![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where is the primary function of the cerebellum |
It coordinates motor commands with sensory inputs to control movement rate range and force |
|
|
True or false the vermis is a fissure |
True |
|
|
What's another name for the anterior lobe |

Superior lobe |
|
|
What's another name for the middle lobe |

Inferior lobe |
|
|
Where you call a singular foccullarnodular lobe |

Fiocculus |
|
|
What separates the anterior lobe from the middle lobe |
Primary fissure |
|
|
What's the function of anterior lobe of The cerebellum |
Coordinates postural adjustments |
|
|
What part of the cerebellum controls fine motor movement adjustments |

Middle lobe |
|
|
True or false speech involves fine motor movements |
True |
|
|
What is the function of the flocculonodular lobe |
Coordinates bodies position in space |
|
|
... what causes ataxia |
Infections injuries or degenerative diseases that affect the cerebellum |
|
|
What is ataxia |
It's impaired coordination it can cause impairment for writing walking speech and swallowing |
|
|
What is the function of the brain stem |
It's responsible for basic body functions to maintain life such as blood pressure respiration and heart rate |
|
|
Which nerves extend off the brainstem |
Cranial nerves |
|
|
Where does contralateral commands occur |
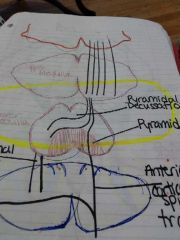
At the pyramidal decussation in the lower medulla |
|
|
Where is the Olivery complex located |
Pons |
|
|
What is the function of the olivery complex |
The localization of sound and noise |
|
|
What is the function of the cerebral peduncles in the midbrain |
To provide communication to and from the cerebrum to the midbrain |
|
|
What is the substantia nigra |
Apart from being part of the basal ganglia it is located in the midbrain and manufactures dopamine |
|
|
. What is dopamine |
A neurotransmitter essential for normal movement |
|
|
What are symptoms of Parkinson's disease |
slowness of voluntary movement trembling of hands at rest decrease facial expression and monotone speech a shuffling gait and swallowing problems |
|
|
True or false dysphasia is a symptom of Parkinson's disease |
True |
|
|
What is the cause of Parkinson's disease |
A degeneration of dopamine containing neurons |
|
|
What are the descending tracts of the spinal cord |
Efferent/motor |
|
|
What are the ascending tracts of the spinal cord called |
Afferrant/sensory |
|
|
What two roots were combined together to form a spinal nerve |
Dorsal and ventral roots |
|
|
What part of the spinal cord contains the ascending and descending fiber tracts |
The white matter |
|
|
What part of the spinal cord is the location of synapses |
Grey matter |
|
|
What's the purpose of the central canal |
It circulate cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
Which root contains sensory or afferent sensory information |
Dorsal |
|
|
Which root contains motor information |
Ventral |
|
|
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there |
31 |
|
|
How many pairs of cervical spinal nerves are there |
8 |
|
|
How many pairs of thoracic spinal nerves |
12 |
|
|
How many pairs of lumbar spinal nerves |
5 |
|
|
How many pairs of sacral spinal nerves are there |
5 |
|
|
How many pairs of coccygeal spinal nerves |
1 |
|
|
What is a spinal reflex arc |
It's a simple stimulus-response that sends sensory information to the spinal cord and back as motor information to the muscle without traveling to the brain |
|
|
Where you call the First cranial Nerve |
Olfactoy |
|
|
What type of nerve is cranial 1 |
Sensory |
|
|
which is the optic nerve |
Cranial 2 |
|
|
What type of nerve is cranial 2 |
Sensory |
|
|
What number cranial nerve is the oculomotor |
3 |
|
|
What's the function of the oculomotor cranial nerve 3 |
Innervates eye movement and pupil size |
|
|
What type of nerve is cranial nerve 3 |
Motor |
|
|
What number is the trochlear cranial nerve |
4 |
|
|
What's the function of cranial nerve 4 |
It also innervates eye movements but only downward and outward |
|
|
Number of Trigeminal |
5 |
|
|
Function of cranial 5 |
Both motor and sensory muscles of mastication tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani, |
|
|
What are the sensory components of cranial nerve v |
Communicated sensation from face mouth and teeth tongue |
|
|
Cranial nerve 6 |
Abducens |
|
|
Function of abducens |
Motor- lateral eye movement |
|
|
What number is the facial cranial nerve |
7 |
|
|
What's the function of the cranial nerve number 7 |
It's a motor nerve innervates muscles of facial expressions and it's a sensory nerve it serves the taste of the anterior 2/3 of the tongue |
|
|
What is bells palsy |
Compression of facial nerve due to stress or injury |
|
|
What number is the vestibulococlear nerve |
8 |
|
|
What type is cranial nerve 8 |
Sensory |
|
|
What function is 8/vestibulocochlear |
Auditory |
|
|
What does ipsilateral mean |
Same side |
|
|
Damage to which cranial nerve causes vertigo |
Vestibulocochlear/8 |
|
|
Number for glossopharyngeal nerve |
9 |
|
|
What type is the glossopharyngeal nerve/9 |
It's a both motor and sensory |
|
|
What are the sensory functions of cranial nerve 9 |
It provides taste to the posterior third of the tongue and portions of the soft palate |
|
|
What are the motor functions of the glossopharyngeal cranial nerve number 9 |
It innervates the Stylophaeyngeal muscle and the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle |
|
|
What is cranial nerve 10 |
Vagus |
|
|
What type is nerve 9 |
Both motor and sensory |
|
|
What are the motor functions of cranial nerve 10 |
an interface the muscles of the larynx used for Pho nation and protection of the airway it innervates all the velopharyngeal muscles except the tensor veli palatini |
|
|
Which velopharyngeal muscle is not innervated by the Vegas |
The tensor veli palatini |
|
|
What are the sensory functions of cranial nerve 10 or Vegas |
It delivers pain touch and temperature sense from the eardrum posterior Oracle and the external auditory meatus |
|
|
Which cranial nerve serves the autonomic nervous system |
10/vagus |
|
|
What number is the accessory nerve |
11 |
|
|
What is the function of the cranial nerve 11 |
It's a motor nerve that activates the sternocleidomastoid muscle and a trapezius muscles |
|
|
What number is hypoglossal |
12 cranial nerve |
|
|
What is the function of cranial nerve 12 |
It's a motor nerve that innervates the muscles of the tongue |

