![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
major type of muscle in the body is |
skeletal muscle |
|
|
main function of skeletal muscle |
to provide movement |
|
|
level of organization for muscle (largest to smallest) |
muscle ---> fibers ---> myofibrils ---> myofilaments |
|
|
types of myofilaments and their function |
actin & myosin..slide past eachother for contraction |
|
|
muscle fiber |
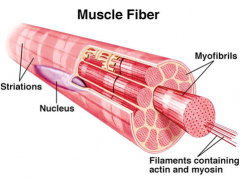
|
|
|
the sarcomere is |
the contractile unit of the muscle |
|
|
thin filaments are |
actin |
|
|
thick filaments are |
myosin |
|
|
I band has |
only actin |
|
|
A band has |
actin & myosin |
|
|
H zone has only |
myosin |
|
|
Z line has |
bisect I band, compose one sarcomere |
|
|
sarcolemma is |
the covering of each muscle fiber |
|
|
sarcoplasm is |
the cytoplasm of a muscle fiber |
|
|
sarcosome is |
the mitochondria of muscle tissue |
|
|
muscle fiber |
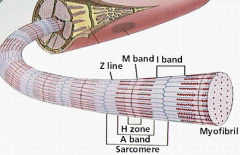
|
|
|
sarcoplasmic reticulum is |
endoplasmic reticulum of muscle tissue |
|
|
endomysium is |
thin areolar connective tissue surrounding each individual fiber |
|
|
perimysium |
collagenic membrane surrounding bundle of fibers |
|
|
epimysium |
CT around entire muscle |
|
|
deep fascia is |
CT that binds muscles into functional groups |
|
|
tendons connect |
muscle to bone (strong, rope like) |
|
|
aponeuroses conenects |
muscle to muscle or muscle to bone (flat, sheet like) |
|
|
origin is |
fixed attachement of muscle |
|
|
insertion |
moveable attachment of muscle |
|
|
neuromuscular junctions are found where |
between nerve fibers and muscle cells |
|
|
synaptic cleft is |
the gap seperating neuron and muscle fiber |
|
|
Neuromuscular junction |
acetylcholine (ACh) leaves neuron --> goes to synaptic cleft --> and binds receptor on muscle sarcolemma --> ACh is then released --> sarcolemma channels then open --> K+ an Na+ flow across membrane --> ACTION POTENTIAL |
|
|
Agonists |
responsible for producing movement |
|
|
Antagonists |
oppose or reverse a movement, provides resistance |
|
|
synergists |
aid antagonists |
|
|
fixators |
specialized synergists, immobilize and allow you to pose |
|
|
Orbicularis occuli |
origin: frontal & maxillary bones insertion: tissue of eyelid Action: closes eye |
|
|
Orbicularis occuli location |
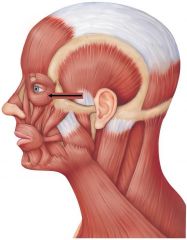
|
|
|
Levator labii superioris |
origin:zygomatic bone & infraorbital margin of maxilla insertion: skin & muscle of upper lip Action: opens lip, raises& furrows upper lip |
|
|
Levator labii superioris location |
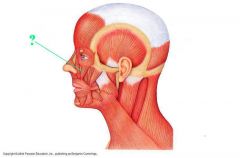
|
|
|
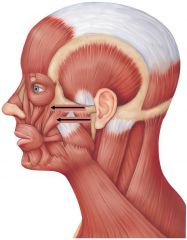
zygomaticus |
origin:zygomatic insertion: corners of mouth action: smiling |
|
|
zygomaticus location |
|
|
|
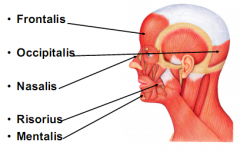
Risorius |
origin: Fascia of masseter muscle insertion:skin at angle of mouth actiion: draws corner of lip lateral |
|
|
Risorius location |
|
|
|
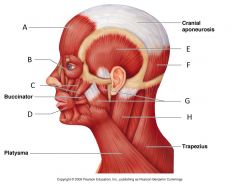
Buccinator |
origin: molar region of maxilla&mandible Insertion:orbicularis oris action:draws corners of mouth
|
|
|
Buccinator location |
|
|
|
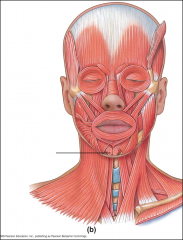
mentalis |
origin: madible below incisors insertion: skin of chin action: protrudes lower lip, wrinkles skin |
|
|
mentalis location |
|
|
|
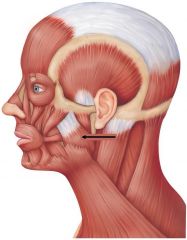
masseter |
origin: zygomatic arch insertion:angle & ramus of mandible action:elevate mandible |
|
|
masseter location |
|
|
|
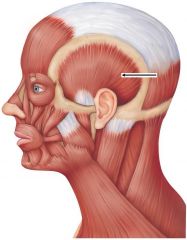
temporalis |
origin: temporal fossa insertion: coronoid process of mandible action: elevate & retract mandible |
|
|
temporalis location |
|

