![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why do cells need energy? |
Undergo mitosis Maintain homeostasis Make energy Active Transport Nerve Transmission Muscle contraction Bioluminescence |
|
|
What is metabolism? |
All of the chemical reactions that happen in an organismtwov |
|
|
Two type of metabolism? |
Catabolic - releases energy by breaking down larger molecules Anabolic - uses energy created by catabolic pathways to build larger molecules |
|
|
Example of catabolic reaction? |
Cellular respiration - catabolic patch say in which organic molecules are broken down to release energy |
|
|
What is the equation of cellular respiration? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What are the two stages of cellular respiration? (First one) |
Glycolysis - Anaerobic Happens in cytoplasm Produces 2 ATP molecules |
|
|
Second stage of cellular respiration? |
Krebs Cycle - Aerobic Electron transport chain 34 ATP Happens in mitochondria For every cycle 1 ATP is made |
|
|
Example of anabolic reaction? |
Photosynthesis - Two stage anabolic pathway in which suns light energy is converted into chemical energy to be used by cell |
|
|
Example of anabolic reaction? |
Photosynthesis - Two stage anabolic pathway in which suns light energy is converted into chemical energy to be used by cell |
|
|
Equation for photosynthesis? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Metabolism is relationship of? |
Relationship of catabolic and anabolic pathways results in continuous energy within organisms |
|
|
Metabolism is relationship of? |
Relationship of catabolic and anabolic pathways results in continuous energy within organisms |
|
|
How do cells store energy and what is it made of? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Why the need for ATP? |
Light energy is not absorbed in plants quickly enough without ATP
In animals energy is used too quickly |
|
|
Why the need for ATP? |
Light energy is not absorbed in plants quickly enough without ATP
In animals energy is used too quickly |
|
|
ADP? ANP? Stands for? And made of? Energy is what? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Draw the ATP creation cycle? |
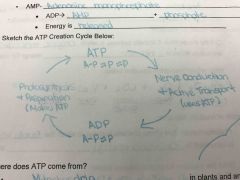
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Draw the ATP creation cycle? |
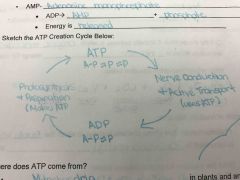
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Where does ATP come from? |
Mitochondria in plants and animals that break down food to glucose to make ATP energy |
|
|
Draw the ATP creation cycle? |
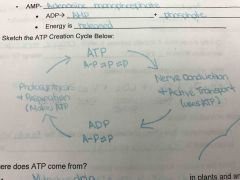
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Where does ATP come from? |
Mitochondria in plants and animals that break down food to glucose to make ATP energy
An animal (consumer) must eat a plant to get food (glucose)
|
|
|
Where does the food (glucose) come from? |
Photosynthesis in plants |
|
|
Photo? _____ Synthesis _____ What is it |
Photo = light Synthesis = to make The process in which plants use solar energy to create energy |
|
|
Photo? _____ Synthesis _____ What is it |
Photo = light Synthesis = to make The process in which plants use solar energy to create energy |
|
|
Plants use? To make? |
CO2 To make O2 |
|
|
Where does photosynthesis happen? And what does this organelle contain? |
Chloroplast Chlorophyll |
|
|
Describe the chloroplast |
Chloro = green Plast = plastid Contains chlorophyll which absorbs energy Has a double membrane made of phospholipids and proteins |
|
|
Thylakoid is the Grams is the Stroma is the |
Thylakoid is the membrane that absorb the suns energy Grana are the stacks of thylakoids Stroma is the fluid find in the chloroplast |
|
|
Equation for photosynthesis? |
6CO2 + 6H2O ---> C6H12O6 + 6O2 |
|
|
Where does cellular respiration take place? |
Mitochondria |
|
|
Folds inside mitochondria are? And how many layers |
Cristae Double layered |
|
|
What happens after Krebs cycle is oxygen is not present? |
Fermentation |
|
|
Describe fernentation |
Happens after Krebs cycle if oxygen isn't present In plants it's called alcoholic fermentation In animals it's called lactic acid |
|
|
Describe alcoholic fermentation |
End product is ethyl alcohol Used in brewing and baking (yeast) End product is glucose |
|
|
Describe lactic acid |
Accumulates in human muscle tissue End product is muscle fatigue Used to make pickles yogurt buttermilk and sauerkraut End product is glucose |
|
|
ATP YIELD BROKEN DOWN? Glycolysis - Krebs cycle - Electron Transport - Total = |
Glycolysis 2 Krebs 2 Electron 34 Total 38 |
|
|
All organisms require |
Energy |
|
|
Living organisms are divided into two groups? |
Autotrophs Heterotrophs |
|
|
Describe autotroph |
Auto = self Troph = feeder |
|
|
What happens in a photosynthesis reaction? |
Light energy is transferred to electrons in the chlorophyll
The chlorophyll molecules raise the energy level providing energy for the reaction to begin
Chlorophyll is the catalyst |
|
|
Describe heterotrophs |
Hetero = other Troph = feeding Animals are either herbivore or carnivores |
|
|
Give 2 examples of autotrophs |
Photosynthesis - green plants and algae
Chemosynthesis - energy is used from inorganic chemical reactions Ex some bacteria |
|
|
Give 5 examples of heterotrophs |
Fungi Parasites - lives off the host Saprophytes - live off dead bacteria Bacteria Animal |
|
|
Light dependent vs Calvin cycle? |
Light needs energy from sun to act as catalyst for reactions to happen
In Calvin it uses the NADPH made in light dependent to make glucose |
|
|
Where does the Calvin cycle happen? |
Stroma |
|
|
Where does light dependent happen? |
Thylakoid |
|
|
Summary of light dependent? |
Chlorophyll traps light energy and stored as potential chemical
Water splits 2H+ O-2
Adp to atp
O2 released |
|
|
Summary of Calvin cycle? |
Does not require light Fixation of carbon in carbohydrate
CO2 ---> 5 carbon sugar |
|
|
What is cell respiration? |
Chemical energy from glucose and other food molecules is released
Process where plants and animal release atp |
|
|
Where does energy come from? |
Sun - stored in chemical bonds of glucose
|
|
|
Photosynthesis releases/stores Respiration releases/stores |
Photosynthesis stores Respiration releases |

