![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell |
The smallest unit of matter that can carry out all the processes of life |
|
|
Characteristics of Life |
-Energy use -Homeostasis -Growth and development -Reproduction -Organization -Composed of cells |
|
|
Cell Theory |
-All living organisms are made of cells -Cells are the basic unit of structure and function -Cells only come from pre-existing cells |
|
|
Prokaryotic Cells |
-Oldest type of cell (3.5 billion years old) -Very small in size -Lack membrane-bound organelles -No nucleus (DNA concentrated in nucleoid region) -Bacteria, Archaea |
|
|
Eukaryotic Cells |
-More recent and complex (2.5 billion years old) -Relatively large (10x larger than prokaryotics) -Have membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus -Major types: Animal cells, Plant cells, Fungi, Protists (amoeba |
|
|
Why Cells Are Small |
-Smaller cells have a larger surface area-to-volume ratio -Take in nutrients and distribute them throughout the cell -Get rid of wastes faster |
|
|
Organelles |
-Nucleus and nucleolus -Chloroplast and chlorophyll -Mitochondria -Vacuole and lysosomes -Cilia and flagella -Golgi apparatus -Endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes -Cytoskeleton -Cell membrane and cell wall |
|
|
Nucleus and Nucleolus |
-Nucleus is the central part of the cell that controls all functions (found in eukaryotic cells) -Nucleolus is inside the nucleus and the site of ribosome synthesis |
|
|
Chloroplast and Chlorophyll |
-Only in plant cells -Contains a green pigment that absorbs light and converts it into energy -Produces energy, amino acids and lipid components -Chlorophyll causes photosynthesis -Makes plants green -Like a solar panel |
|
|
Mitochondria |
-Powerhouse 1. Shaped to maximize productivity2. Like skin 3. Folds over and creates layers (cristae) 4. 4 parts 5. Breaks nutrients down into energy 6. Keeps cells energy 7. Found in most eukaryotic cells |
|
|
Vacuole and Lysosomes |
1. Vacuoles are large membrane bound sacks that store undigested nutrients
|
|
|
Cilia and Flagella |
1. Made of proteins
|
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
1. An organelle that packages molecules for storage and to send out of the cell.
|
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum and Ribosomes |
1. Can be smooth or rough (ribosomes)
2. Rough ER makes proteins with ribosomes 3. Smooth ER transports lipids and proteins |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
1. Intercellular proteins that help with shape, support and movement
|
|
|
Cell Membrane and Cell Wall |
1. Creates a flexible, porous container for the cell
|
|
|
Cell Membrane Structure |
-Phospholipid bilayer -Thin, selectively permeable -Described as fluid mosaic model?????? -Components: phospholipids, proteins, carbohydrates
|
|
|
Phospholipids |
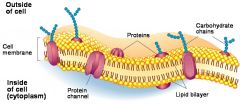
-Main component of the cell membrane -Hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails form cell membrane |
|
|
Proteins |
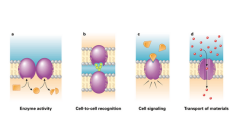
-Embedded in phospholipid layer -For transport, cell recognition, cell signaling and enzymes
|
|
|
Carbohydrates |
-Attached to phospholipids or embedded proteins -For cell recognition and cell adhesion |
|
|
Passive Transport |
-The movement of molecules from a high to low concentration across a membrane without the use of energy (ATP). Also known as movement down the concentration gradient. (simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis) |
|
|
Simple Diffusion |
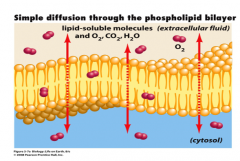
-The movement of particles down the concentration gradient across a membrane (small molecules such as CO2 and O2) |
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion |
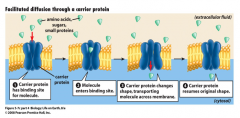
-The passage of large or charged molecules down a concentration gradient through a carrier protein (such as sugars) |
|
|
Osmosis |
-The passage of water from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration |
|
|
Isotonic |
-Concentration of solute of solution outside of the cell = concentration of solute inside of the cells |
|
|
Hypertonic |
-Concentration of solute of solution outside of the cell is HIGHER than the concentration of solute inside the cells |
|
|
Hypotonic |
-Concentration of solute of solution outside of the cell is LOWER than the concentration of solute inside the cells |
|
|
Active Transport |
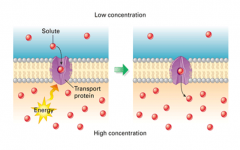
-The movement of molecules or ions from a high to a low concentration across a membrane that requires the use of energy (ATP). Also known as movement against the concentration gradient. |
|
|
Endocytosis |
-The movement of large molecules into the cell |
|
|
Exocytosis |
-The movement of large molecules out of the cell |

