function?
|
Temperature / pressure / [solute]/ gibbs free energy / enthalpy / entropy
Not state function = work done |
|
|
Spontaneous reaction (favorable)
|
irreversible process that is far from equilibrium
|
|
|
What are the 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics?
|
1. law of conservation
2. total disorder of universe increase in every process |
|
|
What are the 7 non-covalent interactions?
|
h-bond / charge-charge / charge-dipole / dipole-dipole / charged-induced dipole / dipole-induced dipole / London
|
|
|
Hydrogen bond (3 requirements)
|
1. N/O/F/S
2. must have lone pair of e- 3. strongest is linear 180 degrees +/-45 exist |
|
|
Charge - charge interaction
|

electrostatic / ionic interaction between molecules/atom with permanent charge; nondirectional
|
|
|
Charge - dipole interaction
|
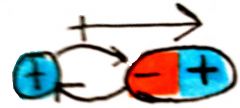
between a charged species and 1 dipole; directional
|
|
|
dipole-dipole
|
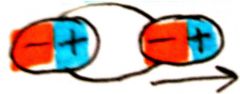
interactions between 2 molecules with a permanent dipole; directional
|
|
|
charged-induced dipole
|
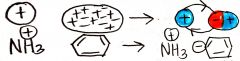
polarizable molecule (e- are displaced to give momentary charge) placed near a charge molecule; a dipole will be induced with charge; non-directional
|
|
|
dipole-induced dipole
|

molecule with a permanent dipole induces a dipole in a polarizable molecule; non-directional
|
|
|
London forces
|
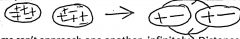
2 induced dipoles set up & break apart; non-directional
|
|
|
Draw base pairing for G-C
|
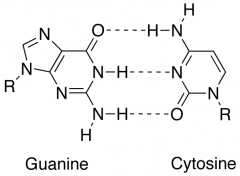
|
|
|
Draw base pairing for A-T
|
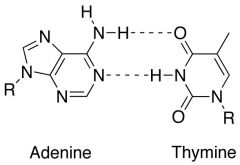
|
|
|
draw dAMP
|
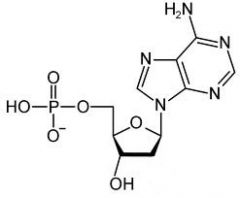
2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-monophosphate
|
|
|
draw dGMP
|
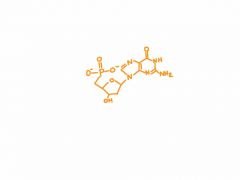
2'-deoxyguanosine 5'-monophosphate
|
|
|
draw dTMP
|
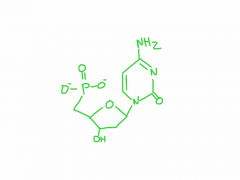
2'-deoxythymidine 5'-monophosphate
|
|
|
draw dCMP
|
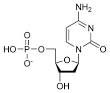
2'-deoxycytidine 5'-monophosphate
|

