![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Cytology |
The study of cells |
|
|
|
The role of the cell |
The cell: 1) provides structure for an organism 2) extract nutrients from food 3) contain hereditary material 4) carry out specialised functions |
|
|
|
Types of Cells |
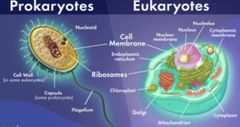
Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic Cells |
|
|
|
What is an Eukaryotic cell & An example |
Has membrane-bound organelles and a true nucleus. An animal cell |
|
|
|
BONUS QUESTION What is the largest animal cell |
An ostrich egg. Stretching to over 5.1 inches. |
|
|
|
Cell membrane |
Semipermeable that protects the cell and controls what enters and exits the cell |
Gate keeper |
|
|
Nuclear membrane |
Double- membraned structure that surrounds the nucleus |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Contains the DNA ( genetic material) for the cell |
Prime Minister |
|
|
Centrosomes |
Has a thick centre with radioactive tubules and is responsible for transporting materials in the cell. |
|
|
|
Lysosome |
Surrounded by a digestive enzyme membrane and is plays a role in digestion, excretion and cell renewal. |
Handyman |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
A jelly like substance which wholes all the organelles within a cell together. |
|
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
A flat sac like organelle that is flat and smooth. Responsible for manufacturing, storing, packing and transporting particles throughout the cell. |
The maker |
|
|
Mitchondrion |
Responsible for converting nutruients into energy/ATP |
The powerhouse |
|
|
Ribosome |
Responsible for making proteins for the cell / protein synthesis |
|
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
Transports materials throughout the cell |
|
|
|
Vacuole |
Stores the cell's food, water and waste and maintains the shape of cell wall |
|
|
|
Nucleopore |
Tiny holes in the nuclear membrane that are responsible for the movement of nucleic acids and proteins within the cell. |
|
|
|
List 6 differents between Animal and Plant cells |
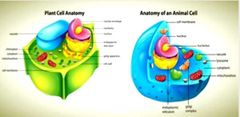
• Size • Shape • Energy storage (complex carbonhydrate glycogen vs starch) • Cell wall • Vacuoles • Plastids (chloroplast) |
|

