![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A sex cell is |
A gamete |
|
|
What is mitosis |
Cell growth and repair, the cells cycle |
|
|
Interphase |
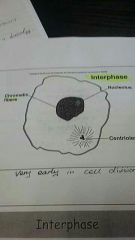
DNA replicates chromosomes are duplicated forming chromatin joined at the centre by a centomere |
|
|
Prophase |
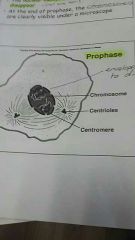
Centroles start forming spindle fibres (microtubules) and start to move apart. Nuclear membrane starts to breakdown. |
|
|
Metaphase |
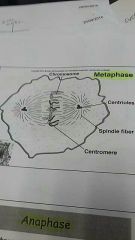
Spindles occupy most of cell. Centrioles are at the poles. Spindles attach to the centomere connecting the chromatids to the centrioles . Chromatids form a line across the cell |
|
|
Anaphase |
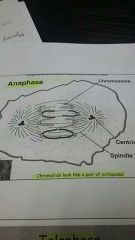
Centimeters break apart. Spindle fibres break apart and contract back towards the poles. Rapid phase.chromatids look like v or octopuses. |
|
|
Telophase |
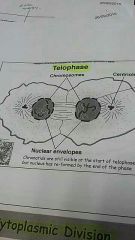
Spindles break down. Chromosomes lengthen. Membrane reappears. 2 nuclei are formed |
|
|
Remember mitosis |

|
|
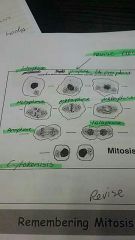
|
List them! |
|
|
Cytoplasmic division |
Cytokinesis. The cell separates, this phase overlaps the telophase |
|
|
Why do we need mitosis? |

|
|
|
Meiosis |
Cell division which produces gametes. Also known as reduction division because it produces four haploid cells from a diploid cell |
|
|
Gametes |
23 chromosomes and are either egg cells or sperm cells |
|
|
Fertilisation |
When two gametes come together to combine chromosomes making 46. These then duplicate . Chromosomes then pair up Swap sections of DNA There is now 2 lots of 46 chromosomes These split in miosis 1 to form 2 daughter cells with 46 chromosomes each. In meiosis 2 these daughter cells divide again to have 23 chromosomes |

