![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Distinguish between active versus passive transport |
active transport requires energy and work and passive transport does not |
|
|
Describe the direction water or solutes will travel in a hypertonic,hypotonic, and isotonic solution |
In hypertonic water will move across the cell membrane in order to even out the concentration of solutes in both the cell and the environment around the cell. In hypotonic Water will move from the environment into the cell in order to balance the concentration of solute. In a isotonic water will diffuse both in and out of the cell, but no effects will be seen. |
|
|
Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis |
Endocytosis is the cellular uptake of biological molecules and particulate matter via formation of new vesicles from the plasma membrane. Exocytosis is the cellular secretion of biological molecules by the fusion of vesicles containing them with the plasma membrane. |
|
|
Describe how the maintenance of a realistically stable internal environment is required for survival |
It is process of maintaining constant internal environment despite the variations in external |
|
|
Describe cell specialization in multicelllar organisms |
The specialization of a multicellular organism is that they live longer than single celled organisms do with just one job. |
|
|
List the levels of organization in eukaryotes beginning with organelles & ending with an organism |
non-living components of life |
|
|
Draw and describes the basic structure of ATP, where its energy is located, & why it is needed by cells. |
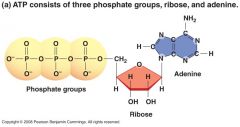
A nitrogenous base (in this case, Adenine) attached to a 5 Carbon sugar (Ribose), which is attached to 3 phosphate groups in a row. |
|
|
Write the reduced equation for photosynthesis |
6CO2 + 6H2O ------> C6H12O6 + 6O2 |
|
|
List the products of the light- dependent versus the light-independent ractions |
Light-independent - chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and other compounds into glucose. Light-dependent- light energy from the sun is used to split water which has been sucked in by plants by transpiration. Water, when broken, makes oxygen, hydrogen, and electrons.
|
|
|
Describe the organelle where the parts of photosynthesis occurs |
photosynthesis takes place inside an organelle called a chloroplast. |
|
|
What factors affect photosynthesis |
The main factors affecting rate of photosynthesis are light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration and temperature |
|
|
Write the equation for cellular respiration |
C6H12O6 + O2 =======> H2O + CO2 + Energy |
|
|
What are the three parts |
glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and the electron transport chain. |
|
|
What happens at each part |
Glycolysis- The glucose-phosphate molecule splits into two sugar molecules, each with three carbons and one phosphate. Eventually, these molecules will be converted into pyruvate molecules. Krebs Cycle- generates a pool of chemical energy from the oxidation of pyruvate, the end product of glycolysis. Pyruvate is transported into the mitochondria and loses carbon dioxide to form acetyl-CoA, a 2-carbon molecule. The electron transport chain involve NADH and FADH, which act as electron transporters as they flow through the inner membrane space. In complex I, electrons are passed from NADH to the electron transport chain, where they flow through the remaining complexes.
|
|
|
Compare and Contrast photosynthesis and cellular respiration |
Photosynthesis biological process in which green plant cells form their food in presence of light, and during this process oxygen gas is evolved. Cellular Respiration is biological process in which living organism inhale oxygen from atmosphere and in cell this oxygen is used for oxidation of food to produce energy,carbon dioxide is evolved through this mechanism.
|
|
|
Describe how cells break down macromolecules to provide energy |
large polymeric molecules in food are broken down during digestion into their monomer subunits proteins into amino acids, polysaccharides into sugars, and fats into fatty acids and glycerol through the action of enzymes |
|
|
Describe how the organelle where cellular respiration occurs. |
mitochondria |
|
|
List the number of ATPs created in cellular respiration compared to fermentation |
38 from cellular respiration 4 from fermentation |
|
|
Compare alcoholic vs lactic acid fermentation; the organisms where each occurs & the products formed |
Lactic acid fermentation would occur in muscle and ethanol fermentation would occur by yeast. |

