![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
161 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy |
Study of internal & external body structures & their physical relationships |
|
|
Physiology |
Study of how living organisms perform their vital functions |
|
|
Gross Anatomy |
Examining fairly large structures, Conducted without using a microscope |
|
|
Surface Anatomy |
Studies general form of the body's surface |
|
|
Regional Anatomy |
Studies anatomical organization of specific areas of the body |
|
|
Sectional Anatomy |
Studies relationship of the body's structures by examining cross sections of the tissue or organ |
|
|
Systemic Anatomy |
Studies structure of organ systems |
|
|
Clinical Anatomy |
Subspecialties important in clinical practice (e.g. pathological anatomy, surgical anatomy) |
|
|
Developmental Anatomy |
Studies changes in form that take place between conception and adulthood |
|
|
Embryology |
Study of early developmental processes |
|
|
Microscopic Anatomy |
Studies structures not visible without magnification |
|
|
What type of microscope can be used to examine tissue structure? |
Dissecting Microscope |
|
|
What type of microscope can be used to study basic details of cell structure? |
Light Microscope |
|
|
What type of microscope can be used to study individual molecules? |
Electron Microscope |
|
|
Cytology |
Study of the internal structure of individual cells |
|
|
Histology |
Examination of tissues |
|
|
Cell Physiology |
Study of the functions of cells |
|
|
Organ Physiology |
Study of the function of specific organs |
|
|
Systemic Physiology |
Studies aspects of the functioning of specific organ systems |
|
|
Pathological Physiology |
Study of effects of diseases on organ functions or system functions |
|
|
Signs |
Objective disease indications, such as a fever |
|
|
Symptoms |
Subjective disease indications, such as tiredness |
|
|
Scientific Method |
System of advancing knowledge by proposing a hypothesis to answer a question, and testing that hypothesis with data collected through observation & experimentation |
|
|
Chemical Level of Organization |
Atoms -- the smallest stable units of matter that can combine to form molecules |
|
|
Cellular Level of Organization |
Cells -- the smallest living units in the body |
|
|
Tissue Level of Organization |
Tissues -- group of cells working together to perform specific functions |
|
|
Organ Level of Organization |
Organs -- made of two or more tissues working together to perform specific functions |
|
|
Organ System Level of Organization |
Organ system -- group of organs interacting to perform a particular function |
|
|
Organism Level of Organization |
Organism -- an individual life form (human) |
|
|
Integumentary System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - skin, hair, sweat glands, nails
Functions - protects against environmental hazards, helps regulate body temperature, provides sensory information |
|
|
Skeletal System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - bones, cartilage, associated ligaments, bone marrow
Functions - provides support and protection for other tissues, stored calcium and other minerals, forms blood cells |
|
|
Muscular System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - skeletal muscles and associated tendons Functions - provides movement, protection and support for other tissues, generates heat that maintains body temperature |
|
|
Nervous System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, sense organs Functions - directs immediate responses to stimuli, coordinates or moderates activities of other organ systems, provides and interprets sensory information |
|
|
Endocrine System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal glands, gonads, endocrine tissues in other systems Functions - directs long-term changes in activities of other organ systems, adjusts metabolic activity, controls structural/functional changes during development |
|
|
Cardiovascular System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - heart, blood, blood vessels Functions - distributes blood cells, water, and dissolved materials including nutrients, oxygen, waste products, and carbon dioxide, distributes heat assisting in control of body temperature |
|
|
Lymphatic System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - spleen, thymus, lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, tonsils
Functions - defends against infection & disease, returns tissue fluids to bloodstream |
|
|
Respiratory System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - nasal cavities, sinuses, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, alveoli Functions - delivers air to alveoli, provides oxygen to bloodstream, removes carbon dioxide from bloodstream, produces sounds for communication |
|
|
Digestive System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - teeth, tongue, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder, pancreas Functions - processes and digests food, absorbs and conserves water, absorbs nutrients, stores energy reserves |
|
|
Urinary System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra Functions - excretes waste products from blood, controls water balance by regulating volume of urine produced, stores urine, regulates blood in concentrations and pH |
