![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
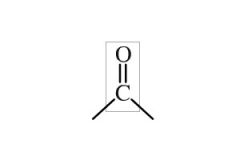
What is a carbonyl group |
|
|
|
what is a class 1 carbonyl |
carbonyl bonded to a leaving group that can be replaced by a nucleophile |
|
|
what is a class 2 carbonyl |
carbonyl NOT bonded to a leaving group when reacted with a nucleophile
ex: Ketones & Aldehydes |
|
|
What is a nucleophile and its charge? |
*a proton attracting atom *generally has a negative charge |
|
|
What is an electrophile and its charge |
*an electron attracting atom *generally has a positive charge |
|
|
Explain the geometry of a carbonyl |
*120 degree angles all around *trigonal planer/flat *C is sp2 hybridized *O is sp2 hybridized *polar
|
|
|
What kind of reaction do class 1 carbonyls have? |
*addition of Nuc, elimination of LG *known as a substitution rxn |
|
|
What makes a class 1 carbonyl substitution rxn move forward? |
Nucleophile must be a stronger base than LG on carbonyl |
|
|
Weak bases are ________ LG less stable |
GOOD |
|
|
Strong bases are _______LG more stable |
POOR |
|
|
relative reactivity rates of Class 1 carbonyls, from most reactive to least. |
acyl halides > acid anhydrides > esters = carboxylic acids> amides |
|
|
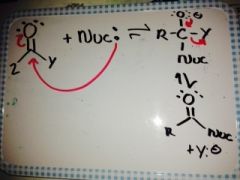
What is the general reaction for an addition/elimination ? |
|
|
|
General addition/elimination with a charged Nucleophile? |
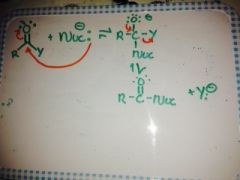
|
|
|
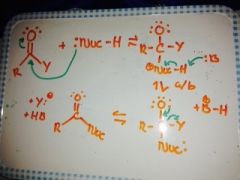
General addition/elimination with a neutral nucleophile? |
|
|
|
What are the rxns of acyl halides? |
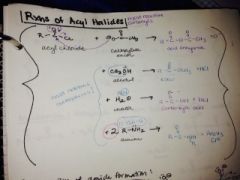
|
|
|
What are the rxns of acid anhydrides |

|
|
|
What are the rxns of esters?
|

|
|
|
What is the definition of Hydrolysis |
H2O converts 1 cpd into 2 cpds |
|
|
What is the definition of Alcoholysis |
ROH converts 1 cpd into 2 cpds, also transesterfication and nucleophillic |
|
|
What is aminolysis? |
RNH2 converts 1 cpd into 2 cpds |
|
|
What is transesterfication? |
one ester is converted into a different ester |
|
|
Show mechanism for acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of an ester |

|
|
|
What are the reactions of carboxylic acid? |

|
|
|
Why is there no aminolysis reactions of carboxylic acids?
|
acid/base rxns run faster so the amine will take the acidic H off of O
|
|
|
How can amides be formed from a carboxylic acid and show mechanism. |

|
|
|
How can you make an amide more reactive? |
*make the carbonyl a better electrophile make LG more stable/weaker base
how? *catalyze w/ a lewis acid to protonate the carbonyl O |
|
|
Show esterfication of amides with ROH
|

|
|
|
how do you convert an alkyl halide into an amine and what are the conditions? |
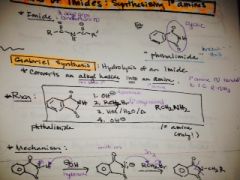
|
|
|
Show the gabriel synthesis mechanism |
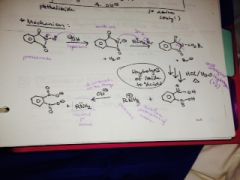
|
|
|
what is the rxn for acid-catalyzed of nitriles to a carboxylic acid? |

