![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sources of Economic Growth
|
Land
Capital Goods Labor Entrepreneurial Ability |
|
|
3 social institutions that are preconditions to economic growth
|
Market prices
Property Rights Monetary Exchange |
|
|
3 activities necessary for persistent economic growth
|
1. Saving and investment in new capital
2. Investment in Human Capital 3. Discovery of new technologies |
|
|
Coefficient of Determination
|
R^2 or
Explained Variation / Total Variation |
|
|
Impact of labor productivity increase on employment, real wage rate, and potential GDP
|
increase employment
increase wages increase potential GDP |
|
|
Impact of population increase on employment, real wage rate, and potential GDP
|
increase employment and potential GDP but lowers wage rate
|
|
|
Required return from H Model Equation
|
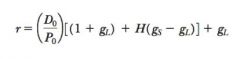
|
|
|
currency forward premium equation
|
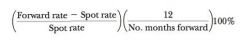
|
|
|
Interest Rate Parity equation
|
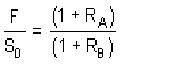
|
|
|
Current Account includes
|
exchange of goods and services
investment income unilateral transfers (net of aid) |
|
|
Implied growth rate from residual income equation
|
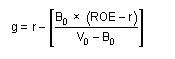
|
|
|
Financial Account Includes
|
Payment for securities
direct investment bank deposits |
|
|
Justfied PB equation (Gordon)
|
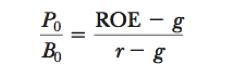
|
|
|
Impact of expansionary fiscal policy on currency, current account, and financial account
|
currency appreciation
current account decrease financial account increase |
|
|
Impact of expansionary monetary policy on currency, current account, and financial account
|
currency depreciation
current account decrease financial account decrease |
|
|
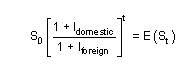
Relative PPP equation
|
|
|
|
International Fisher equation
|
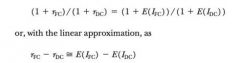
|
|
|
Net national income
|
gross national income - depreciation
|
|
|
GDP measures that use factor prices
|
income based measures
|
|
|
Economic profit of a capital project
|
NOPAT - $WACC
|
|
|
Justified PS equation
|
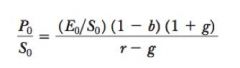
|
|
|
agency costs of equity
|
monitoring costs
bonding costs residual losses |
|
|
Effective tax rate under double taxation
|
corporate tax rate + (1 − corporate tax rate) × (individual tax rate)
|
|
|
target payout calculation for stable dividend
|
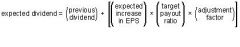
|
|
|
HHI Calculation
|

|
|
|
Weighted Harmonic Mean
|
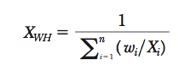
|
|
|
inputs for pricing stock options that decrease fair value
|
lower volatility
shorter term lower risk free rate higher expected dividend yield |
|
|
When to use current rate method
|
If functional currency and parent presentation currency differ
|
|
|
translation methods for hyperinflationary
|
GAAP - temporal
IFRS - restate for inflation and then current rate |
|
|
Recognition of fair value hedge using derivatives
|
ineffective portion of hedge recognized in income statement
|
|
|
Recognition of cash flow hedge with derivatives
|
bypass income and go to OCI but are reclassed through income when transaction is complete
|
|
|
recognition of a net investment hedge of a foreign subsidiary
|
recognized in OCI
|
|
|
Accruals Ratio CF
|
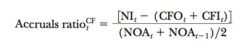
|
|
|
Adjusted Beta
|
2/3 * regression beta + 1/3 * 1.0
|
|
|
2 central questions for firm's choice of competitive strategy
|
Industry Attractiveness
Competitive Advantage |
|
|
Management actions to gain competitive advantage
|
Position for current forces
Exploit changes in forces Shape the Industry Structure |
|
|
key components of industry analysis
|
-industry classification – life cycle position, business cycle
- external factor review – technology, government, social, demographic, foreign - demand analysis – end users, real/nominal growth, trends and variations around trends - supply analysis – degree of concentration, easy of entry, Industry capacity - profitability analysis – supply/demand, cost factors, pricing - international competition and markets review. |
|
|
4 stages of Lifecycle
|
- Pioneer. Acceptance of the product or service is uncertain, and the correct strategy may be unclear.
- Growth. Growth companies can prosper in all stages of the business cycle. - Mature. Industry growth now corresponds to the growth of the general economy. - Decline. Shifting tastes or technologies have overtaken the industry, and demand for its products steadily decreases |
|
|
Business Cycle Classifications
|
- Growth industry stocks experience accelerating sales and high profit margins during all phases of the business cycle.
