![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Selectivley permeable |
Lets selected substances through |
|
|
|
Permeable |
Allows material through |
|
|
|
Non-permeable |
Doesnt allow substances through. |
|
|
|
Diffusion |
Dispersion of particles from high to low concentration. |
|
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion of water through a membrane. |
|
|
|
Active Transport |
Movement of particles from low to high concentration. Requires input enegy. |
|
|
|
Concentration Gradient |
High Concentration <-------> Low Concentration |
|
|
|
Isotonic |
Both solutions have reached the same concentrations, there is no net flow. |
|
|
|
Hypertonic |
The solution with higher concentration of solute, lower concentration of water. Water flows into this solution. |
|
|
|
Hypotonic |
The solution has a lower concentration of solute, higher concentration of water. Water flows out of this solution. |
|
|
|
Osmotic pressure |
Caused by a difference in concentrations within two solutions. |
|
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion |
Proteins dictate which particles can diffuse through a membrane. High to low concentration. |
|
|
|
Endocytosis |
Vesicle gets rid of wastes by merging with the membrane. |
|
|
|
Exocytosis |
Vesicle collects substances and transports them throughout the cell. |
|
|
|
Phagocytosis |
Exocytosis, collection of solid particulates. |
"Devouring cell action" |
|
|
Pinocytosis |
Exocytosis, collection of liquids and dissolved nutrients. |
|
|
|
Receptor Mediated Endocytosis |
Specialized receptors allow small amount of a specified substance in. |
|
|
|
Brownian Motion |
Erratic, constant movement of particles at all times. |
|
|
|
Hydrophillic (Polar) |
Attuned to water. |
|
|
|
Hydrophobic (Non-polar) |
Doesnt combine with water. |
|
|
|
Phospholipid Bilayer |
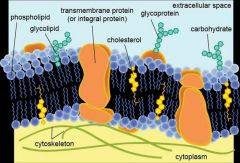
|
|
|
|
Phospholipid |
Hydrophillic phosphorus head Hydrophobic lipid tail |
|
|
|
Integral Protein |
Protein that spans through the entire bilayer |
|
|
|
Peripheral Protein |
Protein residing on either side of the bilayer |
|
|
|
Channel Protein |
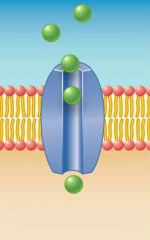
Allows diffusion of certain substances. |
|
|
|
Protein pump |
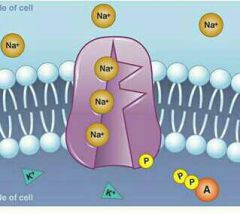
Uses ATP to collect and throw out certain substances. |
|
|
|
Carrier Proteins |
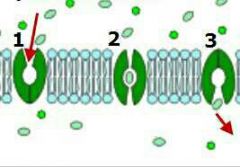
Allows diffusion of specific substances. |
|
|
|
Enzyme Proteins |
Spead up chemical reactions in the cell. |
|
|
|
Horomone Receptor Proteins |
Recieve hormones in the blood stream. |
|
|
|
Attachment Proteins |
Can link cells to other cells. Connect cell membrane to it's cytoplasm. |
|
|
|
Glycoprotein |
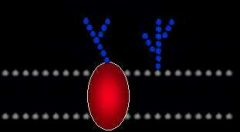
Glucose chain attached to a protein. Used for communication. |
|
|
|
Glycolipid |
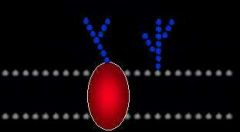
Glucose chain attached to lipid. Used to communicate. |
|
|
|
Cholestreal |
Helps cell membrane's structural integrity and fluidity. |
|

