![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is mitosis? |
Mitosis is the division of the nucleus into two genetically identical daughter nuclei. |
|
|
How do particles move across cell membranes? |
Particles move across membranes through simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. Why a |
|
|
Why are cell membranes fluid? |
The fluidity of the membranes allows materials to be taken into the cells by endocytosis or released by exocytosis. |
|
|
How are bilayers formed? |
Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of the molecule. |
|
|
What is the fluid mosaic model? |
The current model of membrane structure. It includes a phospholipid bilayer in which proteins are embedded or attached to the surface. |
|
|
What is a phospholipid? |
Phospholipids are made up of a polar, hydrophilic area containing a phosphate group bonded to glycerol and a non-polar, lipophilic area containing fatty acids. |
|
|
Integral v. Peripheral proteins |
Integral proteins are embedded in the bilayer while peripheral proteins are attached to the surface. |
|
|
Cholesterol |
Often present in mammal cells and commonly found in the plasma membrane. One end of the cholesterol molecule associated with the polar heads of phospholipids while other parts are imbedded in the membrane next to the non-polar fatty acid chain. This interaction makes the membrane less fluid and more rigid and less permeable to water-soluble molecules. |
|
|
Define simple diffusion. |
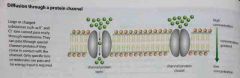
Diffusion a passive process which takes places as molecules move randomly. No energy is required and movement occurs over a simple concentration gradient. |
|
|
Define facilitated diffusion. |
A carrier protein first combines with the diffusing molecules on one side of the membrane, carries them through a the channel protein and then releases them on the other side. |
|
|
Define facilitated diffusion. |
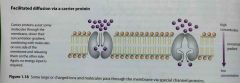
A carrier protein first combines with the diffusing molecules on one side of the membrane, carries them through a the channel protein and then releases them on the other side. |
|
|
Define osmosis. |
Osmosis is the diffusion (passive movement) of water across a semi-permeable membrane due to a concentration gradient. |
|
|
Define active transport. |
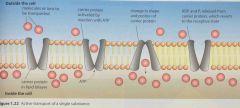
The transport of a substance across a membrane against the concentration gradient, involving a carrier protein and energy. |
|
|
Describe cycling. |
Cyclins are compounds that are involved in the control of the cell cycle through their interaction with CDKs to form enzymes that direct cells through the cell cycle and control specific events. |
|
|
Describe cell theory. |
1. All organisms are composed of cells. 2. Cells are the smallest units of life. 3. Cells can only come from pre-existing cells. |
|
|
What is the equation for magnification? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Surface area to volume ratio. |
The volume of a cell determines the rate of metabolic activity that takes place within it while surface area determines the rate of exchange materials with the outside environment. |
|
|
The structures of a prokaryotic cell. |
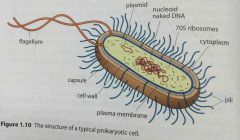
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Difference b/w plant and animal cells. |
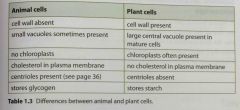
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Prokaryote v. Eukaryote |
Back (Definition) |