- Defensive industry stocks are much less cyclical than the overall market because demand for their products tends to be relatively independent of the business cycle. - Cyclical industry stocks vary directly with the business cycle because product demand tends to increase during the expansion and peak phases and drop off significantly during the recessionary phase. |
|
|
implied growth rate of dividends from Gordon Growth model
|
g = r − (D1 / P0)
|
|
|
FCFF from EBIT
|
[EBIT × (1 − tax rate)] + Dep − FCInv − WCInv
|
|
|
FCFF from EBITDA
|
[EBITDA × (1 − tax rate)] + (Dep × tax rate) − FCInv − WCInv
|
|
|
FCFE from FCFF
|
FCFF − [Int × (1 − tax rate)] + net borrowing
|
|
|
Code of Ethics
|
Act with Integrity, Diligence, Respect
Place integrity of profession and clients above own Use Reasonable care and independent judgement practice and encourage others to practice in an ethical manner promote integrity of rules governing capital markets maintain and improve professional competence |
|
|
5 principles of prudent investor rule
|
1. Diversification is Fundamental
2. Risk must be considered 3. duty to avoid fees 4. balancing of current income and growth 5. duty and authority to delegate as prudent investors would. |
|
|
Sample Correlation Equation
|
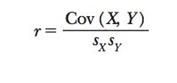
|
|
|
t-test for correlation coefficient r
|
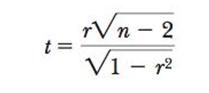
|
|
|
F stat for multiple regression
|
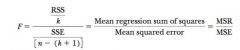
|
|
|
Serial Correlation
|
Residuals are correlated, durbin watson except for time series then have to check correlation of residuals, hanson method to correct standard errors
|
|
|
Multicollinearity
|
Two or more independent variables are correlated, F and t values conflict, drop a correlated independent variable
|
|
|
Test for autoregressive model fit
|
check to see if autocorrelations of residuals is significant
|
|
|
mean reversion equation for AR(1)
|
b0 / (1-b1)
|
|
|
adjustment of discount rate for probability of failure for private equity
|
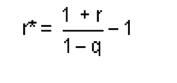
|
|
|
Price of a Forward Rate Agreement
|
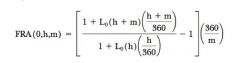
|
|
|
Value of a currency forward at time t
|
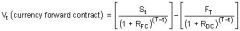
|
|
|
Pi equation for options prices
|
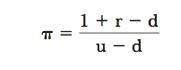
|
|
|
Variance Equation
|
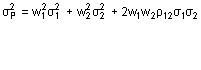
|
|
|
Beta calc from Cov
|
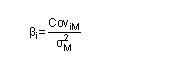
|
|
|
Covariance from Market Model
|
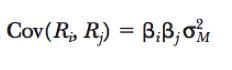
|
|
|
Foreign Currency Risk Premium equation
|
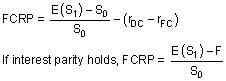
|
|
|
model that says depreciating currency should increase domestic economic activity
|
Traditional Trade or J-Curve
|
|
|
model that says an increase in economic activity causes increased demand in domestic currency
|
money demand model
|
|
|
theory that increased rates causes appreciation of domestic currency
|
free markets theory
|
|
|
theory that bonds have positive exposure to currency risk
|
government intervention theory
|
|
|
Option Cost =
|
Z-Spread - OAS
|
|
|
Convexity Equation
|
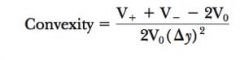
|
|
|
Duration Equation
|
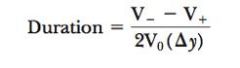
|
|
|
PSA calculation for t <30
|
CPR = 6% x (t/30)
|
|
|
CPR from SMM
|
1 - (1-SMM) ^ (12)
|
|
|
Reasons for differences in effective durations calculated by dealers
|
1. differences in delta y
2. OAS differences from monte carlo model 3. differences in assumed spreads between 1m rates and refinancing rates |
|
|
Objectives of Corporate Governance System
|
Eliminate or reduce conflicts of interest
Use the company’s assets in a manner consistent with the best interests of investors and other stakeholders |
|
|
n ratio equation for option binomial model
|
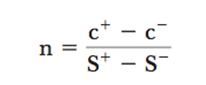
|
|
|
Uncovered Interest Rate Parity
|
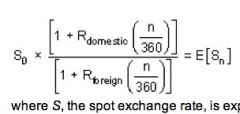
|
|
|
conditional heteroskedasticity
|
variance of residuals is not constant and is correlated with level of independent variables, t stats are inflated. Bruesch-Pagan Chi square test nR2
|
|
|
Asset Beta equation
|
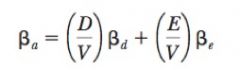
|
|
|
Cost of Equity with Debt added equation
|
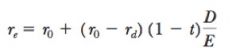
|