|
|
|
what is the rxn for the reduction of nitriles and what does it form? |

|
|
|
what is williamson ether synthesis and what is it used for? |
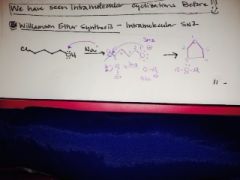
|
|
|
what are some ways to convert a carboxylic acid to an acyl halide |

|
|
|
how do you convert a carboxylic acid into an acid anhydride? |

|
|
|
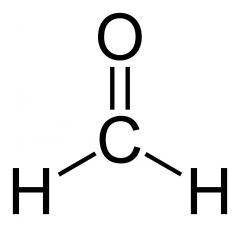
What is formaldehyde? |
|
|
|
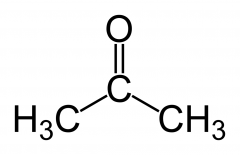
what is a ketone? |
|
|
|
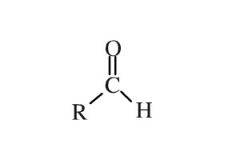
what is an aldehyde? |
|
|
|
what is reactivity of ALL carbonyl compounds from most reactive to least? |
acyl halide >acid anhydride > formaldehyde > aldehyde> ketone> ester = carboxylic acid > amide |
|
|
aldehydes and ketones undergo what kind of reactions? |
addition reactions w/ a nucleophile |
|
|
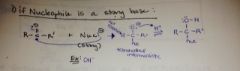
what is the general addition rxn for an aldehyde or ketone if the Nuc is a strong base? |
|
|
|
what is the general addition rxn for an aldehyde or ketone if the Nuc is a weak base? |

|
|
|
what is the general addition rxn for an aldehyde or ketone if the Nuc has a lone pair of e's |

|
|
|
what is the advantage of using a grignard reagent and how are they formed? |
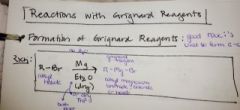
|
|
|
Why should there be no water in your reaction when doing a grignard? |
will destroy the grignard reagent to make an alkane |
|
|
what does a grignard reagent and formaldehyde make? |
primary alcohol |
|
|
what does an aldehyde make with a grignard? |
secondary alcohol |
|
|
what does a ketone and a grignard make? |
tertiary alcohol |
|
|
what does a carbon dioxide and a gringard reagent make? |
carboxylic acid |
|
|
why can the grignard reagent not react twice with CO2? |
because after first reaction it forms an acidic H which will react with the grignard reagent (good base) and perform an acid base rxn instead. |
|
|
when using a grignard with a class 1 carbonyl what 2 rxns ensue? |
1. addition/elimination (overall substitution) 2. Nuc addition to carbonyl, overall 2 equivs of grignard are added |
|
|
Recall acetylide formation |

|
|
|
what is pyridinium chloride and what is it good for? |
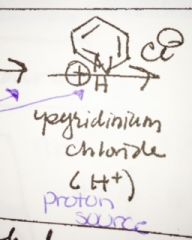
|
|
|
how does a acetylide ion react with a ketone or aldehyde? |
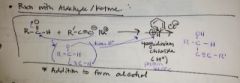
|
|
|
how does an acetylide ion react with and ester or acyl halide? |
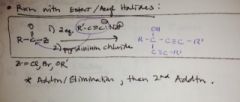
|
|
|
what is sodium borohydride and what is it good for? |
NaBH4 a weak reducing agent used as a hydride source removes double bond |
|
|
what do you use sodium borohydride with and what does it react with? |
*ketones, aldehydes, and acyl halides (2 eq) *use H30 as a workup |
|
|
what is lithium aluminum hydroxide (LAH) what is it used for, what is needed to react |
*used for really weak carbonyls (esters, carboxylic acids, and amides) *use an H30+ workup except with amides which need H20 *very strong reducing agent, adds H and knocks out carbonyl double bond |
|
|
what is dibal H and what is it used for |
* di iso butylaluminum hydride * a mild reducing agent used with esters |
|
|
what is the general rxn of an ester with DIBALH |

