![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
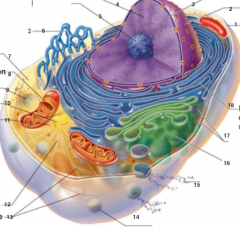
What is 1 pointing to? |
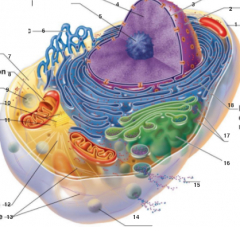
Plasma Membrane |
|
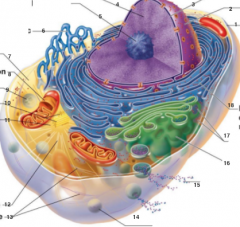
What is 2 pointing to? |
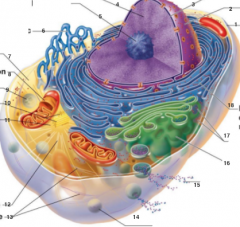
Nucleus |
|
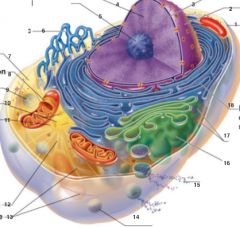
What is 3 pointing to? |
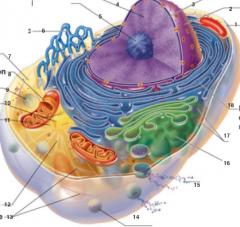
Nuclear Envelope |
|
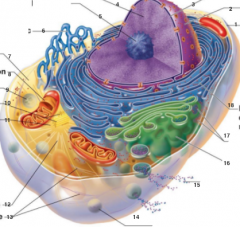
What is 4 pointing to? |
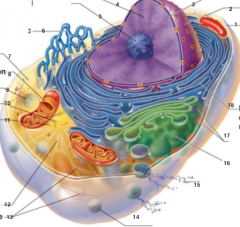
Chromatin |
|
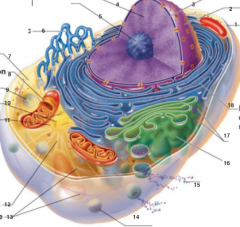
What is 5 pointing to? |
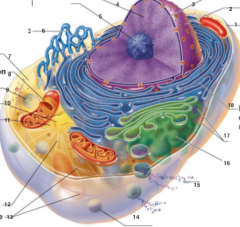
Nucleolus |
|
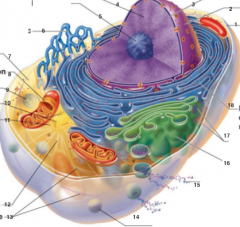
What is 6 pointing to? |
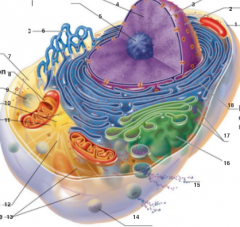
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum |
|
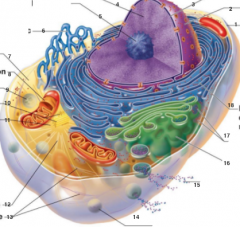
What is 7 pointing to? |
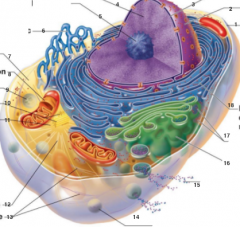
Cytosol |
|
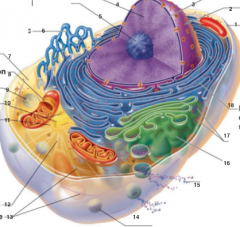
What is 8 pointing to? |
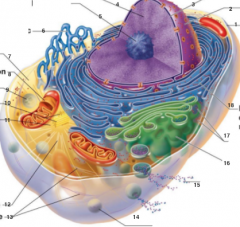
Mitochondrium |
|
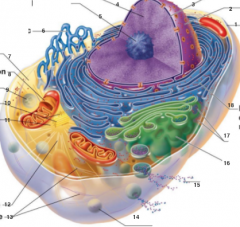
What is 9 pointing to? |
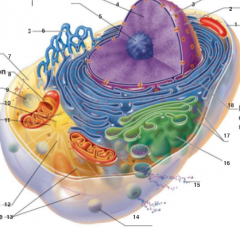
Lysosome |
|
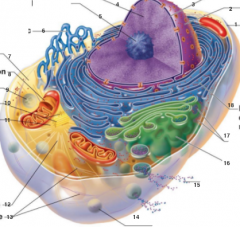
What is 10 pointing to? |
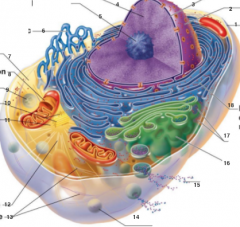
Centrioles |
|
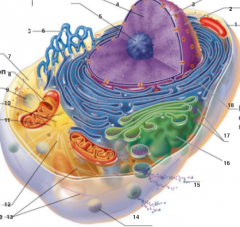
What is 11 pointing to? |
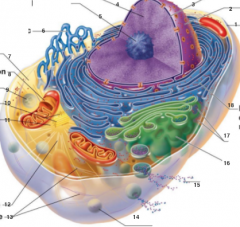
Centrosome matrix |
|
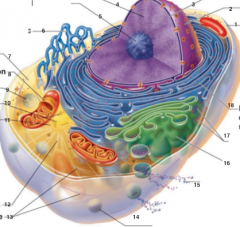
What is 12 pointing to? |
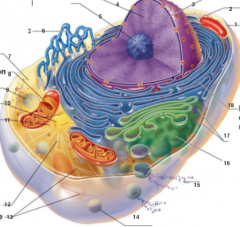
Microtubule |
|
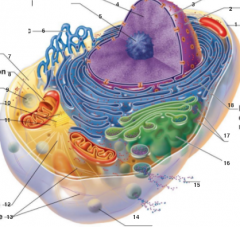
What is 13 pointing to? |
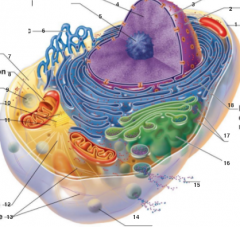
Intermediate filaments |
|
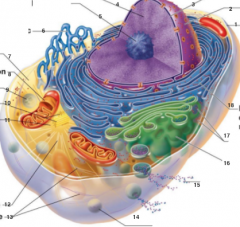
What is 14 pointing to? |
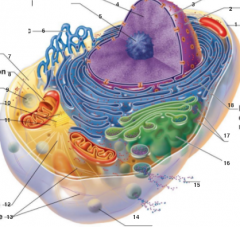
Peroxisome |
|
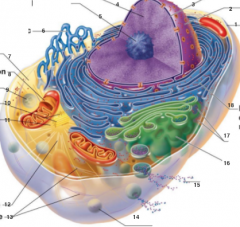
What is 15 pointing to? |
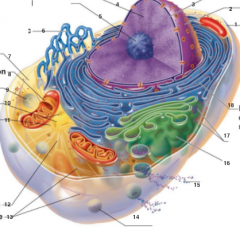
Secretion being released from the cell by exocytosis |
|
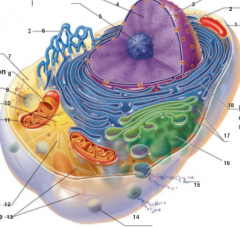
What is 16 pointing to? |
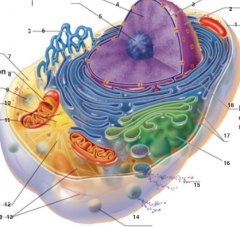
Golgi Apparatus |
|
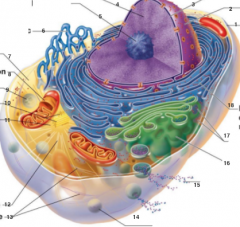
What is 17 pointing to? |
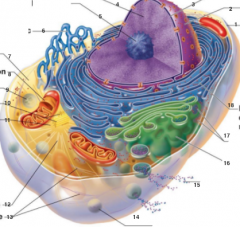
Ribosomes |
|
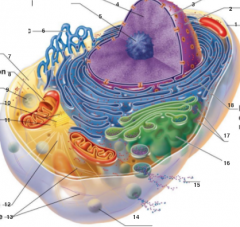
What is 18 pointing to? |
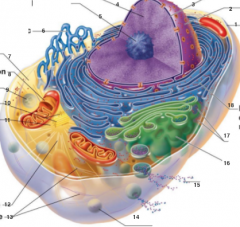
Rough endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
What is the plasma (cell) membrane? |
