![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
State two features of a nucleus membrane |
It's a double membrane bound organelle which has nuclear pores. |
|
|
|
Describe the function of the nuclear pores. |
- it allows exchange of various material e.g. RNA - it transport nutrients through the pores to the cyctoplasm |
2 points |
|
|
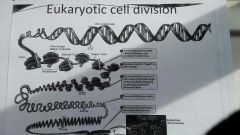
What are chromosmomes made out of? |
Loops and coils of Chromatin (DNA + protein histones) |
|
|
|
What is the function of the protein in histones? |
they enable the DNA to form nucleosomes (which are the bumps on a DNA molecule.) |
|
|
|
What is the nucleoli composed of? |
Parts of chromatin DNA along with RNA and proteins. |
|
|
|
What is the function of the nucleolus? |
- Ribosome subunits are built - Ribosome rRNA is manufactured. |
|
|
|
What is the nucleoplasm? |
its a solution containing dissolved materials. |
|
|
|
How does material enter the nucleoplasm? |
Material enters by going through the nuclear pore. |
|
|
|
Red blood cells have nucleus. TRUE OR FALSE |
FALSE |
|
|
|
State the number of chromosomes in a Eukaryotic cell nuclei and whether they are identical or non identical from their parent cell. |
The nuclei has diploid number of chromosomes and they are identical (1 set from mother and father). |
|
|
|
State a characteristics of a diploid chromosome and give examples. (other than identical) |
- they have 2 copies of homologous chromosome which are smililar in... - shape, size and gene (hereditary material) |
|
|
|
What is the number of chromsome in each cell after meiotic division? |
Haploid |
|
|
|
What is the number of chromosomes in gametes? |
Haploid (one copy of each chromosome) |
|
|
|
What is the last stage of gamete formation |
Meiotic division |
|
|
|
What division occurs for organ developement? |
Mitotic division |
|
|
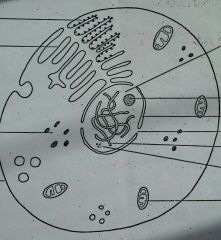
Label this diagram |
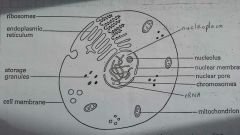
|
|
|
|
Why does cell division take place? |
- Cell division for growth (cell number increase .:. increase in size - cell replacement (e.g. small cut) - Reproduction for species continuation |
3 points |
|
|
What cell function are controlled by the nucleus? |
Metabolism and protein synthesis |
|
|
|
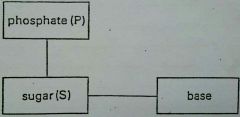
Whats the difference between a nucleoside and nucleotide? |
Nucleoside: deoxyribose sugar (5C pentose sugar) + organic, N-containing base (heterocyclic base) Nucleotide also contains a phosphate group unlike the nucleoside. |
|
|
|
The DNA is a polymeric molecule (polymer), what does this mean? |
It means that the DNA is made up of many repeating units of nucleotides. |
|
|
|
What type of bases are adenine and guanine? |
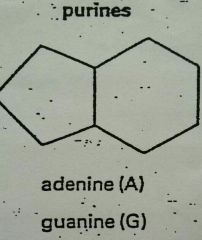
|
|
|
|
What type of bases are cytosine and thymine? |
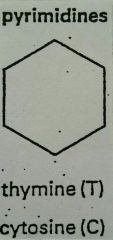
|
|
|
|
What is the structure of a double helix DNA? |
- each chain has an alternating sugar-phosphate backbone (rungs of ladder). - each base is attached to the backbone and both chains are held together by specific base paring. |

|
|
|
State the base pairs along with the hydrogen bonds formed |
A = T ... 2H bonds C ≡ G ... 3H bonds |
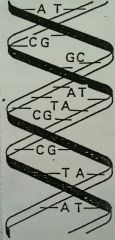
|
|
|
What are the differences between DNA and RNA? |
RNA - has single strand - T is replaced with Uracil - is smaller than DNA - has lower molecular weight than DNA |
4 points |

