![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Starts with softening of the skin at the angle of the mouth; followed by fissuring.
|
Angular Cheilitis (PM)
|
|
|
Caused by excessive exposure to sunlight; primarily affects lower lip.
|
Actinic Cheilitis (Def)
|
|
|
Lip loses normal redness and may become scaly, somewhat thickened, and slightly everted.
|
Actinic Cheilitis (PM)
|
|
|
Caused by malnutrition or more commonly, by overclosure of the mouth (no teeth).
|
Angular Cheilitis (etiology)
|
|
|
recurrent, painful vesicular eruptions of the lips and surrounding skin.
|
Herpes Simplex (def)
|
|
|
small cluster of vesicles develop first, they break and form yellow-brown crusts. healing takes 10-14 days
|
Herpes Simplex (PM)
|
|
|
localized SQ or submucosal swelling caused by leaking of intravascular fluid into interstitial tissues. Usually benign, resolves in 24-48 hours.
|
Angioedema (def)
|
|
|
NSAIDs, ACE-inhibitors
|
Drugs associated with angioedema.
|
|
|
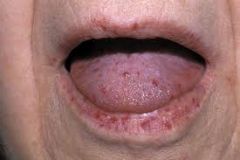
Multiple red spots on the lips, oral mucosa and fingertips. Nosebleeds, GI bleeding and iron deficiency anemia are common with this condition.
|
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
(Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome) -PM |
|
|
an autosomal dominant endothelial disorder causing vascular fragility and arteriovascular malformations.
|
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
(Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome) - Def |
|
|
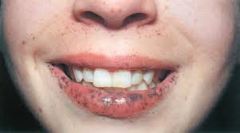
Prominent small brown pigmented spots in dermal layer of lips, buccal mucosa and fingertips.
|
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PM)
|
|
|
Autosomal dominant syndrome also associated with development of numerous intestinal polyps. The risk of developing GI and other CAs ranges from 40-90%.
|
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (Def)
|
|
|
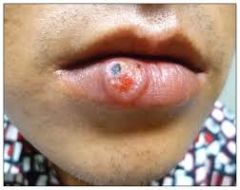
ulcerated papule with indurated edge. The lesion resemble a carcinoma or cold sore; painless, nonsuppurative and heal spontaneously in 3-6wks.
|
Chancre -Primary Syphilis (PM)
|
|
|
lesion caused by infection with the spirochete Treponema Pallidum; Super infectious.
|
Chancre -Primary Syphilis (def)
|
|
|
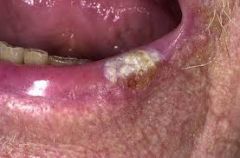
Usually affects the lower lip; appears as a scaly plaque, an ulcer, or as a nodular lesion
|
Carcinoma of the lip
|
|
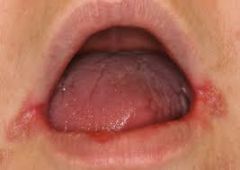
|
Angular Cheilitis (P)
|
|
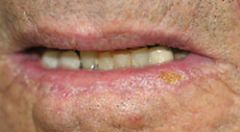
|
Actinic Cheilitis (P)
|
|
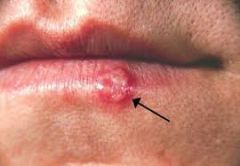
|
Herpes Simplex (P)
|
|
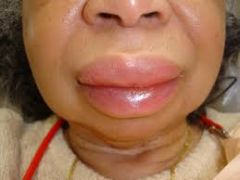
|
Angioedema (P)
|
|
|
Osler-Weber-Rendu Syndrome (P)
|
|
|
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome (P)
|
|
|
Chancre of Syphilis (P)
|
|
|
Carcinoma of the Lip (P)
|
|
|
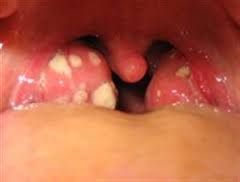
Reddening of the throat with white exudate on the tonsils.
|
Exudative Tonsilitis (Def) -ET
|
|
|
ET with fever and enlarged anterior cervical lymph nodes
|
Group A Strep
|
|
|
ET with fever and enlarged posterior cervical lymph nodes
|
Infectious Mononucleosis
|
|
|
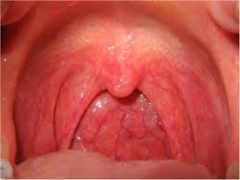
redness and vascularity of pillars and uvula; caused by bacteria or virus
|
Pharyngitis
|
|
|
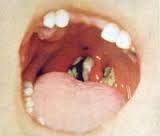
acute infection; dull red throat with gray exudate on uvula, pharnyx, and tongue. airway may become obstructed
|
Diptheria
|
|
|
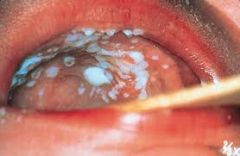
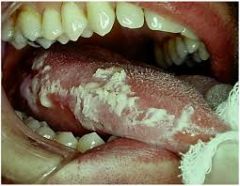
Thick white plaques; somewhat adherent to the underlying mucosa
|
Thrush
|
|
|
deep purple colored, low-grade vascular tumor; may be raised or flat; associated with human herpesvirus 8.