|
|
Male Reproductive System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - testes, epididymides, ductus deferentia, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, penis, scrotum Functions - produces male sex cells (sperm), seminal fluids, and hormones, sexual intercourse |
|
|
Female Reproductive System: Major Organs & Functions? |
Major Organs - ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, labia, clitoris, mammary glands Functions - produces female sex cells (oocytes) and hormones, supports developing embryo from conception to delivery, provides milk to nourish newborn infant, sexual intercourse |
|
|
Medical Terminology |
Using word roots, prefixes, suffixes, and combining forms to build terms related to the body in health and disease, many derived from Greek & Latin |
|
|
Word Roots |
Basic, meaningful parts of a term, cannot be broken down |
|
|
Prefixes |
Word elements attached to the beginning of words |
|
|
Suffixes |
Word elements attached to the end of words |
|
|
Combining Forms |
Independent words or word roots used in combination with words, prefixes, suffixes, or other combining forms to build a new term |
|
|
Eponyms |
Commemorative names named after either the discoverer or (in the case of diseases) the most famous victim |
|
|
Terminologia Anatomica |
Established the worldwide standard for human anatomical terminology |
|
|
Anatomical Landmarks |
Structures that can be felt of palpated |
|
|
Anatomical Regions |
Specific areas used for reference purposes |
|
|
Anatomical Position |
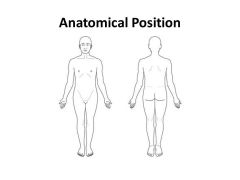
Standard anatomical reference for the human form -- hands at the sides with palms facing forward, feet together |
|
|
Supine |
Person lying down face up |
|
|
Prone |
Person lying down face down |
|
|
Abdominopelvic Quadrants |
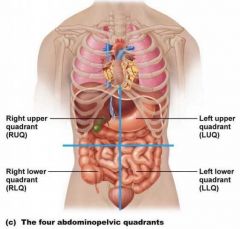
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic Regions |
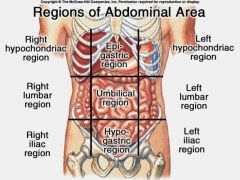
|
|
|
Anterior |
AKA Ventral - Front of the body when viewed in anatomical position |
|
|
Posterior |
AKA Dorsal - Back of the body when viewed in anatomical position |
|
|
Left & Right |
Always refers to right & left sides of the subject, NOT the observer |
|
|
Superior |
Above; at a higher level; in the human body, toward the head |
|
|
Inferior |
Below; at a lower level; in the human body, toward the feet |
|
|
Medial |
Toward the midline |
|
|
Lateral |
Away from the midline |
|
|
Proximal |
Toward the point of attachment of a limb to the trunk |
|
|
Distal |
Away from the point of attachment of a limb to the trunk |
|
|
Cranial |
AKA Cephalic - toward the head |
|
|
Caudal |
Toward the tail (coccyx in humans) |
|
|
Section |
A slice through a three-dimensional object |
|
|
Frontal |
Forehead |
|
|
Nasal |
Nose |
|
|
Ocular |
Eye |
|
|
Orbital |
Eye |
|
|
Cephalic |
Entire Head |
|
|
Cranial |
Skull |
|
|
Facial |
Face |
|
|
Otic |
Ear |
|
|
Buccal |
Cheek |
|
|
Oral |
Mouth |
|
|
Mental |
Chin |
|
|
Cervical |
Neck |
|
|
Thoracic |
Chest |
|
|
Mammary |
Breast |
|
|
Axillary |
Armpit |
|
|
Brachial |
Arm |
|
|
Antecubital |
Front of Elbow |
|
|
Antebrachial |
Forearm |
|
|
Olecranal |
Elbow |
|
|
Carpal |
Wrist |
|
|
Palmar |
Palm of Hand |
|
|
Pollex |
Thumb |
|
|
Digits |
Fingers and Toes |
|
|
Abdominal |
Abdomen |
|
|
Umbilical |
Navel |
|
|
Pelvic |
Pelvis |
|
|
Manual |
Hand |
|
|
Acromial |
Shoulder |
|
|
Dorsal |
Back |
|
|
Lumbar |
Lower Back |
|
|
Inguinal |
Groin |
|
|
Pubic |
Pubis |
|
|
Gluteal |
Buttock |
|
|
Femoral |
Thigh |
|
|
Patellar |
Kneecap |
|
|
Popliteal |
Back of Knee |
|
|
Crural |
Leg |
|
|
Sural |
Calf |
|
|
Tarsal |
Ankle |
|
|
Pedal |
Foot |
|
|
Hallux |
Big Toe |
|
|
Plantar |
Sole of Foot |
|
|
Calcaneal |
Heel of Foot |
|
|
Frontal Plane |
AKA Coronal Plane - vertical plane that divides the body or organ into anterior & posterior portions |
|
|
Coronal Plane |
AKA Frontal Plane - vertical plane that divides the body or organ into anterior & posterior portions |
|
|
Sagittal Plane |
Vertical plane that divides the body into left & right portions |
|
|
Midsagittal Plane |
A sagittal plane that lies in the middle of the body |
|
|
Parasagittal Plane |
A sagittal plane that is offset from the middle of the body |
|
|
Transverse Plane |
Horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior portions |
|
|
Cross Section |
Another name for a transverse section, a cut in the transverse plane |
|
|
X-Rays |
Form of high-energy radiation that can penetrate living tissue, oldest & most common form of imaging |
|
|
Radiopacity |
Ability to stop the passage of x-rays |
|
|
Radiopaque |
Areas impenetrable to x-rays that appear light or white |
|
|
CT Scan |
Computed Tomography Scan - uses computers to reconstruct a sectional view from an x-ray source rotating around the body, shows 3D relationships and soft tissue structures |
|
|
MRI |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging - uses a magnetic field which causes particles in the body to line up in a uniform direction, energy from pulses of radio waves is absorbed & released by atoms, released energy used to create a detailed image of soft tissue structure |
|
|
PET |
Positron Emission Tomography - assesses metabolic & physiological activity of a structure |
