![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell Theory |
All organisms are made up of cells Cells are the basic unit of life Cells come from existing cells Robert Hooke-gave us the term cell Antwon Van Leeanhook- Discovered bacteria (named them animalcules) Matthios Schlieden- all plants are made out of cells Robert Virchow- all cells arise from preexisting cells Theadore Schwan- all animals are made of cells |
|
|
Prokaryote (Before nucleus) vs. Eukaryote (True Nucleus) |
Prokaryote: oldest type, small and simple, lack nucleus, lack organelles, single-celled, single circular chromosome Both: both have DNA, ribosomes, cytoplasm, plasma membrane Eukaryote: evolved from prokaryote, larger and more complex, contains nucleus, contains organelles, single-celled or multicellular, multiple linear chromosome |
|
|
Cell Organelles |
Rough ER- assemble protein Smooth ER- regulates calcium and processes toxins Mitochondria- convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use Ribosomes- make protein from RNA Vacuole- store water and might store food for the cell Lysosomes- break down waste material and cellular debris Chloroplasts- absorbs sunlight and uses it in conjunction with water and carbon dioxide to make food for the plant Golgi Apparatus- gathers simple molecules to make more complex molecules Cell Wall- the outer layer of a plant cell that gives plants their stiffness Cell Membrane- regulates what enters and leaves the cell, also supports and protects the cell Cytoplasm- everything within the cell/holds everything together Plant cells have a large vacuole while animals don't (plants can't move to get water, so they need to store a lot while animals can move to get water) Plant cells have a cell wall while animals don't (plants can't move to protect themselves while animals can move to get away from danger) Plant cells have chloroplast to make their own food while animals don't(animals can move to get food but plants can't, so they make their own food) |
|
|
Passive Transport |
Diffusion- the process by which particles move from one area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Facilitated Diffusion- the process in which molecules cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels Osmosis- the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane |
|
|
Active Transport |
Definition-The movement of materials against a concentration difference Active Transport requires energy Endocytosis- the process of taking material into the cell by means of infoldings, or pockets of the cell membrane Exocytosis- the process of releasing large amounts of material from the cell |
|
|
Fluid Mosaic Model |
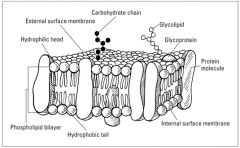
|
|
|
Protein Synthesis |
1. Proteins are assembled on ribosomes 2. Proteins targeted for export to the cell membrane, or to specialized locations within the cell, complete their assembly on ribosome bound to the rough endoplasmic reticulum 3. Newly assembled proteins are carried from the Rough ER to the Golgi Apparatus in vesicles 4.RNA bring amino acids to ribosome according to the original DNA code 5. Vesicles from the Golgi Apparatus are shipped to their final destination in or out of, the cell |
|
|
Properties Of Water |
Polar Molecule- A molecule with uneven positive and negative charges Cohesion - Two molecules that bond together Adhesion- Combine or bond to different molecules Universal Solvent- Water is capable of dissolving a variety of different substances |
|
|
pH Scale |
Acid-An acid is a substance that donates hydrogen ions. Because of this, when an acid is dissolved in water, the balance between hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions is shifted. Now there are more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions in the solution. This kind of solution is acidic. Base-A base is a substance that accepts hydrogen ions. When a base is dissolved in water, the balance between hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions shifts the opposite way. Because the base "soaks up" hydrogen ions, the result is a solution with more hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions. This kind of solution is alkaline. Buffer-A solution which can maintain an almost constant pH value when dilute acids or alkalis are added to it. |
|
|
|
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. Elements that bond with carbon for life- Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous, Sulfur, and Nitrogen |
|
|
Macromolecule: Lipids |
Monomer- Carbon and Hydrogen Function- Store energy, some are important parts of biological membranes and water proof covering Ex: Milk Butter Olive Oil |
|
|
Macromolecule: Protein |
Monomer - Contain nitrogen as well as carbon and hydrogen and oxygen Function- Some control the rate of reactive and regulate cell processes while others form important/cellular structure and others transport substances into or fight disease Ex: Meat Seafood Beans |
|
|
Macromolecule: Carbohydrates |
Monomer- Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen Function- For animals it's energy and for plants it's used for structural purposes Ex: Glucose Monosaccharide's Bread Pasta Rice |
|
|
Macromolecule: Nucleic Acid |
Monomer - Nucleotide Function- Store and transmit hereditary or genetic information Ex: Ribonucleic acid, and Deoxyribonucleic acid |
|
|
Enzymes |
Role of enzymes- Speed up the rate of chemical reactions in cells Catalase- A substance that speeds up the rate of chemical reaction Negative- Steroids |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
CO2 + H2O -Light> C6H12O6 + O2 Reactants Products Light reaction- Light is needed to produce energy molecules Dark Reaction- No light needed. Uses ATP and NADPH to produce energy molecules |
|
|
Respiration
|
C6H12O6 > 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy Glycolysis-Occurs in Cytoplasm. Does not require O2. Needs 2 ATP to begin with. ATP produced. Net gain 2 ATP. Kreb Cycle-Occurs in mitochondria. Requires O2. Co2 realeased. Electron Transport Chain-Occurs in Mitochondria. Requires O2. Water is Formed. Net gain 34 ATP |
|
|
Compare and contrast photosynthesis and respiration |
Photosynthesis- Different equation Needs sunlight anabolic Endothermic Both- Occurs in cells Both processes have almost exact same equation Cellular- Different equation, Needs ATP, Catabolic, Exothermic |
|
|
Mitosis
|
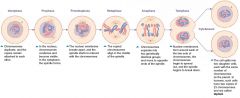
Somatic Cells, which means non sex cells 46 total chromosomes in mitosis Asexual Reproduction Crossover- |
|
|
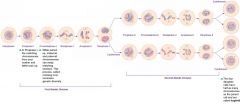
Meiosis
|
Haploid- 23 Chromosomes Crossover - XX+XY Diploid- 46 Chromosomes |
|
|
Compare and contrast Mitosis and Meiosis |
Meiosis- 4 daughter cells, Chromatids, Do not separate in anaphase, 23 Chromosomes Both-Occurs in stages interphase cell production Mitosis-2 daughter cells, Chromatids in anaphase, one set of stages to reproduce |
|
|
Mitosis: Crossover |
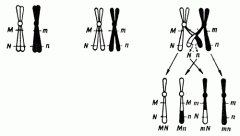
|
|
|
Mitosis: Chromosome |
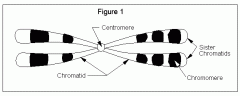
|
|
|
Meiosis: Phases |
|

