![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation |
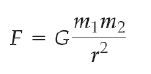
The force of gravity between any two point objects of mass m1 and m2 is attractive and of magnitude.
r is the distance between the masses and G is a constant referred to as the universal gravitation constant. Its value is 6.67 x 10^-11 N x m^2/kg^2 |
|
|
Principle of Superposition |
The net force of several different gravitational forces acting on an object. |
|
|
Gravitational Attraction of Spherical Bodies |
The force is the same as if all the mass of the sphere were concentrated at its center. |
|
|
Keplar's Laws of Orbital Motion |
1. Planets follow elliptical orbits, with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse.
2. As a planet moves in its orbit, it sweeps out an equal amount of area in an equal amount of time.
3. The period, T, of a planet increases as its mean distance from the Sun, r, raised to the 3/2 power. |
|
|
Gravitational Potential Energy |
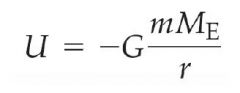
U is a scalar, and goes to zero as the mass become infinitely apart. |
|
|
Energy Conservation |

|
|
|
Black Hole |
An object that is sufficiently massive and sufficiently small that the escape speed is equal or exceeding the speed of light. |
|
|
Tidal Force |
The difference in gravitational force across an object due to its size. |
|
|
Acceleration of Gravity |

|
|
|
Mass of the Earth |

|
|
|
Orbital Period |

|
|
|
Escape Speed |

|
|
|
Total Mechanical Energy |

|

