![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Metabolism |
All chemical reactions that help keep an organism alive |
|
|
|
Byosynthesis |
The act of small organic molecules bonding together to make a bigger and more complex one |
This can be done to make proteins me necleic acids for cell growth |
|
|
Decomposition |
Breaking down larger molecules into smaller ones |

|
|
|
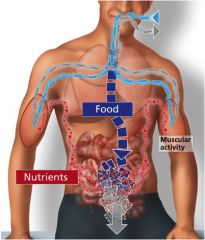
Cell respiration |
When cells breakdown substances to get energy |
|
|
|
Aerobic |
The cells ability to do work with the use of exercise oxygen |
Hard work outs Carbs fats and proteins are needed |
|
|
Anarobic |
the cells ability to do work without the use of oxygen |
Walking or stretching |
|
|
Formentation |
Turns sugars into acids or gases |
This only occurs mostly in bacteria |
|
|
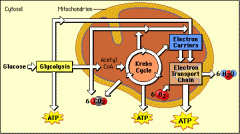
Glycolysis |
The oxidization of glucose to create a small amount of ATP by using some phosphate and ATP |
This is the first stage in aerobic respiration |
|
|
Glucose |
A bonded molecule that contains energy for cells to do work |
It's also called sugar |
|
|
Krebs cycle |
Two left over carbon molecules are left over from glycolysis and are completely oxidized to creat carbon dioxide |
This allows some additional ATP to form while conserving some energy This is the second stage in aerobic respiration |
|
|
NAD/NADH |
As glucose loses electrons it reduces to NAD. As hydrogen is released for, stages one and two of aerobic respiration, NAD is reduced to NADH. |
Nicotine adenine dinucleotide This is similar to the molecule NADP that is released in plants during photosynthesis Also helps to reduce oxygen to make water this reaction creates some ATP |
|
|
FAD/FADH2 |
During the Krebs cycle, some hydrogen reduces to FAD. When FAD bonds with two more hydrogen sulfide it turns into FAD2 |
Flavin adenine dinucleotide Reduces oxygen to help create water. The energy released by doing this is used to make ATP |
|
|
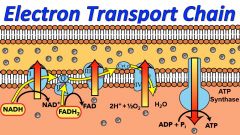
Electron transport system |
A system of easily reduced and oxidized molecules |
|
|
|
ATP |
Energy able to be used by the cell to do work |
A major carrier of energy for the cell |
|
|
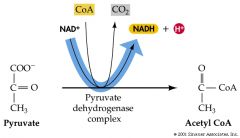
Pyruvate |
An acid produced during the fourth step in glycolysis |
|
|
|
Lactate |
a three carbon atom produced by Pyruvate when enough oxygen isn't present |
If oxygen isn't present for Pyruvate acid to bond with, then Pyruvate will be cycled back onto the glygolyisis cycle by reversing oxidization and turning it it into NAD and lactate.
|
|
|
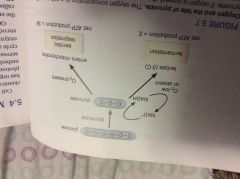
Lactic acid fermentation |
The cycle of Pyruvate continually being cycled back into the glycolysis cycle until enough oxygen is present |
|
|
|
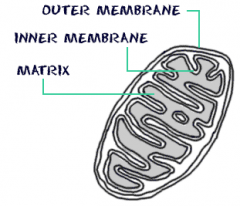
Mitochondrion
|
An organism in which the Krebs cycle takes place |
Mitochondria is the power house of the cell it is litereally the only thing remember from science Where most ATP is synthesized Singular form |
|
|
Matrix |
The inside of the Cristae |
|
|
|
Cristae |
Folds inside of a mitochondrion |
Enzymes are stored here that are used for the Krebs cycle |
|
|
Acetate |
Left over from a Pyruvate molecule |
Two carbon organic acid also during the same step it reduces one NAD to NADP |
|
|
Citrate |
When acetyl CoA bonds to oxaloacetate it forms citrate |
A six carbon acid |
|
|
coenzyme A/acetyl CoA
|
When Coenzyme A (carrier) binds to acetate it forms acytyl COA |
Carries acetate to the Krebs cycle within the mitochondria |
|
|
Cytochromes
|
Easy to reduce amd oxidized molecules that are carried in the electron transport system |
These proteins are emended in the inner membrane of the mitochondria |
|
|
Facultative aerobes
|
A type of bacteria that can go long periods of time by using aerobic respiration or fermentation |
|
|
|
Obligate anaerobes
|
Bacteria that are poisoned by oxygen. These bacteria can only create energy through fermentation or Anarobic respiration |
These organisms are always bacteria |
|
|
Obligate aerobes
|
Organisms that require oxygen in order to create ATP |
These organisms are always animals and plants |
|
|
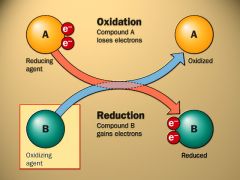
Oxidize
|
Adding oxygen to a molecule to release energy |
|
|
|
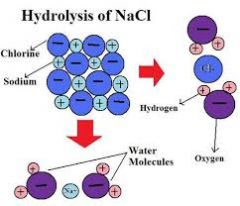
Hydrolysis
|
Instead of breaking a bond with water, a bond is broken by adding water |
|
|
|
Reduce |
When molecules gain electrons |

|
|
|
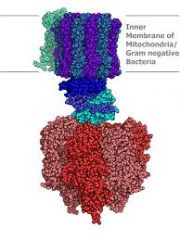
ATP synthase |
An important enzyme that is used to create ATP |
|