|
Karposi's Sarcoma
|
|
|
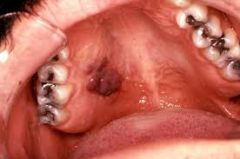
Midline bony growth in the hard palate; size and lobulation vary; harmless
|
Torus Palatinus
|
|
|
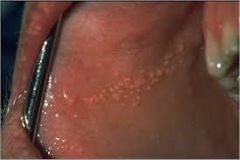
Small yellowish spots in buccal mucosa or on lips; seen best anterior to the tongue and lower jaw
|
Fordyce Spots
|
|
|
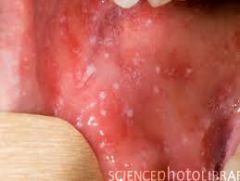
Small white specks that resmeble grains of salt on a red background; appear in the buccal mucosa near the 1st and 2nd molars
|
Koplik's Spots (PM)
|
|
|
Early sign of measles (appears within 24 hours).
|
Koplik's Spots (~D)
|
|
|
small red spots caused by blood that escapes from the capillaries into the tissues
|
Petechiae (D+PM)
|
|
|
in buccal mucosa could be caused by biting the cheek; elsewhere in the mouth, usually due to infection, decreased platelets or trauma
|
Petechiae (Etiology)
|
|
|
thickened whit patch; this benign process may turn into CA -BIOPSY
|
Leukoplakia (PM)
|
|
|
Likely from chewing tobacco
|
Leukoplakia (Etiiology)
|
|
|
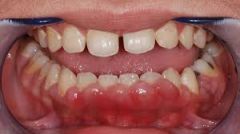
gingival margins red and swollen, interdental papillae blunted, swollen and red; gums bleed upon brushing
|
Marginal Gingivitis
|
|
|
ulcers appear on interdental papillae and spreads to gum margins where grayish psuedomembrane develops; accompanied by fever, malaise and enlarged lymph nodes and foul breath
|
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis
|
|
|
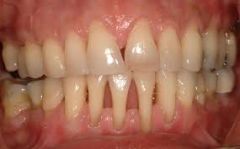
Gums swollen into heaped masses that may cover teeth; with possible redness
|
Gingival hyperplasia (PM)
|
|
|
phenytoin therapy, puberty, pregnancy or leukemia may bring about this condition of the gums
|
Gingival hyperplasia
|
|
|
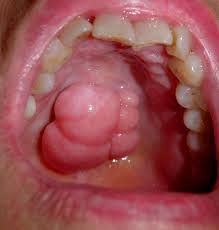
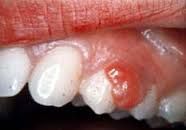
red-purple papules or granulation tissue form in gingival interdental papillae; red, soft, painless and bleed easily
|
Pregnancy tumor
|
|
|
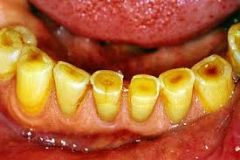
chewing surfaces of the teeth are worn down by repetitive use so that the yellow-brown dentin is exposed
|
Attrition of the teeth
|
|
|
roots of the teeth exposed
|
recession of the gums
|
|
|
interior enamel of the teeth chemically eroded; commonly by frequent emesis or bulimia
|
Erosion of the teeth
|
|
|
biting surface of the teeth become abraded or notched by recurring trauma (holding nail or bobby pins bwtn teeth); contours, size and spacing of the teeth are unaffected
|
Abrasion of the teeth with notching
|
|
|
teeth are smaller and more widely spaced than normal and are notched on biting surfaces; sides of teeth taper toward biting edge
|
Hutchinson's teeth- congenital syphilis
|
|
|
Exudative Tonsilitis (P)
|
