![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
4 ways to represent a function |
verbally numerically (table) visually (graph) algebraically (formula) |
|
|
symmetry |
even = f(-x) = f(x) odd = f(-x) = -f(x) |
|
|
sin(x) and cos(x) |
Domain: all real numbers Range: -1 to 1 Period: 2pi |
|
|
Translations |
f(x) + c means graph shifted upwards by c f(x-c) means graph sifted c units to the right |
|
|
Transformations |
y =cf(x) when c>1, means stretched by a factor of c in the vertical direction y=-f(x) means reflected across x axis y=f(cx) when c>1, means shrink horizontally by a factor of c y=f(-x) = reflect across y axis |
|
|
Composition |
f o g = f(g(x)) Domain of f(g(x)) is wherever both f and g are defined |
|
|
Laws of exponents |
b^x+y = (b^x)(b^y) b^x-y = (b^x)/b^y) (b^x)^y = b^xy (ab)^x = (a^x)(b^x) |
|
|
one-to-one |
A function is one-to-one if it never takes on the same value twice no y values are the same passes horizontal line test |
|
|
inverse functions |
a functions inverse is a function if the function is one to one (passes HLT) domain of inverse = range of function range of inverse = domain of function f^-1(f(x)) = x for domain of function f(f^-1(x)) = x for domain of inverse |
|
|
how to find an inverse function |
set f(x) = y and solve for x, switch x and y graph obtained by reflecting f(x) across line y=x |
|
|
laws of logs |
log b (xy) = log b x + log b y log b (x/y) = log b x - log b y log b (x^r) = rlog b x |
|
|
Unit Circle |
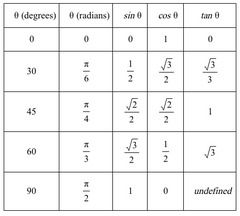
|
|
|
Trig Identities |
sin^2x + cos^2x = 1 1+tan^2x = sec^2x sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx |

