![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
194 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Anatomy |
The study of organs and systems of the body |
Study |
|
|
Physiology |
The study of the functions of these organs and systems |
|
|
|
Gross anatomy |
Can be seen with the naked eye |
|
|
|
Histology |
The study of structures too small to be seen except through microscope |
Microscope |
|
|
Building blocks human body |
Cells Tissue Organs Body systems |
|
|
|
Building blocks human body |
Cells Tissue Organs Body systems |
|
|
|
Cells |
Basic units of life |
|
|
|
Building blocks human body |
Cells Tissue Organs Body systems |
|
|
|
Cells |
Basic units of life |
|
|
|
Protoplasm |
A colorless gel- like substance that contains water , salt and nutrients obtained from food |
|
|
|
Cells contain three basic parts |
Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell membrane |
|
|
|
Cells vary in size shape structure and function |
But all have certain characteristics in common |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of cell activities , is vitally important for reproduction |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of cell activities , is vitally important for reproduction |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The production department of the cell |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of cell activities , is vitally important for reproduction |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The production department of the cell |
|
|
|
Organelles |
Is a small structure, performs most of the cells activities . Organelles store food for growth as well as repair and restore the cell |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of cell activities , is vitally important for reproduction |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The production department of the cell |
|
|
|
Organelles |
Is a small structure, performs most of the cells activities . Organelles store food for growth as well as repair and restore the cell |
|
|
|
Cell membrane |
The outer surface of the cell |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of cell activities , is vitally important for reproduction |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The production department of the cell |
|
|
|
Organelles |
Is a small structure, performs most of the cells activities . Organelles store food for growth as well as repair and restore the cell |
|
|
|
Cell membrane |
The outer surface of the cell |
|
|
|
Mitosis or indirect division |
Human cells reproduce by dividing in half |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of cell activities , is vitally important for reproduction |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The production department of the cell |
|
|
|
Organelles |
Is a small structure, performs most of the cells activities . Organelles store food for growth as well as repair and restore the cell |
|
|
|
Cell membrane |
The outer surface of the cell |
|
|
|
Mitosis or indirect division |
Human cells reproduce by dividing in half |
|
|
|
Metabolism |
A chemical process by which Cells receive nutrients into energy and reproduction and store for later use |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of cell activities , is vitally important for reproduction |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The production department of the cell |
|
|
|
Organelles |
Is a small structure, performs most of the cells activities . Organelles store food for growth as well as repair and restore the cell |
|
|
|
Cell membrane |
The outer surface of the cell |
|
|
|
Mitosis or indirect division |
Human cells reproduce by dividing in half |
|
|
|
Metabolism |
A chemical process by which Cells receive nutrients into energy and reproduction and store for later use |
|
|
|
Metabolic rate depends on |
Heredity, health conditions ,medications , exercise , diet and eating habits |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of cell activities , is vitally important for reproduction |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The production department of the cell |
|
|
|
Organelles |
Is a small structure, performs most of the cells activities . Organelles store food for growth as well as repair and restore the cell |
|
|
|
Cell membrane |
The outer surface of the cell |
|
|
|
Mitosis or indirect division |
Human cells reproduce by dividing in half |
|
|
|
Metabolism |
A chemical process by which Cells receive nutrients into energy and reproduction and store for later use |
|
|
|
Metabolic rate depends on |
Heredity, health conditions ,medications , exercise , diet and eating habits |
|
|
|
Human life depends on |
The body ability to obtain nutrients from foods which broken down into smaller components |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of cell activities , is vitally important for reproduction |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The production department of the cell |
|
|
|
Organelles |
Is a small structure, performs most of the cells activities . Organelles store food for growth as well as repair and restore the cell |
|
|
|
Cell membrane |
The outer surface of the cell |
|
|
|
Mitosis or indirect division |
Human cells reproduce by dividing in half |
|
|
|
Metabolism |
A chemical process by which Cells receive nutrients into energy and reproduction and store for later use |
|
|
|
Metabolic rate depends on |
Heredity, health conditions ,medications , exercise , diet and eating habits |
|
|
|
Human life depends on |
The body ability to obtain nutrients from foods which broken down into smaller components |
|
|
|
Two phases of metabolism |
Anabolism Catabolism |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of cell activities , is vitally important for reproduction |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The production department of the cell |
|
|
|
Organelles |
Is a small structure, performs most of the cells activities . Organelles store food for growth as well as repair and restore the cell |
|
|
|
Cell membrane |
The outer surface of the cell |
|
|
|
Mitosis or indirect division |
Human cells reproduce by dividing in half |
|
|
|
Metabolism |
A chemical process by which Cells receive nutrients into energy and reproduction and store for later use |
|
|
|
Metabolic rate depends on |
Heredity, health conditions ,medications , exercise , diet and eating habits |
|
|
|
Human life depends on |
The body ability to obtain nutrients from foods which broken down into smaller components |
|
|
|
Two phases of metabolism |
Anabolism Catabolism |
|
|
|
Anabolism |
Process of building up larger molecules from smaller ones Body stores water,food and oxygen |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control center of cell activities , is vitally important for reproduction |
|
|
|
Catabolism |
The process of breaking down larger molecules or substances into smaller ones Realese energy within the cell |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The production department of the cell |
|
|
|
Organelles |
Is a small structure, performs most of the cells activities . Organelles store food for growth as well as repair and restore the cell |
|
|
|
Cell membrane |
The outer surface of the cell |
|
|
|
Mitosis or indirect division |
Human cells reproduce by dividing in half |
|
|
|
Metabolism |
A chemical process by which Cells receive nutrients into energy and reproduction and store for later use |
|
|
|
Metabolic rate depends on |
Heredity, health conditions ,medications , exercise , diet and eating habits |
|
|
|
Human life depends on |
The body ability to obtain nutrients from foods which broken down into smaller components |
|
|
|
Two phases of metabolism |
Anabolism Catabolism |
|
|
|
Anabolism |
Process of building up larger molecules from smaller ones Body stores water,food and oxygen |
|
|
|
5 primary types of tissue in human body |
Epithelial Connective tissue Nerve tissue Muscular tissue Liquid tissue |
|
|
|
5 primary types of tissue in human body |
Epithelial Connective tissue Nerve tissue Muscular tissue Liquid tissue |
|
|
|
Epithelial |
Tissue covers and protects body surfaces and internal organs |
Protects |
|
|
Connective tissue |
Supports , protects and holds the body together |
|
|
|
Nerve tissue |
Carries. Messages to and from the brain and coordinates body functions |
|
|
|
Muscular tissue |
Contracts ,when stimulated , to produce motion |
|
|
|
Liquid tissue |
Carries food and waste products and hormones |
Carries using liquid |
|
|
Liquid tissue |
Carries food and waste products and hormones |
Carries using liquid |
|
|
8 organs primary importance |
Brain Eyes Heart Lungs Stomach / intestines Liver Kidneys Skin |
|
|
|
Liquid tissue |
Carries food and waste products and hormones |
Carries using liquid |
|
|
8 organs primary importance |
Brain Eyes Heart Lungs Stomach / intestines Liver Kidneys Skin |
|
|
|
Brain |
Controls all body functions |
Controls |
|
|
Liquid tissue |
Carries food and waste products and hormones |
Carries using liquid |
|
|
8 organs primary importance |
Brain Eyes Heart Lungs Stomach / intestines Liver Kidneys Skin |
|
|
|
Brain |
Controls all body functions |
Controls |
|
|
Eyes |
Provides Sight |
|
|
|
Liquid tissue |
Carries food and waste products and hormones |
Carries using liquid |
|
|
8 organs primary importance |
Brain Eyes Heart Lungs Stomach / intestines Liver Kidneys Skin |
|
|
|
Brain |
Controls all body functions |
Controls |
|
|
Eyes |
Provides Sight |
|
|
|
Heart |
Circulates the blood |
|
|
|
Liquid tissue |
Carries food and waste products and hormones |
Carries using liquid |
|
|
8 organs primary importance |
Brain Eyes Heart Lungs Stomach / intestines Liver Kidneys Skin |
|
|
|
Brain |
Controls all body functions |
Controls |
|
|
Eyes |
Provides Sight |
|
|
|
Heart |
Circulates the blood |
|
|
|
Lungs |
Supply blood with oxygen |
Oxygen |
|
|
Liquid tissue |
Carries food and waste products and hormones |
Carries using liquid |
|
|
8 organs primary importance |
Brain Eyes Heart Lungs Stomach / intestines Liver Kidneys Skin |
|
|
|
Brain |
Controls all body functions |
Controls |
|
|
Eyes |
Provides Sight |
|
|
|
Heart |
Circulates the blood |
|
|
|
Lungs |
Supply blood with oxygen |
Oxygen |
|
|
Stomach / intestines |
Digest food |
|
|
|
Liver |
Removes the toxic by - products of digestion |
|
|
|
Liquid tissue |
Carries food and waste products and hormones |
Carries using liquid |
|
|
8 organs primary importance |
Brain Eyes Heart Lungs Stomach / intestines Liver Kidneys Skin |
|
|
|
Brain |
Controls all body functions |
Controls |
|
|
Eyes |
Provides Sight |
|
|
|
Heart |
Circulates the blood |
|
|
|
Lungs |
Supply blood with oxygen |
Oxygen |
|
|
Stomach / intestines |
Digest food |
|
|
|
Liver |
Removes the toxic by - products of digestion |
|
|
|
Kidneys |
Eliminates water and waste products |
Eliminates |
|
|
Liquid tissue |
Carries food and waste products and hormones |
Carries using liquid |
|
|
8 organs primary importance |
Brain Eyes Heart Lungs Stomach / intestines Liver Kidneys Skin |
|
|
|
Brain |
Controls all body functions |
Controls |
|
|
Eyes |
Provides Sight |
|
|
|
Heart |
Circulates the blood |
|
|
|
Lungs |
Supply blood with oxygen |
Oxygen |
|
|
Stomach / intestines |
Digest food |
|
|
|
Liver |
Removes the toxic by - products of digestion |
|
|
|
Kidneys |
Eliminates water and waste products |
Eliminates |
|
|
Skin |
Body's largest organ Which forms the external protective layer of the body |
Protective |
|
|
10 body systems I will study |
Skeletal Muscular Circulatory Nervous Digestive Excretory Respiratory Endocrine Reproductive Integumentary |
|
|
|
10 body systems I will study |
Skeletal Muscular Circulatory Nervous Digestive Excretory Respiratory Endocrine Reproductive Integumentary |
|
|
|
Sketal |
Provides framework of the body |
Frame |
|
|
10 body systems I will study |
Skeletal Muscular Circulatory Nervous Digestive Excretory Respiratory Endocrine Reproductive Integumentary |
|
|
|
Sketal |
Provides framework of the body |
Frame |
|
|
Muscular |
Moves the body |
Moves |
|
|
10 body systems I will study |
Skeletal Muscular Circulatory Nervous Digestive Excretory Respiratory Endocrine Reproductive Integumentary |
|
|
|
Sketal |
Provides framework of the body |
Frame |
|
|
Muscular |
Moves the body |
