![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anatomy |
Studies the structure of the body parts and their relationship to one another |
|
|
|
Physiology |
The function of the body. How body parts work and carry out their life-sustaining activities |
|
|
|
Gross anatomy |
Study of large structures visible to the naked eye |
|
|
|
Regional anatomy |
All of the structures in a particular region are examined at the same time |
|
|
|
Systemic anatomy |
Studied system by system |
|
|
|
Surface anatomy |
The study of internal structures as they relate to the underlying skin surface |
|
|
|
Microscopic anatomy |
Studies the structures too small to be seen with the naked eye |
|
|
|
Cytology |
Study of cells |
|
|
|
Histology |
Study of tissues |
|
|
|
Developmental anatomy |
Studies structural changes that occur throughout life span |
|
|
|
Principle of complementarity of structure and function |
Structure will always reflect function and fubction is dependent on structure |
|
|
|
Structural order |
Cell, tissue, organ, organsim |
|
|
|
Maintain boundaries |
The bodies ability to keep the internal environment disticnt from the external environment |
|
|
|
Movement |
Bones, muscles, nutrients, and waste |
|
|
|
Responsiveness |
Ability to sense change in the environment and respond to them |
If you cut your hand on a broken glass, you involuntarily pull your hand away from the painful stimuli. You don't have to think about doing it. Just happens. |
|
|
Digestion |
The breaking down on ingested food to dimple molecules that can be absorbed into the blood |
|
|
|
Metabolism |
Breaking down substances into simpler building blocks |
|
|
|
Excretion |
Removing waste |
|
|
|
Reproduction |
Cellular level- make new cells Organismal level- make kids |
|
|
|
Survival needs |
Nutrients (food), oxygen, water, and appropriate temperature & atmospheric pressure |
|
|
|
Nutrients |
Our diet. Proteins are essential for building cell structures. Carbohydrates are major energy fuel for body cells |
|
|
|
Water |
50%-60% of our body weight Most abundant chemical substance in the body |
|
|
|
Normal body temperature |
37° C 98.6°F |
|
|
|
What is the name given to all chemical reactions that occur within body cells? |
Matabolism |
|
|
|
Homeostasis |
The body's ability to maintain relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside environment changes continuously |
|
|
|
Homeostatic control |

Communication is essential |
|
|
|
Control center |
Determines the set point, which is the level or range at which a variable is to be maintained. Analyzes the input it recieves and determines how to respond. |
|
|
|
Effector |
Provides the means for the control center's response |
|
|
|
Negative feedback mechanisms |

Most common homeostatic control mechansims. Output ***** off original effect of the stimulus or reduces intensity. Returns it to its ideal value.
|
Shivering or sweating |
|
|
Positive feedback mechansims |
The result or response enhances the original stimulus so that the responsive is accelerated. Called positive because the result proceeds the same direction as the initial change |
Child birth contractions |
|
|
Homeostatic imbalance |
The body losses the ability to maintain homeostasis as we age |
|
|
|
What process allows us to adjist either to extreme heat or exteme cold? |
Negative feedback mechanisms allow us to adjust to conditions outside the normal temperature by causing heat to be lost by the body (in hot conditions) and retained or generated by the body (in cold conditions). |
|
|
|
Superior |

Toward the head end or upper part of a dtructure or the body; above |
The head is superior to the abdomen. |
|
|
Inferior |

Away from the head end pr toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below |
The navel is inferior to the chin. |
|
|
Anterior |

Toward or at the front of the body; in front of |
The breastbone is anterior to the spine. |
|
|
Posterior |
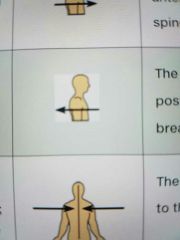
Toward or at the back of the body |
The heart is posterior to the breastbone. |
|
|
Medial |

Toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of |
The heart is medial to the arm |
|
|
Lateral |

Away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of |
The arms are lateral to the chest |
|
|
Intermediate |

Between a more medial and a more lateral structure |
The collar bone is intermediate between the breastbone and the shoulder. |
|
|
Proximal |

Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk. |
The elbow is proximal to the wrist. |
|
|
Distal |

Farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk. |
The kneww is distal to the thigh. |
|
|
Superficial |

