![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
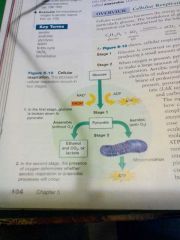
cellular respiration
|
first stage glucose is broken down to pyruvate second stage the presence of oxygen determines whether aerobic respiration or anaerobic process will occur
|
|
|
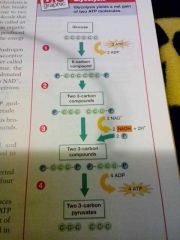
glycolysis
|
1- phosphate groups from two ATP molecules are transferred to a glucose molecule
2-the resulting six-carbon compound is broken down to two three-carbon compounds each with a phosphate group 3- two NADH molecules are produced and one more phosphate group is transferred to each three-carbon compounds 4- each three-carbon compound is converted to a three-carbon pyruvate,producing four ATP molecules in the process |
|
|
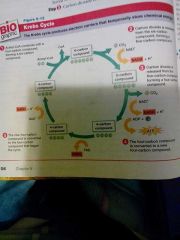
Krebs Cycle
|
1- acetyl-CoA combines with four-carbon compound, forming a six-carbon compound and releasing coenzyme A
2- carbon dioxide is released from the six-carbon compound, forming a five-carbon compound. electrons are transferred to NAD+ making a molecule of NADH 3- carbon dioxide is released from the five-carbon compound forming a four-carbin compound 4- the five-carbon compound is converted to a new four-carbon compound 5- the new four-carbin compound is converted to the four-carbon compound that began the cycle |
main second stage
|
|
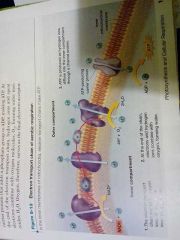
electron transport chain of aerobic respiration
|
1- the electron transport chain pumps hydrogen ions out of the inner compartment
2- At the end of the chain electrons and hydrogen ions combine with oxygen forming water 3- ATP is produced as hydrogen ions diffuse into the inner compartment through a channel |
|

