![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
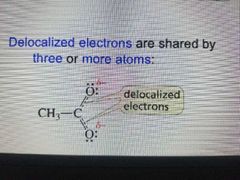
Delocalized Electrons |
Shared by 3 or more atoms. It is the result from the P orbital of one Atom overlapping the porbitals of 2 adjacent atoms. |
|
|
|
Rules for drawing resonance contributors |
1. Only electron's move. Atoms never move. 2. only pi electrons and lone Pair electrons can move. Sigma electrons never move. 3. The total number of electrons in the molecule does not change. 4. Electrons always move to an SP2 or SP Atom; SP3 atoms cannot accept electrons. |

|
|
|
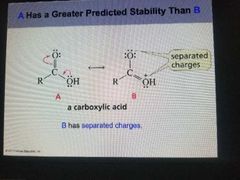
Separated charges stability |
The predicted Stability of a compound with separated charges is less than the stability of a compound without separated charges. |
|
|
|
Features that decrease the predicted stability |
1. An Atom with an incomplete octet. 2. A negative charge that is not on the most electronegative atom. 3. a positive charge that is on an electronegative Atom. 4. separated charges. |
|
|
|
Delocalization Energy |
The delocalization energy is the extra stability of a compound has as a result of having deocalized Electron. |

This energy is also called resonance energy. The resonance hybrid is more stable than any of its resonance contributors are predicted to be. |
|
|
Isolated Diene |
Double bonds are separated by more than one single bond. |
The smaller the heat of hydrogenation the more stable the compound. |
|
|
Conjugated Diene |

Double bonds are separated by one single bond. |

more stable than an isolated dienes. Have delocalized electrons. |
|
|
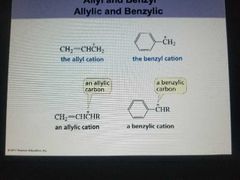
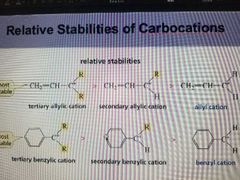
Allyl,benzyl,allylic, Benzylic cation |
|
|
|
|
Resonance contributor to allylic cation |

|
|
|
|
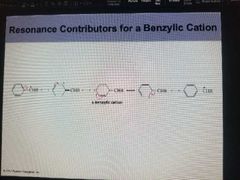
Resonance contributor to Benzylic Cation. |
|
|
|
|
Relative stabilities of Carbocation |
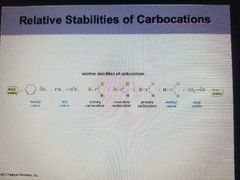
In decreasing order Benzel cation= Allyl cation=tertiary carbocation secondary carbocation, primary carbocation, methyl cation, vinyl cation |
|
|
|
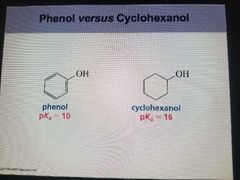
Delocalized electrons affect PKA values |

A carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than an alcohol because of inductive electron withdraw and electron delocalization. |
|
|
|
Electron donation |
Destabilizes the base by increasing the electron density on the oxygen |
Decreases acidity. |
|
|
Electron Withdrawal |
stabilizes the base by decreasing the Electron density on the oxygen. |

Increases acidity. |

