![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Passive transport |
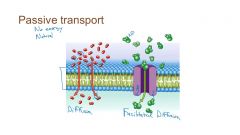
Diffusion of a solute through a channel or carrier protein that spans the lipid bilayer of a cell membrane. *No energy required Protein passively allows solute to follow gradient |
|
|
Diffusion |
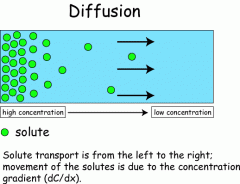
Movement of molecules move down the concentration gradient H ---> L Results in an even distribution |
|
|
Solvent |
The dissolving thing Ex: hot water |
|
|
Solute |
Something dissolved Ex: Kool aid |
|
|
Hypertonic Solution
|
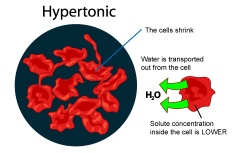
In cells, a solution in which the concentration of dissolved materials is higher in the solution surrounding the cell than the concentration inside the cell, which will shrink as water leaves the cell by osmosis
|
|
|
Active Transport
|
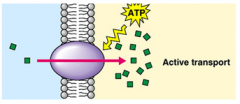
Process requiring energy by which cells move materials against the concentration gradient
|
|
|
Isotonic Solution
|
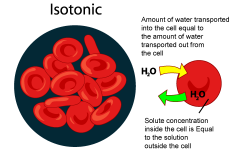
Solution in cells which dissolved materials and water occur in the same concentration as inside the cell.
|
|
|
Channel Proteins
|
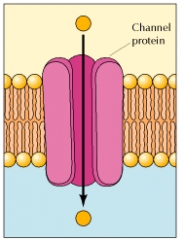
These line a water-filled pore in the membrane so water-soluble molecules can easily pass through.
|
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion
|
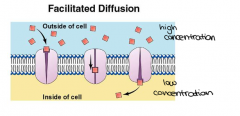
Passive transport of materials such as sugars and amino acids, across the plasma membrane by way of transport proteins.
|
|
|
Ion
|
An atom or molecule that gains electrons and carries a positive electric charge or loses electrons and has a negative electric charge.
|
|
|
Phospholipids
|
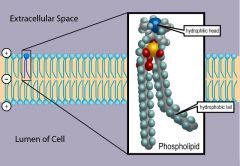
Membrane lipid having an organic section attached to a phosphate group; plasma membranes are formed of a bilayer of phospholipids with embedded proteins.
|
|
|
Osmosis
|
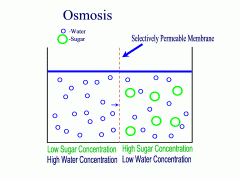
Diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane depending on the concentration of solutes on either side of the membrane.
|
|
|
Endocytosis |
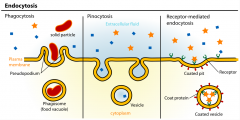
Active transport process by which larger particles enter a cell Endo= in |
|
|
Glycoprotein
|
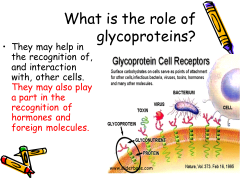
any of a class of proteins that have carbohydrate groups attached to the polypeptide chain. Also called glycopeptide
|
|
|
ATP
|
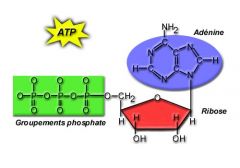
Adenosine, triphosphate; energy storing molecule that serves as the cells "energy currency"; stored energy of glucose is used to attach phosphate groups to ADP to form ATP
|
|
|
Homeostasis
|
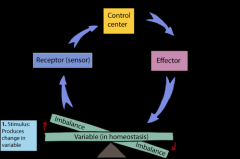
Equilibrium of an organisms internal environment that remains suitable conditions for life.Ex:A human sweating to remain at a steady body temperature
|
|
|
Manipulated variable
|
The variable that is changed Ex amount of water given to plant |
|
|
Responding variable
|
Responding to the manipulated variable Ex how much the plant grows |
|
|
Controlled variable
|
Stays the same Ex amount of sunlight and soil |
|
|
Exocytosis |
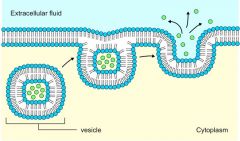
Active transport process by which materials are expelled or stretched from a cell Exo= out |
|
|
Pinocytosis |
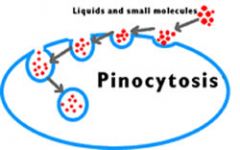
a process by which liquid droplets are ingested by living cells. Pinocytosis is one type of endocytosis |
|
|
Cell membrane
|
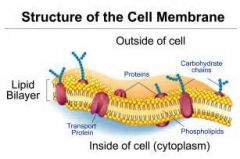
The cell membrane is a thin semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. Its function is to protect the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell, and keeping other substances out.
