![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Colony lift hybridization
|
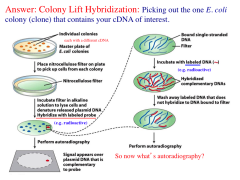
How do we select the colony with the desired cDNA?
1. Place nitrocellulose filter on plate to pick up cells from each colony. 2. Incubate filter in alkaline solution to lyase cells and denature released plasmid DNA hybridize with labeled probes 3. Perform autoradiography. 4. Incubate with labeled DNA. 5. Wash away labeled DNA that does not hybridize to DNA bond to filter. 6. Perform autoradiography to find colony. |
|
|
Autoradiography
|
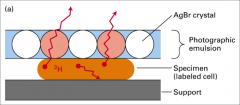
Use 3H because of its very short emission path
Emission is a beta-particle (i.e. a high speed electron) 3H-thymidine to label DNA 3H-uridine to label RNA 3H-amino acid to label protein For colony lift, use 32P-probe and x-ray film |
|
|
Shuttle vectors
|
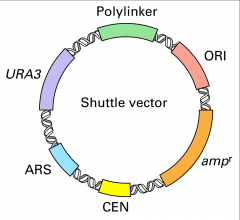
URA3+ is a selectable marker gene (analogous to ampr
Ura3- yeas cells require uracil |
|
|
Origins of DNA replication
|
ARS for eukaryotes
ORI for prokaryotes |
|
|
Overlapping restriction fragments
|
What's need to make a genomic library?
|
|
|
Chromosome walking
|
Why use only a partial digestion with very low concentrations of restriction enzyme?
Important to have the genomic library contain overlapping fragments for sequencing or linkage studies Call ________________. Ex: Sau3A and BamHI leave the same compatible sticky ends. |
|
|
Leland Hartwell
|
Generated many cdc mutations in yeast
cdc mutations block cell cycle progression at various points used genetic complementation to determine which mutations were alleles of each other |
|
|
Fundamental (Molecular) Complementation Screening
|
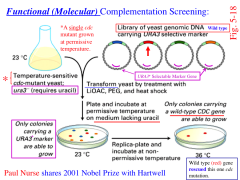
1. A single cdc mutant is grown at permissable temp.
2. Transform yeast by treatment with LiOAC, PEG, and heat shock 3. Plate and incubate at permissive temperature on medium lacking uracil 4. Replica plate and incubate at non-permissive temperature Only colonies carrying a wild-type CDC gene are able to grow MUST KNOW |
|
|
Paul Nurse
|
Started his career at Guinness brewery
Yeast geneticist and molecular-cell biologist Re-isolated the "red" plasmid from the rescud yeast cells and sequenced the red gene Deduced the amino acid sequence to identify the protein product ---these proteins control the cell cycle; his and other labs determined how these regulatory proteins work |
|
|
DNA Gel Electrophoresis
|

Cut insert out of vector.
Resolve on agarose gel. Large DNA fragments more more slowly than do smaller fragments. Stain with ethidium bromide and it fluoresces in UV light Good for .5-2 kbps Polyacrylamide gels are used for 20-1500 bps |
|
|
Pulse-field electrophoresis
|
Agarose again, but current turned off and on at right angles
Resolves huge DNA fragments: --genomic fragements --20 kbp - 10 mega bp --cut the genome with "8-base pair cutters" v "6-bp" |
|
|
Physical map
|
Restriction enzymes provide a _______________.
|
|
|
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
|
Probably the most powerful molecular biology technique ever devised (by Kerry Mullis)
Amplifies specific DNA sequences, but any that you choose --Forward and reverse primers select sequence of DNA to amplify Primer = oligonucleotide Primers are in vast molar excess compared to original template DNA Exponential increase (replication) of target DNA template |
|
|
Cycles in PCR
|
1. Denaturation of DNA and annealing of primers
2. Elongation of primers using special heat-stable DNA polymerase 3. Termination Can also design primers to include restriction sites |
|
|
DNA sequencing (3 techniques)
|
1) Maxam and Gilbert
2) Sanger's dideoxy chain termination technique 3) next generation DNA sequencing |
|
|
Maxam and Gilbert techniqe
|
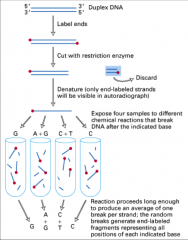
End label, then chemically cleave the DNA
Not used much anymore End label: 32P added to 5' ends by a kinase |

