![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
β-Lactams
|
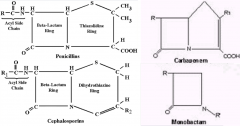
Penicillins
Cephalosporins Carbapenems Monobactems |
|
|
β-Lactams; M.O.A
|
Binds to penicillin binding protein (PBP)
-> Inhibits transpeptidation -> Inhibits cross linking |
|
|
β-Lactams and Other Drug Combinations
|
Synergism; β-Lactams + Aminoglycosides
Antagonism; β-Lactams + Tetracyclines |
|
|
Penicillin: Resistance
|
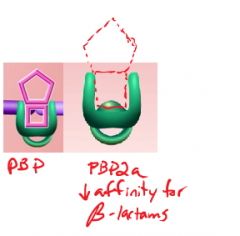
β-lactamase production
Structural changes in penicillin binding proteins (PBP) -> MRSA; has an additional PBP (PBP2a) |
|
|
Penicillin: Elimination
|
Excreted through the kidneys
Pair with probenecid to increase penicillin's time in circulation (competition with secretion mechanism) |
|
|
Penicillin: Adverse Drug Reactions
|
Hypersensitivity; can range from rash to bronchospasm to anaphylactic shock
|
|
|
Penicillin: Classification
|
Natural
Anti-staphylococcal (Oxi) Extended spectrum (Amino) Anti-pseudomonal |
|
|
Natural Penicillins
|
Penicillin G and V
All β-lactamase sensitive Penicillin G: -Strep pyogenes (those not making β-lactamases) -Treponema pallidum (Syphilis) |
|
|
Anti-staphylococcal Penicillin (Oxi)
|
OXACILLIN, ClOXACILLIN, DiclOXACILLIN and Nafcillin
All β-lactamase resistant G+ cocci: Staphylococcus, except MRSA (use Vancomycin) |
|
|
Extended Spectrum Penicillin (Amino)
|
AMoxicillin, AMpicillin
All β-lactamase sensitive More water soluble and pass through porin channels in the cell walls of some G(-) bacteria Treat e. coli |
|
|
Anti-pseudomonal Penicillin
|
Carbenicillin, Piperacillin, Ticarcillin
Mnemonic: Pseudo (fake) Car Pipe(s) Tic (me off) All β-lactamase sensitive |
|
|
β-lactamase Inhibitor Combinations
|
β-lactam + β-lactamase inhibitor
Ampicillin + Sulbactam Amoxicillin + Clavulanic Acid Piperacillin + Tazobactam Ticarcillin + Clavulanic Acid |
|
|
Cephalosporins
|
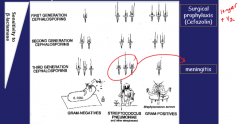
Cef-, Ceph-
Change in spectrum between generations |
|
|
Cephalosporins: Indications
|
3rd generation (Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime and Ceftazidime) cross blood brain barrier -> treat meningitis
-most common causes of bacterial meningitis (NHS) Neisseria meningitidis (young adults) Haemophilus influenza B (toddlers) Strep pneumoniae (elderly) Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
|
|
Cephalosporin: NMTT
|
PMT; cefoPerazone, cefaMandole, cefoTetan
Interfere with vit. K synthesis - prolonged bleeding Interferes with acetaldehyde dehydrogenase -> increase acetaldehyde -> hangover |
|
|
Carbapenems/Monobactams
|
Broadest spectrum of β-lactams
Only Gram(-) rods Administer with cilastatin, inhibits renal enzyme that breaks the drug down to a toxic substance |
|
|
Non β-lactam Cell Wall Inhibitors
|
Vancomycin
Bacitracin |
|
|
Vancomycin: M.O.A
|
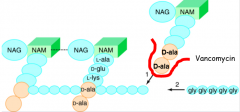
Bind to D-ala-D-ala nuramyl pentapeptide, inhibits transglycosylation and interferes with cross linking of bacterial cell wall
|
|
|
Vancomycin: Resistance
|
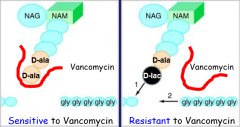
Due to replacement of D-ala by D-lactate
|
|
|
Vancomycin: Adverse Drug Reactions
|
-Red man syndrome
-Ototoxicity -Nephrotoxicity |
|
|
Cell Membrane Inhibitors
|
Daptomycin
Kills G(+) bacteria without lysis |

