![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Cell |
The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism, typically microscopic and consisting of cytoplasm and a nucleus enclosed in a membrane. Microscopic organisms typically consist of a single cell, which is either eukaryotic or prokaryotic.
|
|
Cell Membrane |
The semipermeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell.
|
|
|
Organelle
|
Any of a number of organized or specialized structures within a living cell.
|
|
Nucleus |
A dense organelle present in most eukaryotic cells, typically a single rounded structure bounded by a double membrane, containing the genetic material.
|
|
Prokaryote |
A microscopic single-celled organism that has neither a distinct nucleus with a membrane nor other specialized organelles. Prokaryotes include the bacteria and cyanobacteria.
|
|
Eukaryote |
A eukaryote is any organism whose cells contain a nucleus and other organelles enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes belong to the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota.
|
|

Cell Wall |
A rigid layer of polysaccharides lying outside the plasma membrane of the cells of plants, fungi, and bacteria. In the algae and higher plants, it consists mainly of cellulose.
|
|
|
Ribosome |
A minute particle consisting of RNA and associated proteins, found in large numbers in the cytoplasm of living cells. They bind messenger RNA and transfer RNA to synthesize polypeptides and proteins.
|
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
A network of membranous tubules within the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell, continuous with the nuclear membrane. It usually has ribosomes attached and is involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
|
|
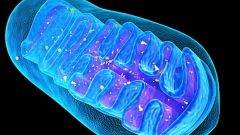
Mitochondrion |
The powerhouses of the cell. They are organelles that act like a digestive system which takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and creates energy rich molecules for the cell. The biochemical processes of the cell are known as cellular respiration.
|

