![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functions of epithilial tissue
|
Proection
Absorption Secretion Form barrier for selective permeability |
|
|
Classification of epithilial cells based on
|
Number of layers present
Shapes of the cell |
|
|
Simple
|
A sinlge layer of ells, all of which rest on a basement membrane
|
|
|
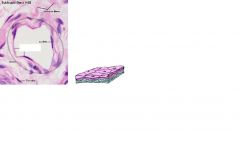
Simple squamous epithelium
Single layer of flat cells forming a ining on moist surfaces Common Line large body cavities, heart, blood vessels and lymph vessels Nuclei are often flattened or ovoid and located close to center of cell |
|

|
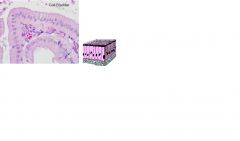
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Single laer of cube shaped cells Occurs in small excretory ducts of many glands like the follicles of the thyroid gland, the tubules of the kidneys, and on the surface of the ovaries |
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium
Single layer of tall cells Nuclei of cells within the epithelium usually located at same height within cells, often close to the base of the cell Lines internal surface of gastrointestinal tract from the cardia of the stomach to the rectum |
|

|
Pseudostratified columnar epithilia
Formed by tall and short cells, all of which rest on the basement membrane Nuclei located at different levels gives a false impression of stratification Found in respiratory tract |
|

|
Transitional
This epithelium appears to be stratified but according to some authors it is pseudostratified Cells on surface do contact basement membrane |
|
|
Stratified
|
Multiple layers present
Basal layer rests on the basement membrane |
|
|
Stratified squamous epithilia
|
Uppermost later of flat cells which may undergo kreatinization and therefore can be described as keratnized or non keratinized
|
|
|
Stratified cuboidal epithilia
|
Uppermost layer of cube shaped cells
|
|
|
Stratified columnar epithilia
|
Uppermost layer of tall cells
|
|
|
Apical or free surface which faces
|
the surface
|
|
|
Lateral or contact surfaces which come in contact
|
with neighboring epithelial cells
|
|
|
Basal surface which rests on the
|
basement membrane
|
|
|
Cilia
|
located on apical surface
Processes on apical surfaces Motile Remove dirt Beat in union and can create currents in overlying fluid medium E.g. trachea and mucus |
|
|
Microvilli
|
located on apical surface
Fine cell processes Non motile Increase surface area for absorption E.g. absorptive cells of the intestine |
|
|
Sterocillia
|
located on apical surface
Large microvilli Non motile Increase surface area for absorption/secretion E.g. epithelial cells of epididymis |
|
|
Junctional complex
|
located on lateral surface
Occluding type (zonula occludens)- tight junction Adhering type ( zonula/macula adherns)- desmosomes Communication type ( nexus)- gap junction |
|
|
Basal striations
|
located on basal surface
Invaginations or infolding of basal surface of cells To increase surface area for active transport of substances into and out of cell |
|
|
Basement memebrane
|
Lamina lucida-lamina densa-lamina fibroreticulus
|
|
|
Hemidesmosomes
|
Structures on the inner basal surface of some epithelial cells involved in adhesion of the cell to basemement membrane.
|
|
|
Glands
|
Structured groups of epithelial cells that are usually located away from surfaces of body
Function is to secrete Require protection from wear and tesr Large apical surface area, allowing for potential greater volumes of secretion to be passed out of cell |
|
|
Endocrine
|
lose their connection to surface
Have no ducts Secretory cells surrounded closely by blood vessels Products refered to as hormones Diffuse into surrounding capillaries for distribution |
|
|
Exocrine
|
retain their connection via the formation of ducts
Produce milk, enzymes sweat and other secretions Further classified morphologically: simple vs compound; tubular vs acinar |
|
|
Merocrines
|
Only secretory product released from cell
E.g. casein secretion by mammary epithelial cell |
|
|
Apocrine
|
Product is membrane bound and secreted along with some cell membrane and cytoplasmic material of cell
E.g. secretion of lipid droplet by mammary epithelial cells |
|
|
Holocrine
|
The whole cell disintegrates to form the secretion
E.g. sebum the oily secretion of sebcaous glands |
|
|
Mucus
l |
Thick and viscus
Cell accumulates material in apical cytoplasm (pale stained) and nucleus pushed toward base and flattened Cell refered to as mucus cel |
|

|

|

