![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
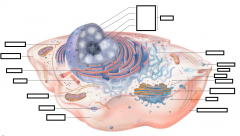
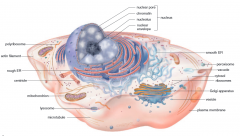
mitochondrion |
cellular respiration, glucose + oxygen > co2 + h2o + atp |
|
|
lysosome
|
intracellular digestion |
|
|
vacuole and vesicle
|
storage and transport of substances
|
|
|
golgi apparatus
|
processing/ distribution of proteins and lipids
|
|
|
peroxisome
|
various metabolic tasks
|
|
|
ribosome
|
helps in protein synthesis in the cell
|
|
|
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
|
lipid synthesis in some cells. can also store lipids and create steroids
|
|
|
rough endoplasmic reticulum
|
helps in protein synthesis in the cell
|
|
|
nuclear envelope
|
double layered membrane that seperates the nucleolus from the cytoplasm
|
|
|
chromatin
|
dna and protein that form chromosomes
|
|
|
nuclear pore
|
lets molecules and ions in and out of the nucleus
|
|
|
nucleolus
|
produces nucleotides
|
|
|
polyribosomes
|
ribosomes connected to messenger rna that synthesizes protein
|
|
|
centriole
|
helps in cell division
|
|
|
microtubule
|
helps support and shape the cell
|
|
|
cytoplasm
|
fluid that fills the cell and gives it shape
|
|
|
plasma membrane
|
defines cell boundaries and lets molecules in and out of cell
|
|
|
chromosome
|
protein and genetic materials/ dna
|
|
|
nucleus |
helps control movement, digestion, and reproduction of cell |
|
|
what percent of total body weight is water? |
60-70% |
|
|
what type of molecule is water and why? |
it's a polar molecule because oxygen has a negative charge and hydrogen has a positive charge |
|
|
what are hydrogen bonds?
|
it's a bond that connects a positive hydrogen to a negative atom
|
|
|
ions and molecules that interact with water are said to be? |
hydrophilic |
|
|
nonionized and nonpolar molecules that do not interact with water are said to be? |
hydrophobic |
|
|
what percent of blood is water? |
92% |
|
|
how does water protect us from rapid temperature changes? |
it takes a calorie of heat energy to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1°C which is double the amount required for other liquids and it holds onto heat so its temperature falls slowly |
|
|
how does water keep you cool? |
when you sweat the water takes away body heat by using it to evaporate itself |
|
|
NaCl + H2O = solution which one is the solute and which one is the solvent? |
NaCl is the solute and H2O is the solvent |
|
|
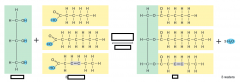
what do organic molecules always contain |
carbon and hydrogen |
|

|
|
|
|
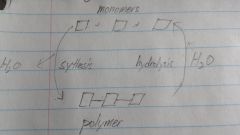
list 4 polymers and 4 monomers |
polymer: carbohydrate, protein, nucleic acid, lipids
monomer: monosacccharide, amino acid, nucleotide, fatty acid |
|
|
list 3 monosaccharides and 3 disaccharides |
monosaccharide: glucose, fructose, galactose
disaccharide: maltose, sucrose, lactose |
|
|
list 3 polysaccharides |
starch, glycogen, cellulose |
|
|
|
|
|
what is the difference between a saturated and unsaturated molecule |
a unsaturated has a double bond between 2 carbon atoms |
|

|

|
|
|
what are the two types of nucleic acids |
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
RNA (ribonucleic acid) |
|
|
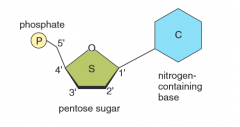
|
|
|
|
|
|
what is the empirical formula of a carbohydrate |
CnH2nOn |
|
|
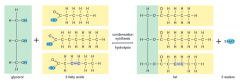
what is the function of phospholipids |
they form the phosolipid bilayer of the plasma membrane and make it selectively permeable to solutes such as proteins, ions and water |
|
|
what is the function of steroids |
it can act as a hormone,regulate carbohydrate metabolism, and maintain blood pressure |
|
|
what type of bond does hydrogen and oxygen have in H2O |
they have a covalent bond |
|
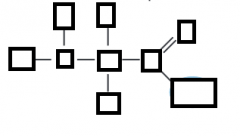
name the parts of the amino acid
|
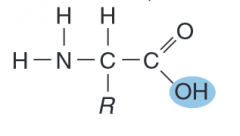
|
|
name the parts of the fatty acid
|
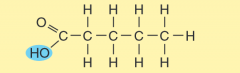
|
|
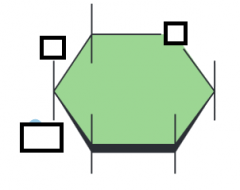
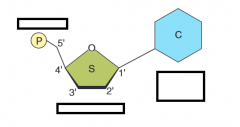
name the parts of the glucose molecule
|
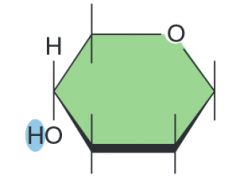
|
|
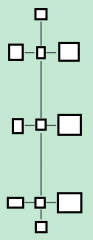
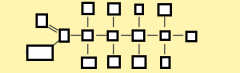
name the part of the glycerol molecule
|
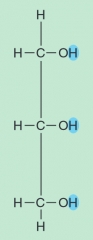
|
|
|
what are buffers and how do they work
|
a buffer is a chemical or a combination of chemicals that keeps pH within normal limits. buffers resist pH changes because they can take up excess hydrogenions (H) or hydroxide ions (OH).
|
|
|
give an example of a buffer
|
our blood contains large amounts of carbonic acid, a weak acid, and bicarbonate, a base. together they help maintain the bloods pH at 7.4. if blood pH falls below 6.8 or rises above 7.8, one can become sick or die. the bicarbonate neutralizes excess acids in the blood while the carbonic acid neutralizes excess bases.
|
|
|
what is the macromolecule when a bunch of the same monomers join together
|
polymer
|
|
|
what is the function of carbohydrates
|
they provide energy for your body
|
|
|
what is the function of lipids
|
they store energy
|
|
|
what is the function of proteins
|
-keratin which makes up hair and nails
-collagen, which lends support to ligaments, tendons, and skin -act as hormomes -proteinsactin and myosin account for the movement of cells and the ability of our muscles to contract -hemoglobin transports oxygen -antibodies in blood and other body fluids are proteins that combine with foreign substances, preventing them from destroying cells and upsetting homeostasis -form channels that allow substances to enter and exit -carriers that transport mole-cules into and out of the cell -enzymes |
|
|
what is the function of nucleic acids
|
carry genetic information in the cell
|