Toward or at the body surface |
The skin is superficial the the skeletal muscles. |
|
|
Deep |

Away from the body surface; more internal |
The lunges are deep to the skin. |
|
|
Anterior body terms |

|
|
|
|
Posterior body terms |

|
|
|
|
Axial part |
Makes up axis of body Includes head, trunck, and neck. |
|
|
|
Appendicular part |
Consistes of appendages or limbs which are attatched to the body's axis |
|
|
|
Sagittal plane |

A vertical plane that divides the body into left and right parts. Midsagittal plane- lies exactly on the midline Parasagittal plane- lies anywheres else off the midline |
|
|
|
Frontal plane |

Lies vertically, but divides the body into anterior and posterior parts AKA Coronal plane |
|
|
|
Transverse (horizontal) plane |

Runs left to right divding the body into superior and inferior parts AKA Cross section |
|
|
|
Dorsal cavity |

Contains cranal cavity and vertebral cavity. |
|
|
|
Thoracic cavity |

Ribs and chest muscles Superior mediastinum Pleural cavity Pericardial cavity |
|
|
|
Pleural cavities |
Each envelope a lung |
|
|
|
Mediastinum |
Contains pericardial cavity, which encloses the heart, esophagus, trachea |
|
|
|
Abdominal pelvic cavity |

Separared into abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Abdonimal cavity |
Contains stomache, intestines, sleen, liver |
|
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and the rectum |
|
|
|
Serosa |
Thin double layed membrane that cover thd outer walls of the organs |
|
|
|
Parietal serosa |
The membrane lining the cavity walls |
Punch hand in ballon, outer ballon wall is comparable to parietal serosa |
|
|
Visceral serosa |
The mambrane covering the organs in the body |
Punch hand in a ballon, the wall touching fist is comoarable to visceral serosa |
|
|
Serous fluid |
Liquid inbetween both the parietal and visceral membranes |
Allows organs to slide without friction and carry out their daily movements |
|
|
Parietal pericardium, visceral pericardium |
Serosa membranes lining the heart |
|
|
|
Parietal pleurae |
Lines the walls of the thoracic cavity |
|
|
|
Visceral pleurae |
Covers the lungs |
|
|
|
Parietal peritoneum |
Walls of the abdomenopelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Visceral peritoneum |
Covers most of the organs within the abdominalpelvic cavity |
|
|
|
Four abdominopelvic quadrants |

|
|
|
|
The nine abdonimopelvic regions |

|
|
|
|
Right hypochondriac region |
Liver and gallbladder |
|
|
|
Right lumbar region |
Ascending colon of large intestine |
|
|
|
Right iliac region |
Cecum and appendix |
|
|
|
Epigastric region |
Stomach |
|
|
|
Umbilical region |
Small intestine |
|
|
|
Hypogastric (pubic) region |
Urinary bladder |
|
|
|
Left hypochondriac region |
Diaphragm and spleen |
|
|
|
Left lumbar region |
Descending colon of large intestine |
|
|
|
Left iliac region |
Initial part of sigmoid colon |
|
|
|
Oral and digestive cavities |
Oral cavity= mouth contains toungue and teeth. Continues with the cavity of digestive organs which opens to the body exterior at the anus |
|
|
|
Nasal cavity |
Located within and posterior to the nose Part of the respiratory passageways |
|
|
|
Of the uterus, small intestine, spinal cord, and heart, which is/ are in the dorsal cavity? |
Of these organs, only the spinal cord |
|
|
|
The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is |
Chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal |
|
|
|
The structural and functional unit of life is |
A cell |
|
|
|
Which of the following is a major functional characteristic of all organs |
Movement, growth, metabolism, responsiveness |
|
|
|
Two of these prgan systems bear the major responsibility for ensuring homeostasis of the internal environment. Which two? |
Nervous system and endocrine system |
|
|
|
What cavity is surrounded by the bony skull, vertebral column, brain, and spinal cord? |
Dorsal cavity |
|
|
|
What cavity includes the thoracic and abdominal cavities, and heart, lungs, and digestive organs? |
Ventral cavity |
|
|
|
Which ventral cavity subdivision has no boney protection? |
Abdonimal cavity |
|

