![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Characteristics of living organisms
|
•Consist of one or more cells•Contain genetic information
•Use genetic information to reproduce themselves •Are genetically related and have evolved•Convert molecules intonew biological molecules •Extractand use energy •Regulate their internal environment (Homeostasis) |
|
|
Emergent properties
|
•Result from the arrangement and interaction of partswithin a system •Characterize nonbiological entities as well |
|
|
Reductionism |
The reduction of complex systems to simplercomponents that are more manageable to study |
|
|
Allcells |
•Thecell is the lowest level of organization that can perform all activitiesrequired for life –Are enclosed by a membrane –Use DNA as their genetic information –Two main forms of cells prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells |
|
|
Eukaryotic Cell (True Nucleus) |
•DNAinside nucleus •Largerthan prokaryotic •Nucleus •DNAarranged in linear chromosomes •DNApresent in nucleus •Membrane-boundorganelle |
|
|
Prokaryotic Cell |
•Smallerthan Eukaryotic •Nonucleus •OneDNA strand •Singularcircular chromosome •DNApresent in nucleoid •Nomembrane bound organelles |
|
|
Chromosomes |
Contain most of a cell’sgenetic material in the form of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) |
|
|
Genes |
Units of inheritance that transmit information from parents tooffspring Encode information for building proteins |
|
|
Histone Protiens |
DNA is wrapped around histone proteins spread in the nucleus |
|
|
Nucleotides |
Each link of a chain is one of 4 kinds of chemical building blocks called nucleotides and nickname A,G,C,T |
|
|
RNA |
Single stranded polymer A,G,C,U |
|
|
Three types of RNA |
mRNA- messaege (only one translated) rRNA- ribosomes tRNA-transfers amino acids |
|
|
RNA Protein |
Is made up of RNA and protein |
|
|
Purines |
A and G |
|
|
Pyramidines |
C, U, T Pyramids are pointy, pointy things "CUT" |
|
|
Gene Expression |
Process of converting information from gene to cellular product Not all RNA in cell are translated |
|
|
DNA -> (Transcription) RNA-> (Translation) Protein |

|
|
|
Genome |
Entire set of genetic instructions Two sets: each has 3 billion pairs |
|
|
Genomics |
Study of sets of genes within and between species |
|
|
Proteomics |
Study of whole sets of proteins encoded by the genome (Also known as Proteomes) |
|
|
Fundamental characteristic of living organisms |
Their use of energy to carry out life's activities |
|
|
Negativefeedback |
As more of a product accumulates, the processthat creates it slows and less of the product is produced (ExcessATP feeds back) |
|
|
Positivefeedback |
As more of a product accumulates, theprocess that creates it speeds up and more of the product is produced (Positivefeed back by platelets) |
|
|
Evolution |
•Organismsare modified descendants of common ancestors •Explains patterns of unity and diversity in living organisms •Similar traits among organisms are explained by descent from common ancestors •Differences among organisms are explained by the accumulation of heritable changes |
|
|
Taxonomy |
Branch of biology thatnames and classifies species into groups of increasing breadth |
|
|
Classification |
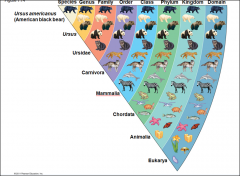
|
|
|
Three Domains |
Bacteria and Archaea compose the prokaryotes, and Eukarya |
|
|
Domain Eukarya |
•DomainEukarya includes all eukaryotic organisms •DomainEukarya includes three multicellular kingdoms: –Plants, which produce their own food by photosynthesis –Fungi, which absorb nutrients –Animals, which ingest their food |
|
|
Darwin's two main points |
–Species showed evidence of “descent with modification” from common ancestors
–Naturalselection is the mechanism behind “descent with modification” |
|
|
Darwinobserved that
|
–Individuals in a population vary in their traits, many of whichare heritable
–More offspring are produced than survive, and competition isinevitable –Species generally suit their environment |
|
|
Darwininferred that
|
–Individuals that are best suited to theirenvironment are more likely to survive and reproduce
–Over time, more individuals in a populationwill have the advantageous traits |
|
|
Ntural Selection |
•Naturalselection results in the adaptation of organisms to their environment
•Darwinproposed that natural selection could cause an ancestral species to give riseto two or more descendent species |
|
|
Data |
Recorded observations oritems of information; these fall into two categories |
|
|
Types of Data |
–Qualitative data, ordescriptions rather than measurements•For example, Jane Goodall’sobservations of chimpanzee behavior –Quantitative data, orrecorded measurements, which are sometimes organized into tables and graphs |
|
|
Inductivereasoning |
Draws conclusions throughthe logical process of induction |
|
|
Hypothesis |
A tentative answer to awell-framed question Must be testable and falsifiable |
|
|
Deductivereasoning |
Uses general premises tomake specific predictions |
|
|
Model Systems |
Using onetype of organism to understand others This is possible because alllife: •are related •have similar building blocks—cells •share a genetic code –Molecular biology compare genomes –More similar = more common ancestor •The fossil record allows study ofevolutionary relationships. |
|
|
DNA consists of |
Two stands of nucleotides twisted to form a double helix |
|
|
Two main types of cells |
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes |

