![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lower-limb motor strip is in _______distribution while upper-extremity motor strip is supplied by _______.
A. ACA/MCA B. MCA/ACA c. PCA/MCA d. PCA/ACA |
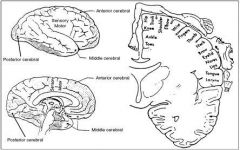
Major vascular supply to brain and functional diagram of motor strip. It is evident that lower-limb motor strip is in anterior cerebral artery distribution while upper-extremity motor strip is supplied by middle cerebral artery. (from Rosen P. Emergency Medicine–Stroke 3rd ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 1992.)
|
|
|
Circle of Willis Arteries
1. anterior cerebral artery (a) 2. internal carotid artery (b) 3. posterior communicating artery (c) 4. posterior cerebral artery (d) 5. basilar artery (e) 6. middle cerebral (f)artery 7. anterior communicating artery (minute connection between the left and right anterior cerebral arteries)(g) |
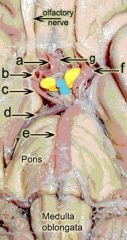
Identify the structures a-g
|
|
|
1. Occlusion of the internal carotid artery may cause all of the following except:
a. Interruption of blood supply to an entire middle cerebral artery b. Infarct of the thalamus c. No neurologic deficit d. Artery-to-artery embolus |
b
|
|
|
2. Stroke etiology is felt to be:
a. About 50% hemorrhagic, 50% embolic b. About 1/3 cardioembolic, 1/3 atherothrombotic c. Often due to a hematologic abnormality d. Indeterminate in most cases |
b
|
|
|
3. Prominent risk factors for stroke include:
a. Hypertension b. Cardiac arrhythmias, atrial fibrillation or valvular heart disease c. Diabetes mellitus d. All of the above |
d
|
|
|
4. All of the following is true about subarachnoid hemorrhage except:
a. It is usually surgically curable b. It may result from rupture of a saccular aneurysm c. It can occur in young, healthy people d. Berry aneurysms tend to occur at major arterial bifurcations |
a
|
|
|
5. The following is true about lacunar infarcts except:
a. They are seen in hypertensive and diabetic patients b. They may be seen asymptomatically on brain scans c. They do not usually cause problems clinically d. They are seen frequently in the basal ganglia and internal capsule region |
c
|
|
|
1. The lateral medullary syndrome may have the following components:
a. Ipsilateral cerebellar ataxia b. Ipsilateral Horner's syndrome c. Contralateral facial numbness d. Acute hoarseness and dysphagia e. All except c |
e
|
|
|
2. The lateral medullary syndrome:
a. Is often a vertebral artery occlusion b. Is typically embolic in nature c. Results in contralateral hemiparesis d. Results in ipsilateral hemisensory deficit e. Is likely to be fatal |
a
|
|
|
3. Lacunar infarctions: Updated 4/2005
a. Are most commonly seen in the face of hypertension b. Raise the need for angiography c. Require full anticoagulation d. Are never asymptomatic |
a
|