|
|
Pharyngitis (P)
|
|
|
Diptheria (P)
|
|
|
Thrush of the Palate (P)
|
|
|
Karposi's Sarcoma (P)
|
|
|
Torus Palatinus (P)
|
|
|
Fordyce Spots (P)
|
|
|
Koplik's Spots (P)
|
|
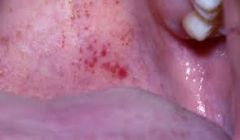
|
Petechiae (P)
|
|
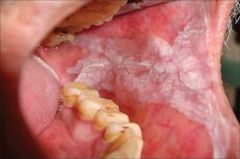
|
Leukoplakia (P)
|
|
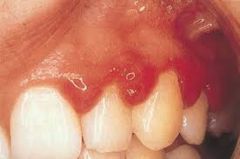
|
Marginal Gingivitis (P)
|
|
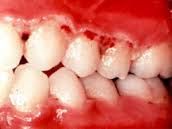
|
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (P)
|
|
|
Gingival Hyperplasia (P)
|
|
|
Pregnancy Tumor (P)
|
|
|
Attrition of the Teeth (P)
|
|
|
Recession of the Gums (P)
|
|
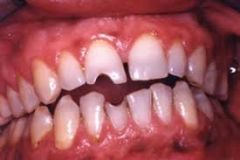
|
Abrasion of the teeth with notching (P)
|
|
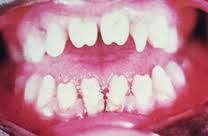
|
Hutchinson's Teeth (P)
|
|
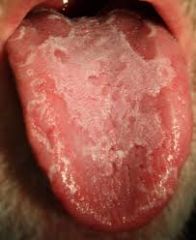
|
Geographic Tongue (P)
|
|
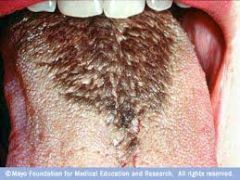
|
Hairy Tongue (P)
|
|
|
Fissured Tongue (P)
|
|
|
Smooth Tongue (P)
|
|
|
Hairy Leukoplakia
|
|
|
Varicose Veins (P)
|
|
|
Apthous ulcer/Canker Sore (P)
|
|
|
Mucous Patch of Syphilis (P)
|
|
|
Leukoplakia (P)
|
|
|
Tori Mandibulares (P)
|
|
|
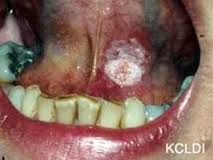
Carcinoma Floor of Mouth (P)
|
|
|
the dorsum of the tongue has scattered smooth red ares without papillae
|
Geographic tongue
|
|
|
Yellowish/brown/black elongated papillae on the back of tongue; benign condition
|
Hairy Tongue
|
|
|
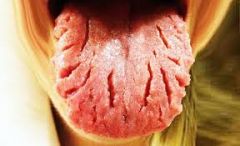
appears with increasing age; food debris may accumulate in crevices
|
Fissured Tongue
|
|
|
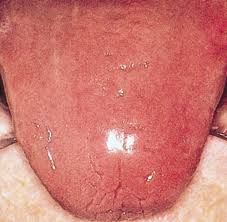
smooth and often sore tongue without papillae; suggests various vitamin and/or mineral deficiencies or chemotherapy treatment
|
Smooth Tongue
|
|
|
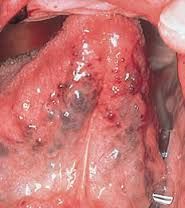
Whitish, raised areas with a feather or corrrugated pattern most often on sides of tongue; cannot be scraped off
|
Hairy Leukoplakia
|
|
|
Small, purplish or blue-black round swellings that appear under the tongue with age.
|
Varicose Veins
|
|
|
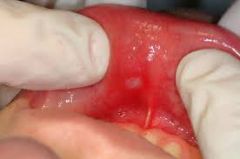
a painful, round or ovular ulcer that it whitish or yellowish-gray and surrounded by halo of red; heals in 7-10 days
|
Apthous Ulcer
|
|
|
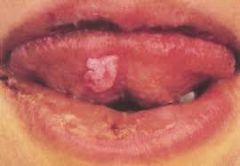
Painless lesion; slightly raised, oval, and covered by grayish membrane; highly infectious
|
Mucous Patch of Syphilis
|
|
|
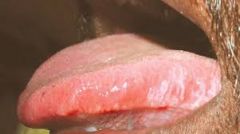
Persisting white patch in oral mucosa; underside of the tongue appears painted white. possible squamous cell carcinoma- BIOPSY
|
Leukoplakia
|
|
|
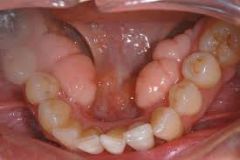
rounded bony growths on the inner surfaces of the mandible; typically bilateral, asymptomatic, harmless
|
Tori Mandibulares
|