Moves |
|
|
Circulatory |
Circulates blood through the body |
Through |
|
|
Nervous |
Sends and receives messages |
Messages |
|
|
Nervous |
Sends and receives messages |
Messages |
|
|
Digestive |
Supplies nutrients to the body |
|
|
|
Nervous |
Sends and receives messages |
Messages |
|
|
Digestive |
Supplies nutrients to the body |
|
|
|
Excretory |
Eliminates waste in body |
Waste |
|
|
Respiratory |
Controls breathing |
Controls |
|
|
Endocrine |
Controls growth, health and reproduction |
|
|
|
Endocrine |
Controls growth, health and reproduction |
|
|
|
Reproductive |
Generates new life to perpetuate the spices |
New life |
|
|
Integumentary |
Covers and protects the entire body |
Covers |
|
|
Skeletal system |
Is a physical foundation of the body |
|
|
|
Osteology |
Study of bones can be long, flat ,or irregular shape |
Bones |
|
|
Functions of the sketch systems |
•Support the body by giving it shape and strength •surround and protect internal organs • provide a frame to which muscles attach • allow body movement • produce red& white blood cells • store calcium |
|
|
|
Skull or facial skeleton |
Enclose and protects the brain and primary organs |
|
|
|
8 bones in cranium |
•Frontal •Parietal •Occipital •temporal •sphenoid •ethmoid |
|
|
|
Facial Skelton 14 bones |
Only 9 effect facial massage • (1)Mandible • (2) Maxillae • (2) Zygomatic •(2) Lacrimal •(2) Nasal |
|
|
|
Neck bones |
1 Cervical vertebrae ( top part of spinal column) 2 Hyoid ( Adams Apple ) |
|
|
|
Neck bones |
1 Cervical vertebrae ( top part of spinal column) 2 Hyoid ( Adams Apple ) |
|
|
|
Myology |
Study of structure ,function and diseases of the muscles |
|
|
|
Functions of the muscular systems maps |
• Movements • Attachments • Protection • Shape |
|
|
|
Belly |
Applied to the midsection of the muscle , between the two attached to none |
|
|
|
Insertion |
The portion of the muscle joined to movable attachments : bones, movable muscles or skin. |
|
|
|
Tendons |
Bands of fibrous tissue that attach the muscle to the bone |
|
|
|
Ligaments |
Are dense, strong bands of fibrous tissue that connect the bones to each other |
|
|
|
Stimulation of muscular tissue can be achieved by using |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Epicranium or scalp |
Covered by a broad muscle called epicranius or occipital- frontalis |
|
|
|
Epicranuis |
Is formed by two muscles joined by the aponeurosis (tendon) |
|
|
|
Anterior |
In front |
|
|
|
Origin |
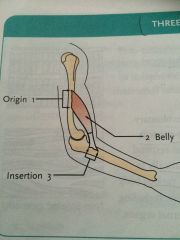
Is non moving (fixed)portion of the muscle attached to bones or other fixed muscle |
|
|
|
Belly |
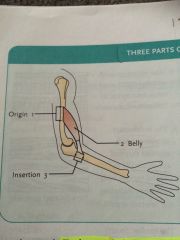
Applied to the midsection of the muscle , between the two attached to none |
|
|
|
Insertion |
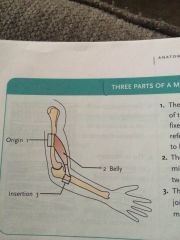
The portion of the muscle joined to movable attachments : bones, movable muscles or skin. |
|
|
|
Levator |
Lifts up |
|
|
|
Depressor |
Draws down or depresses |
|
|
|
Stimulation of muscular tissue can be achieved by using |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
3 Types of muscles tissue |
(1) voluntary or striated (2) involuntary or non- striated (3) cardiac or heart |
|
|
|
Origin |
Is non moving (fixed)portion of the muscle attached to bones or other fixed muscle |
|
|
|
Microbiology |
The study of small organism |
|
|
|
Microbiology |
The study of small organism |
|
|
|
Bacteria |
Called germs or microbes Are one called microorganism |
|
|
|
Microbiology |
The study of small organism |
|
|
|
Bacteria |
Called germs or microbes Are one called microorganism |
|
|
|
Pathogenic |
Disease producing bacteria |
|
|
|
Microbiology |
The study of small organism |
|
|
|
Bacteria |
Called germs or microbes Are one called microorganism |
|
|
|
Pathogenic |
Disease producing bacteria |
|
|
|
Nonpathgentic |
Non producing bacteria |
|
|
|
Microbiology |
The study of small organism |
|
|
|
Bacteria |
Called germs or microbes Are one called microorganism |
|
|
|
Pathogenic |
Disease producing bacteria |
|
|
|
Nonpathgentic |
Non producing bacteria |
|
|
|
Saprophytes |
Are nonpathogenic bacteria that live on dead matter |
|

