![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
damage to an exposed individual |
somatic effects |
|
|
damage to a genetic code of the germ cell contained int he DNA |
genetic effects |
|
|
report that addresses the dose form all sources, to the population of the US |
NCRP #160 |
|
|
natural background radiation contributes what dose and what total percent |
3.11 mSv, 50% |
|
|
medical background radiation contributes what dose amount and what total percent |
3.0 mSv, 48% |
|
|
average effective dose- chest |
.1 mSv |
|
|
average effective dose- C spine |
.2 mSv |
|
|
average effective dose- T spine |
1.0 mSv |
|
|
average effective dose- L spine |
1.5 mSv |
|
|
average effective dose- upper GI |
6.0 mSv |
|
|
average effective dose- Abd (KUB) |
.7 mSv |
|
|
average effective dose- Pelvis and Hip |
.7 mSv |
|
|
average effective dose- extremities |
negligible- .005-.008 mSv |
|
|
two most common tissue interactions in diagnostic radiography |
photoelectric and compton |
|
|
interaction where incoming x-ray strikes a K-shell electron, and energyos x-ray photon is transferred to electron |
photoelectric |
|
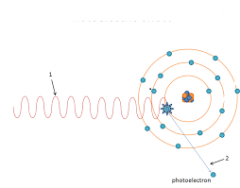
what interaction is this |
photoelectric |
|
|
photoelectric interactions result in increase what to the patient |
dose |
|
|
what does photoelectric absorption produce in the radiography because of differential absorption |
contrast |
|
|
what is compton interaction also called |
compton scattering, modified scattering |
|
|
contains a recoil electron |
compton scatter |
|
|
incoing x-ray photon strikes loosely bound outer shell electron, photon transfers part of energy to the electon |
compton scatter |
|
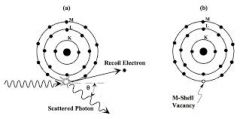
what is this interaction |
compton effect |
|
|
coherent scatter is also called what |
classical or thompson's scatter |
|
|
atomic electrons are not removed but vibrate because of the deposition of energy from the photon |
coherent |
|
|
produced by low energy x-ray photons |
coherent |
|
|
does not affect image less than 70 kVp |
coherent scatter |
|
|
this interaction does not occur in diagnostic radiography |
pair productions |
|
|
produced at photon energies greater than 1.02 million electron volts |
pair production |
|
|
traditional unit for radiation exposure in air |
Roentgen (R) |
|
|
SI unit for radiation exposure in air |
coulomb/kilogram (C/kg) |
|
|
traditional unit for unit of absorbed dose |
rad |
|
|
1 gray = ________ rads |
100 |
|
|
1 rad= ____ gray |
1/100 |
|
|
what is used to modify the absorbed dose amount to account for the greater damage inflicted by some forms of ionizing radiation |
a radiation weighting factor (Wr) |
|
|
Wr takes what into account |
LET (linear energy transfer) |
|
|
Wr for x-rays and gamma rays = ___ |
1 |
|
|
100 rads of x-rays = ___ rem |
100 |
|
|
Wr for neutrons = ___ |
20 |
|
|
100 rads of neutrons = _____ rem |
2000 rem |
|
|
1 Sievert = ____ rem |
100 rem |
|
|
traditional unit for radioactivity |
Curie 1 curie = 3.7 x 10^10 becquerels |
|
|
SI unit for radioactivity |
Becquerels |
|
|
traditional unit for absorbed dose |
Rad |
|
|
SI unit for absorbed dose |
Gray |
|
|
no level of radiation can be considered safe response occurs at every dose degree of response to exposure is directly prop. to amount of radiation received |
liner- nonthreshold |
|
|
lower doses of exposure, no response is expected response is directly proportional to dose received example: cataractogenesis |
linear- threshold |
|
|
indicated lower doses of radiation exposure, no response is expected response is not directly prop. to the dose received |
nonlinear- threshold |
|
|
indicated that no level of radiation can be considered safe response occurs at every dose response is not directly prop. to the dose received |
nonlinear- nonthreshold |
|
|
occupational exposure- annual effective dose is ____ |
50 mSv / 5 rem |
|
|
occupational exposure- annual equivalent dose determinisitc effects lens of the eye? |
150 mSv |
|
|
occupational exposure- annual equivalent dose determinisitc effects localized areas of skin, hands, feet? |
500mSv |
|
|
how to calculate cumulative effective dose (CEfD) limit |
age (in years) X 10 mSv ( 1 rem) |
|
|
general public- annual effective dose limit for infrequent exposure |
5 mSv / .5 rem |
|
|
general public- annual effective dose limit for frequent exposure |
1 mSv / .1 rem |
|
|
embryo-fetus total equivalent dose for gestation |
5 mSv / .5 rem |
|
|
embryo-fetus dose limit per month |
.5 mSv / .05 rem |
|
|
level of negligible risk |
.01 mSv / 1 mrem per year |
|
|
highly reactive ions that have an unpaired electron in the outer shell |
free radicals |
|
|
H2O2 |
hydrogen peroxide |
|
|
carinogenesis |
causes cancer |
|
|
examples of late somatic effects |
carcinogenesis, cataractogenesis, embryologic effects, thyroid, shortened life span |
|
|
two most common gonadal shields used |
flat contact, shadow shield |
|
|
most diagnostic x-ray exams have fetal doses less than ____ rads |
5 rads |
|
|
what law should always be used during fluoro in which close contact is not required |
inverse square law |
|
|
lead apron shield thickness that MUST be worn? |
.25 mm lead equiv. |
|
|
thyroid shield thickness that SHOULD be worn? |
.5 mm lead equiv |
|
|
lead apron thickness that SHOULD be worn? |
.5 mm lead equiv. |
|
|
monitoring device that uses aluminum oxide to record dose |
OSL |
|
|
monitoring device that has a sensitive exposure of 1 mrem |
OSL |
|
|
monitor device that uses lithium fluoride crystals instead of film to record dose |
TLD |
|
|
monitor device that has a sensitivity to exposure at 5 mrem |
TLD |
|
|
monitor device that uses film used that is similar to dental x-rays and measures doses of 10 mrem |
film badges |
|
|
handheld Ionization chamber measures exposure rates of ____. |
1 mR per hour |

