![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Frick’s law of diffusion |
Rate of diffusion between two regions |
|
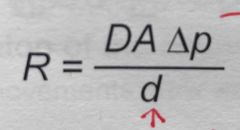
What is R ? |
Rate of diffusion |
|
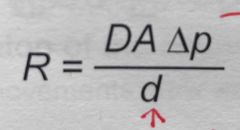
What is D ? |
Diffusion constant |
|
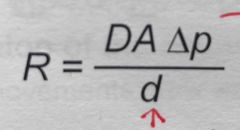
What is A? |
Area over which diffusion takes place |
|
|
What is 🔺P ? |
Pressure difference between two sides |
|
|
What is d? |
Distance over which diffusion occurs |
|
|
Because of evolutionary change, what has occurred and how ? |
Optimize the rate of diffusion by increasing surface area (A) , decrease distance (d) , & increase concentration difference (🔺p) |
|
|
How do gases diffuse? |
Directly into unicellular organisms |
|
|
Which Species respire across their skin ? |
Amphibians |
|
|
Which species protrudes papulae? |
Echinoderms |
|
|
Which Species have an extensive tracheal system? |
Insects |
|
|
Which species have a large network of alveoli? |
Mammals |
|
|
Are red veins oxygenated or deoxygenated? |
Oxygenated |
|
|
What do branchial chambers do ? |
Provide a means of pumping water |
|
|
Where are gills located in bony fishes ? |
Between the oral cavity and the opercular cavities |
|
|
How do fishes breathe ? |
Move water into the mouth , through the gills , & out of the fish through open gill cover |
|
|
What is Ram ventilation? |
Swimming constantly to force water over gills |
|
|
What do gills consist of ? |
Lamellae |
|
|
In lamella, how does blood flow ? |
Blood flows opposite direction of water movement |
|
|
True or false : fish gills are the most efficient of all respiratory organs |
True |
|
|
What do amphibians use for gas exchange? |
Use cutaneous respiration |
|
|
In arthropods, what does the respiratory system consist of? |
Consists of air ducts called trachea |
|
|
Why were gills replaced in terrestrial animals ? |
Air is less supportive than water |
|
|
How does the lung minimize evaporation? |
By Moving air through a branched tubular passage |
|
|
Which animal has a two-way flow system? |
Birds |
|
|
What partial pressure ? |
pressure contributed by a gas to the total atmospheric presure |
|
|
What is based on the % of the gas in dry air ? |
Partial pressures |
|
|
Do frogs have positive or negative pressure breathing ? |
positive |
|
|
What is positive pressure breathing ? |
Force air into their lungs by creating a positive pressure in the buccal cavity |
|
|
What is the negative pressure breathing ? |
Expand rib cages by muscular contractions, creating lower pressure inside the lungs |
|
|
Do you reptiles have positive or negative pressure breathing ? |
Negative pressure breathing |
|
|
Lungs of mammals are packed with millions of what ? |
Alveoli |
|
|
Where does air pass through ? |
the Larynx |
|
|
What is the Alveoli surrounded by ? |
Capillary network |
|
|
What is the capillary network ? |
Connection between veins and arteries |
|
|
Why does air exert a pressure downward? |
Due to gravity |
|
|
What is partial pressure? |
Pressure contributed by a gas to the total atmospheric pressure |
|
|
What is partial pressure based on? |
% |
|
|
True or false : frogs have a negative pressure breathing |
False, frogs have a positive pressure breathing |
|
|
What is positive pressure breathing? |
Force air into their lungs by creating a positive pressure in the buccal cavity |
|
|
What type of breathing pressure do reptiles have ? |
Negative breathing pressure |
|
|
What is negative pressure breathing? |
Expand rib cages by muscular contractions creating lower pressure inside the lungs |
|
|
What are lungs packed with in mammals ? |
Millions of alveoli |
|
|
What is the order of air coming in the mouth ? |
Oral cavity, epiglottis, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchiole, alveoli, & capillary |
|
|
What is alveoli surround by? |
Capillary network |
|
|
What is capillary networks? |
Connection between veins and arteries |
|
|
What is capillary networks? |
Connection between veins and arteries |
|
|
What is parabronuhi |
Tiny air vessels |
|
|
What is the birds breathing cycle? |
1. Inhaled air is drawn from the trachea into posterior air sacs, and exhaled into the lungs 2. Air is drawn from the lungs into anterior air sacs, exhaled through the trachea |
|
|
What is gas exchange driven by ? |
Differences in partial pressures |
|
|
What is the outside of each lung covered by? |
Visceral pleural membrane |
|
|
What is the space between two membranes called ? |
Pleural cavity |
|
|
During contraction , what happens to the intercostal muscles? |
Expands the rib cage |
|
|
During contraction, what happens to the thorax and lungs |
Diaphragm expands volume |
|
|
How is tension released by? |
Relaxation of the external intercostal muscles and diaphragm |
|
|
True or false : thorax and lungs are considered elasticity |
True |
|
|
define tidal volume |
volume of air moving in and out of lungs in a person at rest |
|
|
define capacity |
maximum amount of air that can be expired after a forceful inspiration |
|
|
define hypoventilation |
insufficient breathing |
|
|
define hyperventilation |
excessive breathing |
|
|
What happens when neurons stop producing impulses? |
respiratory muscles relax, and exhalation occurs |
|
|
What is Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ? |
any Disorder that obstructs airflow on a long term basis |
|
|
define chronic |
life long |
|
|
define acute |
short, temporary |
|
|
What happens to the people who suffer from emphysema ? |
become exhausted because they expend 3-4 the normal amount of energy just to breathe |
|
|
How many polypeptide chains does Hemoglobin consist of ? |
4 |
|
|
what is oxyhemoglobin ? |
hemoglobin loads up with oxygen in the lungs |
|
|
What is deoxyhemoglobin ? |
molecules lose O2 as blood passes through capillaries |
|
|
What is hemoglobin? |
protein that holds oxygen in the red blood cells |
|
|
What is the pH effect known for ? |
Bohr shift |
|
|
What reduces hemoglobin's affinity for O2? |
lower pH |
|
|
What is the order of blood/oxygen flow ? |
1. right atrium - deoxygenated 2. right ventricle - deoxygenated 3. lungs - deoxygenated into oxygenated 4. left atrium - Oxygenated 5. left ventricle - oxygenated 6. rest of the body - oxygenated into deoxygenated |

