![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
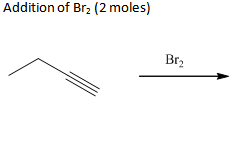
Addn of Br2 (2 moles)
|
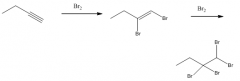
|
|
|
Nomenclature
|
A. Change the ending of the parent name to –yne
B. Locate the position of the double bond using the lowest possible number C. The simplest alkyne is called acetylene. |
|
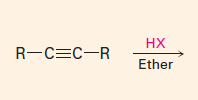
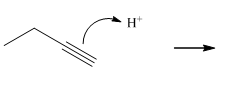
Addition of HX(halides)
|
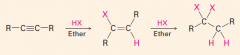
|
|
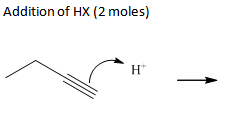
Addn HX-- 2 moles
|

|
|
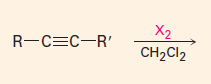
Addition of X2
|
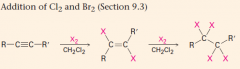
|
|
Addition of H2O
|
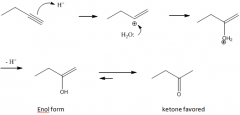
|
|
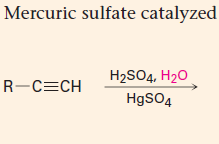
Hydration
|
1. The reagent is H+/H2O with a Hg2+ catalyst present
2. Markovnikov addition of H and OH 3. A ketone is formed |
|
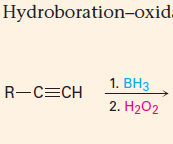
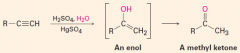
Hydration
|
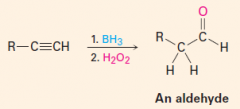
1. The reagent is H+/H2O with a Hg2+ catalyst present
2. Markovnikov addition of H and OH 3. A ketone is formed |
|
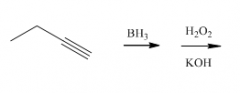
Rules, trends?
|
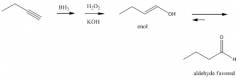
Addition of BH3 followed by H2O2/KOH
1. Anti-Markovnikov addition of H and OH 2. Produces an aldehyde |
|
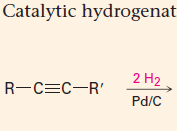
Reduction
|
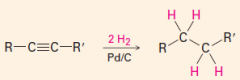
Get alkane
|
|
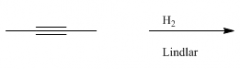
Reduction
Structure? |
Cis
|
|
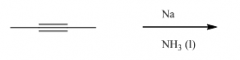
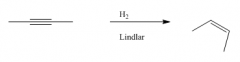
Reduction
|
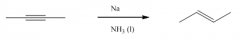
Trans
|
|

Ozonalysis Terminal
|
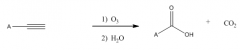
|
|
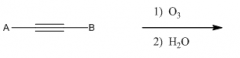
Ozonalysis Internal
|

|
|
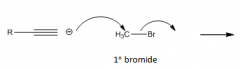
Use of acetylide ion as a nucleophile
|
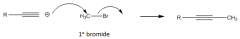
|
|
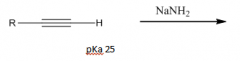
Acidity of Terminal Alkynes
|

|
|
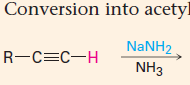
Acidity of term alkyne
|

|