|
|
|
Hydrolysis
|
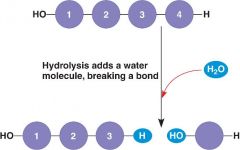
the chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water
|
|
|
ADP
|
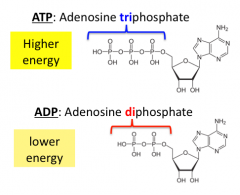
Adenosine diphosphate; molecule occurring from the breaking off of a phosphate group from ATP, resulting in a release of energy to do biological work.
|
|
|
Lipid Bilayer
|
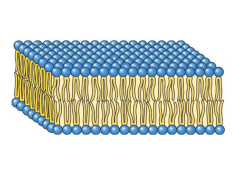
The lipid bilayer is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules.
|
|
|
Hypotonic
|
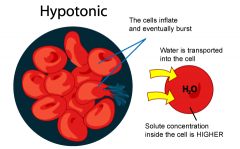
Solution in which the concentration of dissolved materials is lower in the solution surrounding the cell than the concentration inside the cell, which will swell and possibly burst as water enters the cell by osmosis
|
|
|
Negative control
|
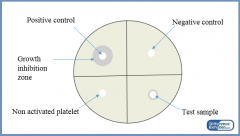
The negative control group is a group in which no response is expected
|
|
|
Cholesterol
|
A waxy type of lipid, a substance that is insoluble in water, like oil or fat.
|
|
|
Concentration gradient
|
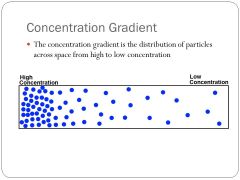
the graduated difference in concentration of a solute within a solution
|
|
|
Osmometer
|
osmotic strength of a solution "a process by which molecules of a solvent tend to pass through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one" (osmotic def) |
|
|
Diffusion factors
|

Factors that influence rate of diffusion
|
|
|
Osmotic Pressure
|
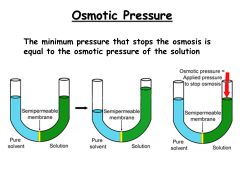
the pressure that would have to be applied to a pure solvent to prevent it from passing into a given solution by osmosis, often used to express the concentration of the solution.
|
|
|
Volume
|
the amount of space that a substance or object occupies, or that is enclosed within a container
|
|
|
Energy
|
Ability to do work or move things; powers of life processes |
|
|
Glucose
|
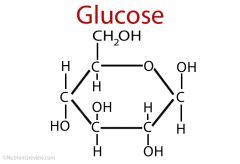
simple sugar
|
|
|
Molecule
|
A group of atoms held together by covalent bonds.
|
|
|
Potassium
|
natural salt that is important for the heart, muscles, and nerves.
|
|
|
Phagocytosis |
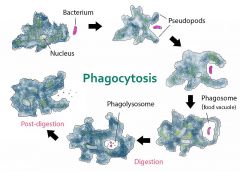
the ingestion of bacteria or other material by phagocytes and amoeboid protozoans Form of endocytosis takes solid things in |
|
|
Sodium
|
Salt
|
|
|
H2O2
|
used as an oxidizer.
(undergo or cause to undergo a reaction in which electrons are lost to another species.) |
|
|
Cell
|
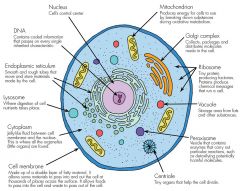
Building block of both unicellular and multicellular organisms
|
|
|
Equilibrium
|
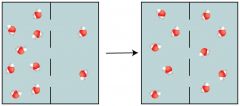
a state in which opposing forces or influences are balanced.
|
|
|
Plasmolysis
|
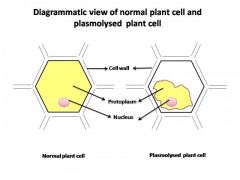
process resulting from a drop of turgor pressure as a result of water loss from a cell causing the plasma membrane to shrink away from the cell wall
|
|
|
Turgor
|
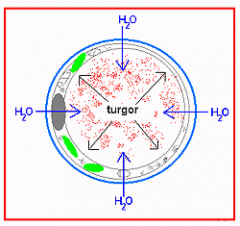
internal pressure of a cell due to water held there by osmotic pressure
|
|
|
Permeability
|
the state or quality of a material or membrane that causes it to allow liquids or gases to pass through it.
|
|
|
Random
|
Randomness is the lack of pattern or predictability in events. A random sequence of events, symbols or steps has no order and does not follow an intelligible pattern or combination.
|
|
|
Ion Pump
|
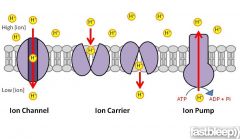
membranal complex of proteins that is capable of transporting ions against a concentration Gradient using the energy from atp.
|
|
|
Catalase
|
An enzyme that separates hydrogen peroxidevxide into water and oxygen
|

