![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The main lobes of brain |
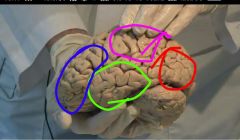
occipital lobe (red) - visual sensation parietal lobe (pink) - somatosensory f frontal lobe (blue) - motor execution Temporal lobe (green) - auditory f
Cerebrum is the largest part of brain. Has right and left hemispheres joined by Corpus callosum. hemispheres are separated by sickld shaped fold of dura. lobes+surface |
|
|
How is 2 hemispheres of brain attached |
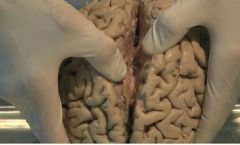
with CORPUS CALLOSUM |
|
|
What is the outer surface of brain like |
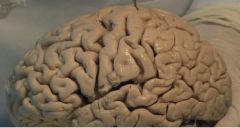
with dips or grooves called sulci and coily bumps called gyri (gyri - giant) Sulci- Central sulcus or fissure of rolando, lateral sulcus or fissure of sylvius, parieto occipital sulcus ans calcarine sulcus. Gyri in figure of sulci n gyri |
|
|
Internal structure of brain |
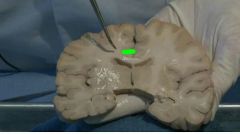
First slice off the brain to obtain a coronal section. Now the grey outlining is grey matter and inner white color is white matter. essentially, white color is axons of neurons and grey color is cell body and dendrites of neurons. We can see the corpus callosum (green) the white matter forming a band of fibres to connect the like areas of both hemispheres. Blue shaded holes are ventricles of brain filled with csf. |
|
|
what do you see in the back of this model or ventral surface in a standing person |
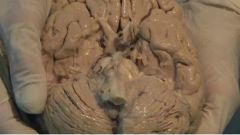
The elongated medulla oblongata the bulgy pons and deep in is the mid brain The flower like blooming on both side is cerebellum |
|
|
demonstrate coverings of brain |
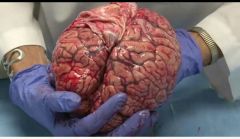
thick white sheet like dura mater (durable strong) the glistening blushy pia mater (pia pink) , colorless clear arachnoid mater |
|
|
functional areas of brain |
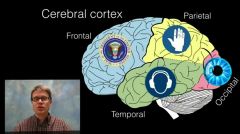
|
|
|
The connected areas of brain |
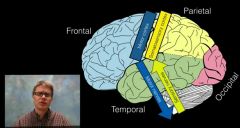
Somatosensory cortex in parietal lobe (receiving sensory nerve) to motor cortex in frontal lobe (going out through the motor nerve. |
|
|
diencephalon |

is embedded within cerebrum and is hidden from surface. it has dorsal part- thalamus, metathalamus( lateral geniculate body for vision and medial geniculate body for hearing),and epithalamus. ventral- hypothalamus and subthalamus. |
|
|
thalamus |

its a mass of grey matter situated in between 3rd ventricle. 2 thalami connected by interthalamic adhesion. parts - anterior(recent memory) , medial(olfactory and sensory) , lateral. function - relay centre. transmit sensory and motor signal to cerebrum. it receive afferent nerve from different part. |
|
|
thalamus figure 2 |
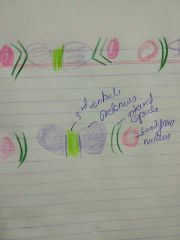
thalamic syndrome - hemiplegia with loss of sensation |
|
|
hypothalamus |
located in lateral wall and floor of 3rd ventricle. supraoptic nucleus - secrete ADH paraventricular nucleus - secrete oxytocin. Function - chief ganglion of ANS.anterior part regulate parasympathetic and post part sympathetic system. hormones regulate thyroid pituitary etc. hence control respiratory and cardiovascular functions. temperature regulation, food n water intake n sexual activity and biological clock. lesions - diabetes insipidus, obesity and abnomal sexuality |
|
|
basal nuclei |
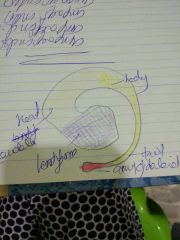
mass of grey matter deep inside cerebrum. include lentiform nucleus (biconvex, boundary of internal capsule). 2 part putamen and globus pallidus. caudate nucleus (space has thalamus and internal capsule)part-head body tail . they both corpus striatum. amygdaloid nucleus - near tail claustrum. Function - muscular tone and voluntary movement. mainly corpus striatum helps in this. applied - degeneration of corpus striatum leads to parkinsonism and muscle rigidity. |
|
|
Corpus callosum |
white matter of cerebrum has association fibres ( one hemispheres cortical areas connected) projection fibres (cortical areas to other part of brain like brainstem) commissural fibres (connects corresponding areas of 2 hemispheres) . Corpus Callosum is largest collection of commissural fibres. 10cm long. it doesn't connect lower part of temporal lobe. Parts- rostrum (directed downward and backward. connected to orbital surface of frontal lobe) genu (its the anterior end with forceps minor fibres connecting frontal lobes. Splenium thickest part with forceps major connecting occipital lobes Trunk middle part. trunk with Splenium has tapetum fibres. |

