![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Towards Central nervous system. Spinal cord and brain |
Afferent |
|
|
Away from brain and spinal cord |
Efferent |
|
|
Sending impulses to skeletal muscles and usually conscious control |
Somatic motor response |
|
|
Sending messages to smooth muscle and bladder and it's not under control |
Autonomic motor respo4 |
|
|
Forms myelin sheaths in the peripheral nervous system |
Schwann cell |
|
|
It's purpose is to transmit impulses to the nerve cells body. Can have many of these, just 1 or none |
Dendrites |
|
|
Type of conduction through the cytoplasm using the high concentration of electrolytes in the nerve cells body |
Electrotonic conduction |
|
|
The exposed section of nerves |
Node of ranvier |
|
|
Nerve cells body meets the axon here. Has voltage gated channels here |
Axon hillock |
|
|
Type of neuron the has many dendrites, one axon and found in brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system |
Multipolar |
|
|
This type of neuron has 1 dendrite, 1 axon, sensory afferent neurons, and found in rods and cones of retina and in olfactory neurons |
Bipolar neuron |
|
|
This type of neuron has no true dendrites, and is found in almost all sensory neurons (such as pain,temp change,vibration). Doesn't transmit to nerve cells body |
Unipolar/pseudopolar neuron |
|
|
This is wrapped around capillaries in the brain and is the 1st component of the blood brain barrier. |
Foot processes of astrocytes |
|
|
2nd component of the blood brain barrier |
Tight junctions |
|
|
Protects the brain from harmful substances |
Blood brain barrier |
|
|
These line the ventricles of the brain and passages to other ventricles |
Ependymal cells |
|
|
CSF is formed here. There is 1 in each ventricle but the most developed are in the 2 lateral ventricles |
Coroid plexus |
|
|
These are the macrophages of the brain. They're part of our innate immune system |
Microglial cells |
|
|
These forms myelin sheaths in the central nervous system |
Oligodendrocyte |
|
|
2 ways speed of conduction is increased |
Larger axon and myelinated |
|
|
This is the type of conduction of an action potential (nerve impulses) in myelinated axons. This is much faster than unmyelinated axons send impulses. |
Saltatory conduction |
|
|
A bundle of axons located in the peripheral nervous system. |
Nerve |
|
|
If it can be damaging to tissues it is conducted in what type of nerve cell |
Type A delta |
|
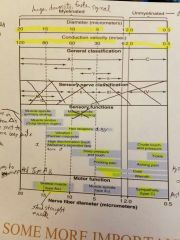
Type A alpha,beta,gamma,delta |
Study this |
|
|
Bundles of axons with each 1 transmitting different type of info such as motor, sensory and autonomic |
Fascicle |
|
|
Bundle of axons and their myelin sheaths that can be ascending or descending in the CNS and connects spinal cord -brain, brains brain, brain spinal cord |
Tract |
|
|
Cluster of nerve cell bodies and their associated dendrites. Composes central part of spinal cord and outer part of brain |
Gray matter |
|
|
Composed of tracts located in the CNS, it's a cluster of gray matter positioned within white matter |
Nucleus |
|
|
Located in the PNS, a cluster of nerve cell bodies and their dendrites where axons synapse with dendrites |
Ganglion |
|
|
This is composed of tracts |
White matter |
|
|
This is where an axon terminates and releases a neurotransmitter. |
Synapse |
|
|
What effect does excitation postsynaptic potentials have on rmp |
Brings rmp closer to tp |
|
|
What effect does inhibitory postsynaptic membrane potentials have on rmp |
Moves rmp farther from tp |
|
|
When 2 or more impulses occurring on different dendritic membranes simultaneously via electrotonic conduction |
Spatial summation |
|
|
When impulses arrive over time at the same dendritic membrane |
Temporal summation |
|
|
What is sensory input that leads to motor or autonomic output and is the basic functional component of the nervous system |
Reflex arc |
|
|
When 2 neurons go to a single cell body. When this happens the output down the axon depends on the output of the 2 neurons. What is this called |
Convergent pathway |
|
|
When a single axons splits towards 2 separate cell bodies. Used if something is hot. Impulse travels to the spinal cord and back to skeletal muscles to remove hand. The other path goes to brain to allow the brain to analyze situation and compose an appropriate response. It can override the initial response |
Divergent pathway |
|
|
This pathway is characterized by periods of activity and periods of fatigue or inactivity. It has constant feedback. Examples are: sleep wake cycle, and respiratory cycle |
Oscillating pathway or circuit |
|
|
How fast does an injured axon take to repair itself when its split in 2. |
They can repair themselves if they are closely approximated. They can repair 1 mm every few days. |