|
|
Ultrasound |
Small transmitter contacts the skin, broadcasts brief burst of high-frequency sound, detects echoes, no adverse effects reported, safe for monitoring fetal development |
|
|
Echogram |
Picture assembles from the pattern of echoes from an ultrasound |
|
|
Spiral CT Scan |
3D imaging technology, platform advances at a steady pace through scanner, imaging source (usually x-rays) rotates continuously, detector quickly and continuously gathers data creating a higher quality image, patient exposed to less radiation than a standard CT Scanner |
|
|
True Body Cavities |
Closed, fluid filled, and lined by a thin tissue layer called a serous membrane or serosa |
|
|
Thoracic Cavity contains which Cavities? |
Two pleural cavities each surrounding a lung, the pericardial cavity surrounding the heart, and the mediastinum, a large tissue mass between the two pleural cavities |
|
|
Diaphragm |
A flat muscular sheet that separates the thoracic & abdominopelvic cavities |
|
|
Viscera |
Internal organs that are enclosed by the thoracic & abdominopelvic cavities |
|
|
Serous Membrane |
Delicate, thin tissue layer that lines the walls of body cavities & covers the surface of the enclosed viscera |
|
|
Serous Fluid |
Watery fluid that moistens serous membranes, coats opposing surfaces, and reduces friction |
|
|
Visceral Serosa |
Portion of the serous membrane that directly covers a visceral organ |
|
|
Parietal Serosa |
Portion of serous membrane that lines the inner surface of a body wall or chamber |
|
|
Pleural Cavities |
Two (left and right) cavities that surround the lungs |
|
|
Mediastinum |
Mass of connective tissue between the two pleural cavities that surrounds, stabilizes, and supports the esophagus, trachea, and thymus, as well as major blood vessels that originate and end at the heart |
|
|
Pleura |
The serous membrane lining a pleural cavity, reduces friction as the lung expands and recoils during breathing |
|
|
Pericardial Cavity |
A small chamber that surrounds the heart that is contained within the mediastinum |
|
|
Pericardium |
Serous membrane that lines the pericardial cavity |
|
|
Abdominopelvic Cavity |
Cavity that extends from the diaphragm to the pelvis, subdivided into abdominal and pelvic cavities |
|
|
Peritoneal Cavity |
A potential space within the abdominopelvic cavity that is lined by a serous membrane known as the peritoneum |
|
|
Peritoneum |
Serous membrane lining the peritoneal cavity that allows organs of the digestive system to slide across one another without causing damage |
|
|
Abdominal Cavity |
Extends from diaphragm to superior margins of pelvis, contains liver, stomach, spleen, small intestine, and most of the large intestine, organs are partially or completely enclosed by the peritoneal cavity |
|
|
Retroperitoneal |
Organs, such as the kidneys and pancreas, that lie between the peritoneal cavity and the muscular wall of the abdominal cavity |
|
|
Pelvic Cavity |
Inferior to abdominal cavity, bones of pelvis form the walls, layer of muscle forms its floor, contains urinary bladder, various reproductive organs, and the distal portion of the large intestine, and the inferior portion of the peritoneal cavity |
|
|
Infraperitoneal |
Organs that extend inferior to the peritoneal cavity such as the urinary bladder and distal portions of the ureters and large intestine |
|
|
Dorsal Body Cavity |
Internal chamber of skull (cranial cavity) and spaces enclosed by vertebrae (vertebral cavity) that are defined by bony structures and are anatomically and embryologically distinct from true body cavities |
|
|
Homeostasis |
The existence of a stable internal environment |
|
|
Homeostatic Regulation |
Adjustment of physiological systems to preserve homeostasis |
|
|
Autoregulation |
Process that occurs when a cell, tissue, organ, or organ system adjusts in response to some environmental change |
|
|
Extrinsic Regulation |
Process that results from the activities of the nervous system or endocrine system |
|
|
Receptor |
Sensor that is sensitive to a particular stimulus or environmental change |
|
|
Control Center |
Receives & processes information supplied by receptors & sends out commands |
|
|
Effector |
Cell or organ that responds to commands of control center resulting in activity that either opposes or enhances the stimulus |
|
|
Negative Feedback |
Keeps variation in key body systems within range, the effector activated by the control center negates or opposes the original stimulus |
|
|
Positive Feedback |
An initial stimulus produces a response that amplifies or enhances the original change in conditions |
|
|
Positive Feedback Loop |
Escalating cycle of positive feedback typically found when a potentially dangerous or stressful process must be completed quickly to restore homeostasis Examples: cut resulting in blood loss causing clotting, labor and delivery |
|
|
State of Equilibrium |
Exists when opposing processes or forces are in balance |
|
|
Dynamic Equilibrium |
Physiological systems are continually adjusting to changing conditions |
|
|
Right/Left Lateral Recumbent |
Laying on right or left side |
|
|
Coelom |
Ventral body cavity divided into thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity |

