![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell cycle |
Produce 2 daughter cells idetical to parent cell |
|
|
phases of cell cycle |
1. Interphase 2. M phase |
|
|
Go phase |
Gap outside phase- nondiving resting cells |
|
|
Interphase |
cell growth G1 S G2 |
|
|
G1 |
Cell grows and proteins are synthesized
Most important checkpoint (depends on cell size) - decides if continue replication or go to Go |
|
|
S |
synthetic phase DNA are replicated and histone and nonhistone proteins are synthesized - results in duplication of chromosomes checkpoint - monitors quality of DNA strand - repair. Apoptosis if cannot be resolved. |
|
|
G2 |
Cell prepares to divide DNA examination |
|
|
M phase |
Mitosis segregation of replicated chromosomes, division of nucleus (karyokinesis) and division of cytoplasm (cytokinesis) |
|
|
checkpoints |
through the cycle serves as quality control - either stimulate cell division or stop |
|
|
stages of mitosis |
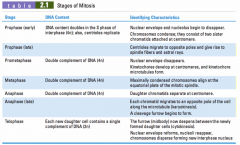
PPMAT |
|
|
stages of mitosis drawing |

|
|
|
Meiosis |
special form of cell division in germ cells chromosome # is reduce from diploid (2n) to haploid (n) |
|
|
stages of Meiosis |

|
|
|
Regulation of cell cycle |
depend mostly on the level of certain cellular proteins
|
|
|
Cyclin - Cdk complexes |
complex of proteins that regulate other proteins in the cell the cyclin determines what CDK will regulate if cyclin leaves then it will continue cell cycle if we want to stop cell cycle i freeze CDK |

