![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of organisms are Prokaryotic? |
Bacteria |
|
|
What type of organisms are Eukaryotic? |
Plants & Animals |
|
|
What 5 organelles do all cells have? |
Cell Membrane, Ribosomes, Cytoskeleton, DNA, and Cytoplasm |
|
|
What is the function of the Nucleus? |
Contains DNA and directs cellular activities |
|
|
What’s the function of the Cell Membrane? |
Protects the cell from its surroundings |
|
|
What is the function of Ribosomes? |
Creates proteins and repairs damage |
|
|
What is the function of the cytoskeleton? |
Gives the cell it’s shape and support |
|
|
What is the function of the Cell Wall? |
Provides protection and structure |
|
|
What is the function of the Endoplasmic Reticulum? |
Transports things to the Golgi Body |
|
|
What is the function of the Lysosomes? |
Removes waste |
|
|
What is the function for the Mitochondria? |
Produces energy |
|
|
Central Vacuole |
Stores water and nutrients |
|
|
Central Vacuole |
Stores water and nutrients |
|
|
What is the function of DNA? |
Long-term storage of information |
|
|
What is the function of the Golgi Apparatus? |
Modifying, sorting, and packaging of protons |
|
|
What is the function of the Chloroplast? |
Work to concert sunlight into energy |
|
|
What is the smallest unit of life? |
A cell |
|
|
Where is the Nucleus located? |
Center of cell |
|
|
Where is the location of the Cell Membrane? |
Usually the outest layer (except in plants) |
|
|
Where is the Ribosome located? |
In the cytoplasm and sometimes attached to the Endoplasmic Reticulum |
|
|
Where is the Cytoskeleton located? |
Anchored to the Cell Membrane |
|
|
Where is the Endoplasmic Reticulum located? |
Usually next to the Nucleus |
|
|
Where is the Lysosomes located? |
In the cytoplasm |
|
|
Where is the Mitochondria located? |
Near the Nucleus |
|
|
Where is the Central Vacuole located? |
In cytoplasm |
|
|
Where is the DNA located? |
The center of cell (prokaryotic) In Nucleus (eukaryotic) |
|
|
Where is the Golgi Apparatus located? |
Near the rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
|
|
Where is the Chloroplast located? |
Corner of the plant cell |
|
|
What types of cells are Mitochondria found in? |
Cells that uses A LOT of energy |
|
|
What is found inside the nucleus? |
DNA |
|
|
Concentration Group |
A difference in the concentrations from one place to another |
|
|
Passive Transport |
The movement of molecules over the Cell Membrane from high to low concentration without the use of energy |
|
|
Diffusion |
Movement of a substance from an array of high concentration to an area of low concentration. DOES NOT USE ENERGY!!! |
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion |
Uses proties to transport molecules from high to low concentration. Form of passive transport and DOES NOT USE ENERGY |
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion if water through a selectively preamble membrane |
|
|
Hypertonic Solution |
(has more salt than water) compare to another solution. causes cell to shrivel |
|
|
Hypotonic Solution |
(more water then salt) Causes cell to bloat and explode |
|
|
Isotonic Solution |
(equilibrium) equal amount of salt to water. Water stays in place and cells stay normal |
|
|
Active Transport |
Moves molecules from low to high concentration (against the concentration gradient) USES ENERGY |
|
|
What cellular movement are a form of Active Transport? |
Requires Energy Osmosis Endocytosis Exocytosis Sodium-Potassium Pump Low to High Concentration |
|
|
What cellular movement uses BOTH Active Transport and Passive Transport? |
Carrier Proteins |
|
|
What cellular movement uses Passive Transport? |
Doesn’t Require Energy Diffusion High to Low Concentration Facilitated Diffusion |
|
|
Endocytosis |
(to enter the cell) The movement of molecules into the cell |
|
|
Exocytosis |
(to exit the cell) The vesicle serves as a Transport compartment that ships the protein out of the cell |
|
|
What does it mean when the cell membrane is Selectively Preamble |
Means that it’s very picky on what it allows into and out of the cell |
|
|
How do cells that are too large move through the cell membrane to get into it out of the cell? |
Facilitated Diffusion (ex glucose uses Facilitated Diffusion) |
|
|
Compare and Contrast Facilitated Diffusion and Active Transport |
Facilitated Diffusion- No energy. High to Low Concentration Both- Uses carrier proteins Active Transport- Uses energy. Low to High Concentration |
|
|
What are 3 different types of transport proteins and what kind of transport do they help with? |
Protein Pump, Transport Proteins, Cartier Proteins; All are Active Transport |
|
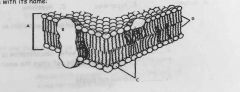
Label The Parts of the Cell Membrane |
A. Lipid Bilayer B. Transport Proteins C. Polar Heads (Lipids) D. Non Polar Tails |
|
|
List the 5 Functions of the Cell or Plasma Membrane |
1. Regulate going in&out of cell 2. Protective barrier 3. Cell recognition 4. Contains cytoplasm 5. Anchoring sites for Cytoskeleton |
|
|
What acts as a passageway in the cell membrane for ions to get through the membrane? |
Ion Channels |
|
|
What cell transports use Channel Proteins? |
Facilitated Diffusion (with glucose crossing membrane AND with ions crossing the membrane) |
|
|
What type of Cell Transport idea the Vesicle? |
Endocytosis Exocytosis |
|
|
What types of Cell Transport need no help? |
Diffusion Osmosis |
|
|
What does a Prokaryotic Cell consist of? |
Pili, Ribosome, Flagella, Cytoplasm, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, DNA |
|
|
What does a plant cell consist of? |
Cell Wall, Mitochondria, Nucleolus, Cell Membrane, Golgi Apparatus, Central Vacuole, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Chloroplast, Ribosome, Nucleus, Cytoplasm |
|
|
What does and Animal Cell consist of? |
Endoplasmic Reticulum, Vacuole, Lysosomes, Cytoplasm, Cell Membrane, Golgi Apparatus, Nucleolus, Nucleus, Mitochondria |

