![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
y=ax+b |
Linear and Constant |
Parent Function is y=x |
|
|
y=ax^2 + bx + c |
Qudratic |
|
|
|
(a>0) or (a<0) |
Concave |
"Curve" |
|
|
y=ax^b |
Power |
y=x^b is parent |
|
|
y=ab^x |
Exponential |
y=b^x is parent |
|
|
y - k = a(x - h)^2 |
Vertex Form |
|
|
|
Transformed Power Function |
y=a(x - c)^b + d |
Think of a vertex form |
|
|
y = ab^x |
Exponential |
Transformed function looks like this: y = ab^x + c |
|
|
Special Exponential Functions |
y = a * 10^(bx) Base 10 y = a * e^(bx) natural (base-e) |
|
|
|
Generalization of Special Exp. Functions |
Generalize them by incorporating translations in x and y directions y = a * e^(b(x - c))+ d for (base-e) |
|
|
|
(Example) How to answer questions that involve concave. |
Linear: "Function is decreasing on its entire domain, no concave in either direction" Quadratic: "Inc. for x<3 and dec. for x>3. Concave down |
|
|
|
Solving by Matrices P1 |

|
|
|
|
Solving by Matrices P2 |
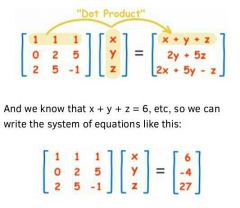
|
|
|
|
Add-Add Pattern |
By saying that every time you add a constant to x, you add a constant (not necessarily the same) to y |
|
|
|
Add-Multiply Pattern |
add a constant to X y value is multiplied by base raised to that constant. |
|