|
|
|
how does a aldehyde/ketone react with cyanide? |
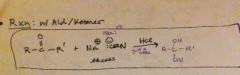
|
|
|
show the mechanism of an aldehyde/ketone with a primary amine and what do you make? |
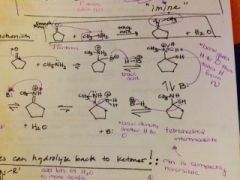
|
|
|
how do you reverse the reaction and change the imine back to a ketone, is that reversible and why? |

|
|
|
what is a wolff-kishner reduction and what is it for? |
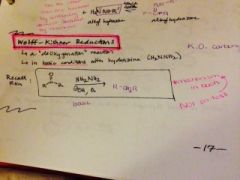
|
|
|
what is a enamine? |
product that has a tertiary N single bonded to an alkene |
|
|
what is the mechanism to make an enamine. and how would you reverse it? |
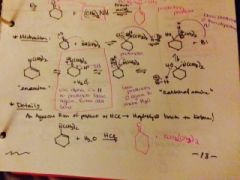
|
|
|
a carbonyl with NH3 and trace acid makes what? |
an unstable imine intermediate |
|
|
what is reduction animation? |

|
|
|
what are other methods to reduce amines? |
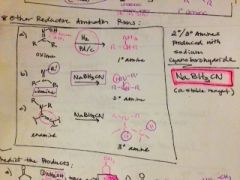
|
|
|
what is the order of stability for gem-diols? |

|
|
|
how do you form a hydrate? |

|
|
|
how do you form a hemiacetal/acetal? |

|
|
|
how do you form a hemiketal/ketal? |
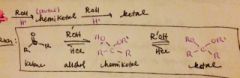
|
|
|
how do you reverse making a ketal/acetal? |
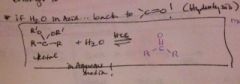
|
|
|
what are protecting groups? |
rxns that easily change functionality of a specific group and can easily be removed (converted back to original structure) |
|
|
show an example on how to add a pg on a ketone |
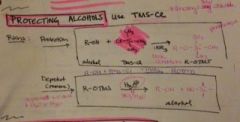
|
|
|
can you selectively protect a functional group? |
aldehydes are more reactive than ketones, so you can protect an aldehyde before a ketone |
|
|
how do you protect an alcohol? |
*use TMS-Cl tri methyl silyl chloride |
|
|
how does TMS-CL work and how is it removed? |
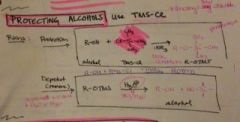
|
|
|
how do you protect a carboxylic acid? |
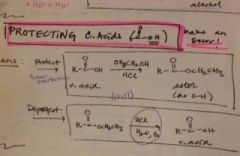
|
|
|
how do you protect an amine? |
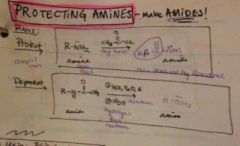
|
|
|
how can you reduce a carbonyl with dithiols? |
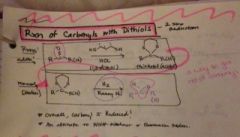
|
|
|
how do you convert a carbonyl to an alkene? |
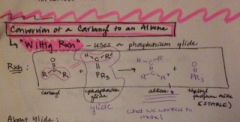
|
|
|
how does the witting mechanism look? |
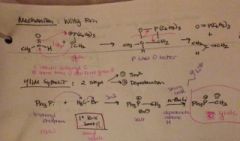
|
|
|
what is a ylide? |
compound with opposite charges on adjacent atoms, both of which have complete octets |
|
|
name the 2 types of ylides and give details |
* stabilized ylides- share (-) charge on carbon chain with a neighboring carbonyl grp, forms E-alkenes (trans) *destabilized ylides- charge on C not shared, forms Z-alkenes (cis) |

