![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List general characteristics |
1. Agents of superficial & subcutaneous mycoses 2. Ubiquitous 3. Humans and animals accidental hosts 4. Classified as slow growing 7 to 10 days or rapid growing lesson 7 days |
|
|
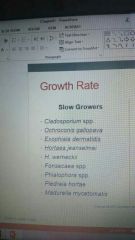
List some slow growers |
|
|
|
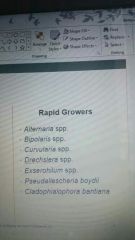
list some rapid growers |
|
|
|
list the various disease spectrum |
Superficial infections, mycetoma, chromoblastomycosis, phaeohyphomycosis |
|
|
List some examples of superficial infection |
1. Tinea nigra: skin infection caused by Hortaea werneckii 2. Black piedra: hair and scalp infection caused by Piedra hortae |
|
|
list examples of mycetoma |
1. Chronic granulomatous infection involving lower extremities 2. bacterial (actinomycotic) or fungal (eumycotic) |
|
|
List examples of chromoblastomycosis |
1. Chronic infection acquired by traumatic inoculation into skin 2. lesions revealing sclerotic bodies and resembling copper pennies |
|
|
List an example of phaeohyphomycosis |
Infections from brown yeast like cells, pseudohyphae, or hyphae |
|
|
What's the differences between the two superficial infections |

|
|
|
list agents of mycetomas |

|
|
|
List an important mycetoma and its attributes |

|
|
|
List agents of chromoblastomycosis and attributes |

|
|
|
List agents of phaeohyphomycosis |

|
|
|
What's the differences among Exophiala |

|
|
|
List differences among Bipolaris (b) and Curvularia (c) |
1. Conidiosphores: bent (b) & geniculate (c) 2. Conidia: oblong & sympodical (b) and golden brown, multicelled, curved & swollen central wall (c) 3. Bipolaris also has hilum protruding and germ tubed at one/both ends |
|
|
this attribute of Alternaria |

|
|
|
What is the name of an atypical opportunistic fungus |
Pneumocystis jiroveci |
|
|
What are some characteristics of P. jiroveci |

|
|
|
List epidemiologic factors of P. jiroveci |

|
|
|
How what is the disease spectrum for P. jiroveci |
Inhaled & adheres to pneumocytes and replicates. Interstitial mononuclear inflammation response. symptoms are non productive cough, low grade fever, dyspnea, chest tightness and night sweats |
|
|
How is P Gervaise diagnose |
Specimen:BAL/induced sputum, biopsy material Stains: Calcoflour white, Methenamine silver, immunofluorescence Other methods for ID include commercial kits using monoclonal antibodies and nucleic acid amplification. Extremely difficult to cultivate |
|
|
What are the morphological characteristics of P. jiroveci |
Troph: predominant form but difficult to visualize with flexible walls and out number cysts 10:1 Cysts: spiracle to concave, uniform in size (4-7 micrometers), do not bud, contained intracystic bodies |

