![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Explain cells |
The basic units of living things. |
|
|
|
Plasma membrane |
Forms the outer boundary of the cell (cell membrane) |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Located centrally, directs cell activity (cell brain) |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Located between plasma membrane and nucleus (cell activity takes place) |
|
|
|
Organelles |
Specialized structures that perform specialized functions |
|
|
|
What is cell metabolism and energy use? |
Chemical reaction |
|
|
|
What is synthesis of molecules? |
Production of proteins, nucleic acids etc |
|
|
|
Communication? |
Produce and respond to chemical or electronically signals |
|
|
|
What is production and inheritance ? |
Transfer of genetic material |
|
|
|
The human cell |
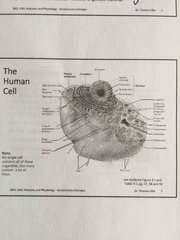
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is the name of a human cell? |
Eukaryotes |
|
|
|
Plasma membranes are? |
Semi permeable Have an electrical charge Outside positive Inside negative |
|
|
|
Plasma membrane cont. explain more |
Boundary separate substances inside the cell (intercellular) from the substances outside (extracellular) Controls what comes in and out of cell |
|
|
|
What is membrane potential in a plasma membrane? |
An electrical charge difference p4 |
|
|
|
What is membrane potential in a plasma membrane? |
An electrical charge difference p4 |
|
|
|
What is the plasma membrane made up of? |
Lipids, proteins & carbs |

|
|
|
What is the predominant lipids of the plasma membrane? |
Phospholipids & cholesterol |
|
|
|
What are phospholipids? |
They readily assemble to form bilateral because they have a polar head and no polar tail. |
|
|
|
What is hydrophilic? |
The polar water loving heads face outward |
|
|
|
What is hydrophobic? |
It’s nonpolar water fearing tails facing inward |
|
|
|
Explain cholesterol? |
They are interspersed among the phospholipids. Accounts for 1/3 of the total lipids in the plasma membrane. Limits movement Provides stability Hydrophilic & hydrophobic |
|
|
|
Explain membrane proteins? |
Many functions of the plasma membrane are determined by the membrane protein. Penetrate deep into the lipid bilayer |
|
|
|
What is peripheral membrane proteins? |
Other membrane proteins attach to either the inner or outer surface of the plasma membrane or to other proteins. |
|
|
|
5 terms for membrane proteins are |
Marker molecules Attachment proteins Transport proteins Receptor proteins Enzymes |
|
|
|
What are marker molecules? |
Are cell surface molecules that allow cells to identify other cells or molecules. Glycoproteins Some are glycolipids Eg. sperm cells are able to identify oocyte cells |
|
|
|
What are attachment proteins? |
They are integral membrane proteins function to allow cells to attach to other cells or to extracellular molecules |
|
|
|
What are cadherins? |
Are proteins that allow cells to attach to other cells |
|
|
|
What are integrins? |
They are proteins that attach cells to extracellular molecules |
|
|
|
What are transport proteins? |
They are integral membrane proteins that allow ions or molecules to move from one side to the other side of the plasma membrane. |
|
|
|
What are 3 characteristics of transport proteins? |
Specificity. Competition. Saturation. |

|
|
|
What are 3 types of transport proteins? |
Channel proteins Carrier proteins ATP powered pumps |
|
|
|
What is a channel proteins? |
One or more integral membrane proteins arranged to form a channel through the plasma membrane.
Ions/molecules of the right size, charge and shape can pass through |
|
|
|
Are leak ion channels open or closed? |
Always open |
|
|
|
Can gated ion channels open? Explain |
They can open or close. Respond to chemical signals, changes in membrane potential (voltage gated ion channels) or ligands (small molecules that bind to proteins). |
|
|
|
What are carrier proteins? |
Bind to specific ions & molecules on one side of the plasma membrane, change shape & move them to the other side. Once released it goes back to its original shape ready to move the next ion or molecule across |
|
|
|
What are Carrier proteins classified as? |
Uniport (1 molecule or ion) Symport (2 same direction) Antiport (2 opposite direction) |
|
|
|
What are ATP- powered pumps? |
Fueled by the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Binding site for specific ions or molecules and binding site for ATP.
|
|
|
|
What happens when ATP is broken down? |
The energy released changes the shape of the protein, moving the bound ion & molecule to the outer side. |
|
|
|
What are Receptor proteins? |
Either peripheral membrane proteins OR integral membrane proteins. Have an exposed receptor site on outer cell surface which responds to chemical signals Signals are part of the intercellular communication system that coordinates cell activity |
|
|
|
What are enzymes that transport proteins? |
Catalyze chemical reactions of either the inner or outer surface of the plasma membrane Some are always active Some are activated by membrane bound receptors |
|
|
|
Are plasma membrane semi permeable? |
Yes . Allowing only certain substances to pass through |
|
|
|
What are the different ways that molecules and ions can pass through the plasma membrane |
Lipid soluble molecules-dissolving in the lipid bilayer Small, non lipid soluble molecules-can diffuse between the phospholipid molecules Larger molecules-move by transport proteins or across in a vesicles (membrane sac) |
|
|
|
What are the Classification of membrane transport mechanisms |
Passive or active membrane transport depending on whether the cell expands metabolic energy during transport |
|
|
|
Does passive membrane transport need the cell to expend metabolic energy? |
Yes by diffusion - osmosis & facilitated diffusion |
|
|
|
What is diffusion? |
Is the movement of solutes from an area of high concentration to low concentration |
|
|
|
What is osmosis? |

The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane |
|
|
|
What is aquaporins? |
Increased membrane permeability in some cell types like kidney cells |
|
|
|
What is osmotic pressure |
Is the force required to prevent water from moving by osmosis across a selectively permeable membrane |
|
|
|
What are the 3 terms that describe the osmotic pressure of solutions? |
Isomotic- 2 solutions with the same osmotic pressure Hyperosmotic- 1st solution has higher osmotic pressure than to the second Hyposmotic- 1st solution has lower osmotic pressure compared to 2nd solution |
|
|
|
Explain isotonic solution... |
Cell neither shrinks or swells Shape of cell remains constant |
|
|
|
Explain hypertonic solution... |
Water moves out of cell Cell shrinks |
|
|
|
Explain hypotonic |
Water moves into the cells The cell swells and can cause the cell to rupture ( lysis) |
|
|
|
Explain facilitated diffusion... |
It moves essential molecules, like amino acids and glucose and products like Urea |
|
|
|
What is mediated transport |
Is the process of moving large water soluble molecules or electrically charged molecules or ions across the plasma membrane |
|