It forms the outer, limiting barrier separating the internal contents of the cell from the external environment |
|
|
What is cytoplasm? |
It is a general term for all cellular contents located between the plasma membrane and the nucleus. |
|
|
What is a nucleus? |
It is a cell's control center. |
|
|
Plasma (cell) membrane - structure |
Structure component: Phospholipid bilayer containing cholesterol and proteins (integral and peripheral) and some carbohydrates (externally) |
|
|
Cytoplasm - structure |
Structure component: Contains cytosol, a viscous fluid, and inclusions and organelles |
|
|
Cytosol - structure |
Structure component: Viscous fluid medium with dissolved solutes (ions, nutrients, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and other small molecules) |
|
|
Organelles - structure |
Structure component: Membrane-bound and non-membrane-bound structures that have unique functions and activities. |
|
|
Inclusions - structure |
Structure component: Droplets of melanin, protein, glycogen granules, or lipid; usually non-membrane bound. |
|
|
Nucleus - structure |
Structure component: Surrounded by double membrane nuclear envelope (each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer); contains nucleolus and chromatin. |
|
|
Nuclear envelope - structure |
Structure component: Double membrane boundary between cytoplasm and nuclear contents. |
|
|
Nuclear pores - structure |
Structure component: Openings through nuclear envelope. |
|
|
Nucleolus - structure |
Spherical, dark-staining, dense granular region in the nucleus. |
|
|
Chromatin and chromosomes - structure |
Filamentous association of DNA and histone proteins. |
|
|
Plasma (cell) membrane - function |
Component Function: contains receptors for communication; forms intercellular connections; acts as physical barrier to enclose cell contents; regulates material movement into and out of the cell. |
|
|
Cytoplasm - fuction |
Component Function: Place of many metabolic processes of the cell; stores nutrients and dissolved solutes. |
|
|
Cytosol - function |
Component Function: Provides support for organelles; serves as viscous medium through which diffusion occurs |
|
|
Organelles - function |
Component Function: Carry out specific metabolic activities of the cell |
|
|
Inclusions - function |
Component Function: Store materials |
|
|
Nucleus - function |
Component Function: Acts as cell control center; controls all genetic information (DNA); site of ribosome subunit assembly |
|
|
Nuclear envelope - function |
Component Function: Pores in envelope regulate exchange of materials with they cytoplasm |
|
|
Nuclear powers - function |
Component Function: Allow for passage of materials between nucleus and cytoplasm. |
|
|
Nucleolus - function |
Component Function: Synthesizes rRNA and assembles ribosomes in the nucleus. |
|
|
Chromatin and chromosomes - function |
Component Function: Site of genes in the DNA |
|
|
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (Smooth ER) - structure |
Structure component: Interconnected network of membrane tubules and vesicles; no ribosomes. |
|
|
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER) - structure |
Structure component: Flattened intracellular network of membrane sacs called cisternae; ribosomes attached on cytoplasmic suraces |
|
|
Golgi apparatus - structure |
Structure component: Stacked series of flattened, smooth membrane sacs with associated transport vesicles (also called shuttle vesicles) |
|
|
Lysosomes - structure |
Structure component: Membranes sacs with digestive enzymes |
|
|
Peroxisomes - structure |
Structure component: Membrane-enclosed sacs; usually contain large amounts of specific enzymes to break down harmful substances. |
|
|
Mitochondria - structure |
Structure component: Double membrane structures with cristae; fluid matrix contents at center |
|
|
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (Smooth ER) - function |
Component Function: Synthesizes lipids, metabolizes carbohydrates; detoxifies drugs, alcohol |
|
|
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER) - function |
Component Function: Synthesizes proteins for secretion, new proteins for the plasma membrane, and lysosomal enzymes; transports and stores molecules |
|
|
Golgi apparatus - function |
Component Function: Modifies, packages, and sorts newly synthesized proteins for secretion, inclusion in new plasma membrane, or lysosomal enzyme synthesis |
|
|
Lysosomes - function |
Component Function: Digest materials or microbes ingested by the cell; remove old/damaged organelles; self-destruct (autolyze) |
|
|
Peroxisomes - function |
Component Function: Convert hydrogen peroxide formed during metabolism to water |
|
|
Mitochondria - function |
Component Function: Synthesize most ATP during cellular respiration; "powerhouses of cell" |
|
|
Ribosomes - structure |
Structure component: Dense cytoplasmic granules with two subunits (large and small); may be free in cytoplasm (free ribosomes) or bound to rough ER (fixed ribosomes) |
|
|
Cytoskeleton - structure |
Structure component: Organized network of protein filaments or hollow tubules throughout the cell. |
|
|
Microfilaments - structure |
Structure component: Actin protein monomers formed into filaments |
|
|
Intermediate filaments - structure |
Structure component: Various protein components |
|
|
Microtubules - structure |
Structure component: Hollow cylinders of tubulin protein; able to lengthen and shorten. |
|
|
Centrosome - structure |
Structure component: Amorphous region adjacent to nucleus; contains a pair of centrioles. |
|
|
Centrioles - structure |
Structure component: Paired perpendicular cylindrical bodies; composed of microtubule triplets |
|
|
Cilia - structure |
Structure component: Short, membrane-attached projections containing microtubules; occur in large numbers on exposed membrane surfaces |
|
|
Flagellum - structure |
Structure component: Long, singular membrane extension containing microtubules |
|
|
Microvilli - structure |
Structure component: Numerous thin membrane folds projecting from the free cell surface. |
|
|
Ribosomes - function |
Component Function: Synthesize proteins for: 1. use in the cell (free ribosomes), 2. secretion, incorporation into plasma membrane, or lysosomes (fixed ribosomes) |
|
|
Cytoskeleton - function |
Component Function: Provide structural support; facilitates cytoplasmic streaming, organelle and cellular motility, transport of materials, and chromosomal movement and cell division. |
|
|
Microfilaments - function |
Component Function: Maintain cell shape; aid in muscle contraction and intracellular movement; separate dividing cells. |
|
|
Intermediate filaments - function |
Component Function: Provide structural support; stabilize cell junctions |
|
|
Microtubules - function |
Component Function: Support cell; hold organelles in place; maintain cell shape and rigidity; direct organelle movement within cell and cell motility as cilia and flagella; move chromosomes at cell division. |
|
|
Centrosome - function |
Component Function: Organizes microtubules; participates in spindle formation during cell division |
|
|
Centrioles - function |
Component Function: Organize microtubules during cell division for movement of chromosomes. |
|
|
Cilia - function |
Component Function: Move fluid, mucus, and materials over the cell surface |
|
|
Flagellum - function |
Component Function: Propels sperm cels in human male |
|
|
Microvilli - function |
Component Function: Increase membrane surface area for increased absorption and/or secretion. |

