![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
communication
|
the passing of info, exchange of ideas, or process of establishing shared meaning between a sender and a receiver
|
|
|
source
|
the sender--person, group, or organization-- of the message
|
|
|
encoding
|
the process of putting thoughts, ideas, or info into a symbolic form
|
|
|
message |
a communication containing info or meaning that a source wants to convey to a receiver
|
|
|
channel
|
the method or medium by which communication travels from a source or sender to a receiver
|
|
|
mass media |
nonpersonal channels of communication that allow a message to be sent to many individuals at one time |
|
|
personal channels |
direct communication b/t 2 or more persons and can occur through interpersonal contact (face to face) or via other methods (email, social media) |
|
|
word-of-mouth communications |
social channels of communication such as friends, neighbors, associates, co-workers, or family members |
|
|
buzz marketing
|
the use of various activities that generate conversations and word-of-mouth communications about a particular topic such as a company, brand or marketing activity
|
|
|
viral marketing
|
the act of propagating marketing-relevant messages through the help and cooperation of individual conusmers
|
|
|
seeding |
the process of identifying and choosing the initial group of consumers who will be used to start the diffusion or spreading of a message
|
|
|
seeding strategy |
determining how many initial consumers are needed and selecting the right influence to plant the model
|
|
|
receiver |
the person or persons with whom the sender of a message shares thoughts or info
|
|
|
decoding |
the process by which a message recipient transforms and interprets a message
|
|
|
field of experience |
the experiences, perceptions, attitudes, and values that senders and receivers of a message bring to a communication situation
|
|
|
noise |
unplanned distortion or interference in message delivery
|
|
|
response |
the set of reactions the receiver has after seeing, hearing, or reading a message
|
|
|
feedback |
part of the message recipient's response that is communicated back to the sender. Can take a variety of forms and provides a sender with a way of monitoring how an intended message is decoded and received
|
|
|
Levels of Audience aggregation
|
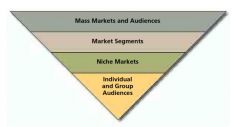
|
|
|
AIDA model |
a model that depicts the successive stages a buyer passes through in the personal-selling process, including attention, interest, desire, and action
|
|
|
hierarchy of effects model |
a model of the process by which advertising works that assumes a consumer must pass through a sequence of steps from initial awareness to eventual action. Stages include: awareness, interest, evaluation, trial, & adoption
|
|
|
innovation adoption model |
a model that represents the stages a consumer passes through in the adoption process for an innovation such as a new product. Stages include: awareness, interest, evaluation, trial, & adoption |
|
|
information processing model |
a model of advertising effects developed by William McGuire that views the receiver of a message as an info processor and problem solver. The model views the receiver as passing through a response hierarchy that includes a series of stages including message presnetaiton, attention, comprehension, acceptance or yielding, retention, and behavior |
|
|
standard learning model |
progression by the consumers through a learn-feel-do hierarchical response
|
|
|
dissonance/ attribution model |
a type of response hierarchy where consumers first behave, then develop attitudes or feelings as a result of that behavior, and then learn or process info that supports the attitude and behavior
|
|
|
low-involvement hierarchy
|
a response hierarchy whereby a message recipient is viewed as passing from cognition to behavior to attitude change
|
|
|
cognitive responses
|
thoughts that occur to a message recipient while reading, viewing, and/or hearing a communication |
|
|
counterarguments
|
a type of thought or cognitive response a receiver has that is counter or opposed to the position advocated in a message
|
|
|
support arguments
|
consumers' thoughts that support or affirm the claims being made by a message
|
|
|
source derogations
|
negative thoughts generated about the source of a communication
|
|
|
source bolsters
|
favorable cognitive thoughts generated toward the source of a message
|
|
|
ad execution-related thoughts
|
a type of thought or cognitive response a message recipient has concerning factors related to the execution of the ad, such as creativity, visual effects, color, and style
|
|
|
attitude toward the ad
|
a message recipient's affective feelings of favorability or unfavorability toward an advertisement
|
|
|
elaboration likelihood model |
a model that identifies two processes by which communication scan lead to persuasion centrally or peripherally
|
|
|
central route to persuasion
|
one of two routes to persuasion recognized by the elaboration likelihood model. this views a message recipient as very active and involved in the communications proves and as having the ability and motivation to attend to and process a message
|
|
|
peripheral route to persuasion
|
in the elaboration likelihood model, one of two routes to persuasion in which the receiver is viewed as lacking the ability or motivation to process info and is not likely to be engaging in detailed cognitive processing
|

