![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell membrane |
Phospholipid bilayer, regulates passage of molecules |
|
|
Smooth ER |
No ribosome, intracellular transport, synthesizes lipids and detoxifies alcohol and drugs |
|
|
Rough ER |
Studded with ribosome, intracellular transport, protein synthesis |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Made of protein, proteins are synthesized at the ribosomes |
|
|
Golgi apparatus |
Not attached to nucleus, processes and packages substances produced by cell, produces vesicles and lysosomes |
|
|
Vesicles |
Stores and transports materials |
|
|
Lysosomes |
Contains digestive enzymes used for intracellular digestion, common in white blood cells |
|
|
Mitochondria |
Involved in cellular respiration |
|
|
Nucleus |
Controls cellular activities, contains chromosomes and DNA |
|
|
Nucleolus |
In nucleus, involved in production of RNA |
|
|
Nuclear envelope |
Membrane containing pores surrounding nucleus, pores allow mRNA to leave nucleus |
|
|
Chromosomes |
Made of DNA and protein, contains all of cells genetic info |
|
|
Vacuole |
Membranous sac, stores substance usually water |
|
|
Cells unity&diversity |
All cells have same organelles but have different number of organelles depending on function |
|
|
Ensymbiotic hypothesis |
Organelles began as free standing bacteria then started living together in colonies |
|
|
Diffussion |
Small molecules diffuse through phospholipid bilayer eg oxygen |
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion of water through semi permeable membrane |
|
|
Hypnotic solution |

Solution with lower solute concentration moves IN to the cell |
|
|
Hypertonic solution |

Solution with great solute concentration moves OUT of cell |
|
|
Isotonic solution |
Same concentration, doesn't move in or out |
|
|
Carrier transport |
Uses protein carrier, 2 types |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion (transport) |
High->low concentration, no energy |
|
|
Active transport |
Low to high concentration, requires energy |
|
|
Exocytosis/endocytosis |
Ingestion of large molecules by vesicles |
|
|
Metabolism |
Sum of all chemical reactions in body |
|
|
Enzymes |
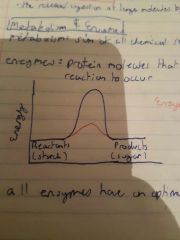
Protein molecules that lower energy required for reaction to occur, all enzymes have optimum Ph |
|
|
Lock and key model |
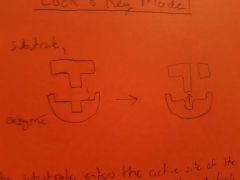
Substrate enters active site then enzyme slightly Changes shape and substrate leaves, heat/Ph will change shape of active site |
|
|
Optimum |
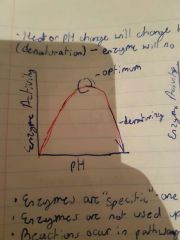
Optimum Ph level, top of graph |
|
|
Denaturing |
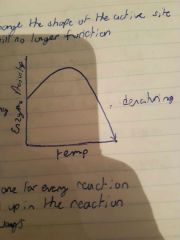
When enzyme will no longer function |
|
|
Enzyme facts |
They are specific - one for every reaction, not used up in reaction, reactions occur in pathways |
|
|
Chromosome |

Made of DNA and protein, found in nucleus |
|
|
Gene |
Segment of chromosome that determines a trait |
|
|
4 bases |
Guanine, cytosine, adenine, thymine |
|
|
Nucleotide |

Both DNA and rna are made of nucleotides, molecular complex made of sugar, phosphate, and a base |
|
|
Structure of DNA |
-chain of nucleotides join together -get a sugar-phosphate backbone -complimentary base pairing -Double strand twists to form double helix (stands held together by hydrogen bonds |
|
|
DNA |
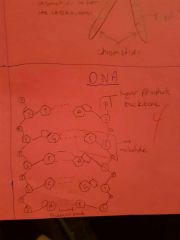
Contains genetic information necessary for life and growth. Controls cells and replicates. Replication is necessary so every cell has dna |
|
|
Watson and Crick |
Tried to figure out why dna twisted but instead figured out base pairing. |
|
|
Difference between prokaryotic and eukarytic cells |
Eukarytic cells have a nucleus and organelles prokaryotic does not and only has ribosomes |

